|
XUnit
xUnit is a label used for an automated testing software framework that shares significant structure and functionality that is traceable to a common progenitor SUnit. The SUnit framework was ported to Java by Kent Beck and Erich Gamma as JUnit which gained wide popularity. Adaptations to other languages were also popular which led some to claim that the structured, object-oriented style works well with popular languages including Java and C#. The name of an adaptation is often a variation of "SUnit" with the "S" replaced with an abbreviation of the target language name. For example, JUnit for Java and RUnit for R. The term "xUnit" refers to any such adaptation where "x" is a placeholder for the language-specific prefix. The xUnit frameworks are often used for unit testing testing an isolated unit of code but can be used for any level of software testing including integration and system. Architecture An xUnit framework has the following general architecture. Test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Test Fixture
A test fixture is a device used to consistently test some item, device, or piece of software. Test fixtures are used in the testing of electronics, software and physical devices. Electronics In testing electronic equipment such as circuit boards, electronic components, and chips, a test fixture is a device or setup designed to hold the device under test in place and allow it to be tested by being subjected to controlled electronic test signals. Examples are a bed of nails tester or smart fixture. Test fixtures can come in different shapes, sizes, and functions. There are several different types of test fixtures, including In-circuit testing, In-Circuit Test Fixtures, Functional testing (manufacturing), Functional Test Fixtures, and Wireless Test Fixtures. In Circuit Test (ICT) fixtures individually test each component on a Printed circuit board, PCB, while functional test fixtures assess the entire board's functionality. Functional test fixtures simulate real-world conditions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JUnit
JUnit is a test automation framework for the Java programming language. JUnit is often used for unit testing, and is one of the xUnit frameworks. JUnit is linked as a JAR at compile-time. The latest version of the framework, JUnit 5, resides under package . Previous versions JUnit 4 and JUnit 3 were under packages and , respectively. A research survey performed in 2013 across 10,000 Java projects hosted on GitHub found that JUnit (in a tie with slf4j-api) was the most commonly included external library. Each library was used by 30.7% of projects. JUnit Lifecycle Every JUnit test class usually has several test cases. These test cases are subject to the test life cycle. The full JUnit Lifecycle has three major phases: # Setup phase - This phase is where the test infrastructure is prepared. Two levels of setup are available. The first type of setup is class-level setup in which a computationally expensive object, such as a database connection, is created and reused, with mini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit Testing
Unit testing, component or module testing, is a form of software testing by which isolated source code is tested to validate expected behavior. Unit testing describes tests that are run at the unit-level to contrast testing at the Integration testing, integration or System testing, system level. History Unit testing, as a principle for testing separately smaller parts of large software systems, dates back to the early days of software engineering. In June 1956 at US Navy's Symposium on Advanced Programming Methods for Digital Computers, H.D. Benington presented the Semi-Automatic Ground Environment, SAGE project. It featured a specification-based approach where the coding phase was followed by "parameter testing" to validate component subprograms against their specification, followed then by an "assembly testing" for parts put together. In 1964, a similar approach is described for the software of the Project Mercury, Mercury project, where individual units developed by dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kent Beck
Kent Beck (born 1961) is an American software engineer and the creator of extreme programming, a software development methodology that eschews rigid formal specification for a collaborative and iterative design process. Beck was one of the 17 original signatories of the Agile Manifesto,"Extreme Programming", ''Computerworld'' (online), 2005, webpageComputerworld-appdev-92. the founding document for agile software development. Extreme and Agile methods are closely associated with Test-Driven Development (TDD), of which Beck is perhaps the leading proponent. Beck pioneered software design patterns, as well as the commercial application of Smalltalk. He wrote the SUnit unit testing framework for Smalltalk, which spawned the xUnit series of frameworks, notably JUnit for Java, which Beck wrote with Erich Gamma. Beck popularized CRC cards with Ward Cunningham, the inventor of the wiki. He lives in San Francisco, California and previously worked at Facebook. In 2019, Beck joined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automated Testing
In software testing, test automation is the use of software separate from the software being tested to control the execution of tests and the comparison of actual outcomes with predicted outcomes. Test automation can automate some repetitive but necessary tasks in a formalized testing process already in place, or perform additional testing that would be difficult to do manually. Test automation is critical for continuous delivery and continuous testing. General approaches There are many approaches to test automation, however below are the general approaches used widely: * Graphical user interface testing. A testing framework that generates user interface events such as keystrokes and mouse clicks, and observes the changes that result in the user interface, to validate that the observable behavior of the program is correct. * API driven testing. A testing framework that uses a programming interface to the application to validate the behaviour under test. Typically API driven te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SUnit
SUnit is an automated testing framework written by Kent Beck in 1989; originally intended and often used for unit testing. It supports testing Smalltalk code via test code also written in Smalltalk. SUnit was adapted for Java as JUnit which was notably popular. Subsequently, adaptations were created for many other languages; many also popular. Frameworks with similar design are labeled xUnit xUnit is a label used for an automated testing software framework that shares significant structure and functionality that is traceable to a common progenitor SUnit. The SUnit framework was ported to Java by Kent Beck and Erich Gamma as JUn .... History SUnit was originally described by Beck inSimple Smalltalk Testing: With Patterns (1989), then published as chapter 30 "Simple Smalltalk Testing", in the book Kent Beck's Guide to Better Smalltalk by Kent Beck, Donald G. Firesmith (Editor) (Publisher: Cambridge University Press, Pub. Date: December 1998, , 408pp) External links * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Test Case
In software engineering, a test case is a specification of the inputs, execution conditions, testing procedure, and expected results that define a single test to be executed to achieve a particular software testing objective, such as to exercise a particular program path or to verify compliance with a specific requirement. Test cases underlie testing that is methodical rather than haphazard. A battery of test cases can be built to produce the desired coverage of the software being tested. Formally defined test cases allow the same tests to be run repeatedly against successive versions of the software, allowing for effective and consistent regression testing. Formal test cases In order to fully test that all the requirements of an application are met, there must be at least two test cases for each requirement: one positive test and one negative test. If a requirement has sub-requirements, each sub-requirement must have at least two test cases. Keeping track of the link between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlassian Bamboo
Atlassian Corporation () is an Australian- American proprietary software company that specializes in collaboration tools designed primarily for software development and project management. Domiciled in the United States as Atlassian Corporation Plc., the company is globally headquartered in Sydney, Australia, with a US headquarters in San Francisco, and over 12,000 employees across 14 countries. Atlassian currently serves over 300,000 customers in over 200 countries across the globe. History In 2001, Mike Cannon-Brookes sent an email to his University of New South Wales classmates asking if any of them were interested in helping him launch a tech startup after graduation. Scott Farquhar was the only one who replied, and together they founded Atlassian in 2002. They bootstrapped the company for several years, financing the startup with a $10,000 credit card debt. The name was derived from the Greek mythological figure Atlas, inspired by his bronze statue in New York's Rocke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jenkins (software)
Jenkins is an open source automation server. It helps automate the parts of software development related to building, testing, and deploying, facilitating continuous integration, and continuous delivery. It is a server-based system that runs in servlet containers such as Apache Tomcat, or by default as a stand-alone web-application in co-bundled Eclipse Jetty. It supports version control tools, including AccuRev, CVS, Subversion, Git, Mercurial, Perforce, ClearCase, and RTC, and can execute Apache Ant, Apache Maven, and sbt based projects as well as arbitrary shell scripts and Windows batch commands. History The Jenkins project was originally named '' Hudson'', and was renamed in 2011 after a dispute with Oracle, which had forked the project and claimed rights to the project name. The Oracle fork, ''Hudson'', continued to be developed for a time before being donated to the Eclipse Foundation. Oracle's Hudson is no longer maintained and was announced as obs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plain-text
In computing, plain text is a loose term for data (e.g. file contents) that represent only characters of readable material but not its graphical representation nor other objects (floating-point numbers, images, etc.). It may also include a limited number of "whitespace" characters that affect simple arrangement of text, such as spaces, line breaks, or tabulation characters. Plain text is different from formatted text, where style information is included; from structured text, where structural parts of the document such as paragraphs, sections, and the like are identified; and from binary files in which some portions must be interpreted as binary objects (encoded integers, real numbers, images, etc.). The term is sometimes used quite loosely, to mean files that contain ''only'' "readable" content (or just files with nothing that the speaker does not prefer). For example, that could exclude any indication of fonts or layout (such as markup, markdown, or even tabs); characters suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human-readable
In computing, a human-readable medium or human-readable format is any encoding of data or information that can be naturally read by humans, resulting in human-readable data. It is often encoded as ASCII or Unicode text, rather than as binary data. In most contexts, the alternative to a human-readable representation is a '' machine-readable format'' or medium of data primarily designed for reading by electronic, mechanical or optical devices, or computers. For example, Universal Product Code (UPC) barcodes are very difficult to read for humans, but very effective and reliable with the proper equipment, whereas the strings of numerals that commonly accompany the label are the human-readable form of the barcode information. Since any type of data encoding can be parsed by a suitably programmed computer, the decision to use binary encoding rather than text encoding is usually made to conserve storage space. Encoding data in a binary format typically requires fewer bytes of storage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
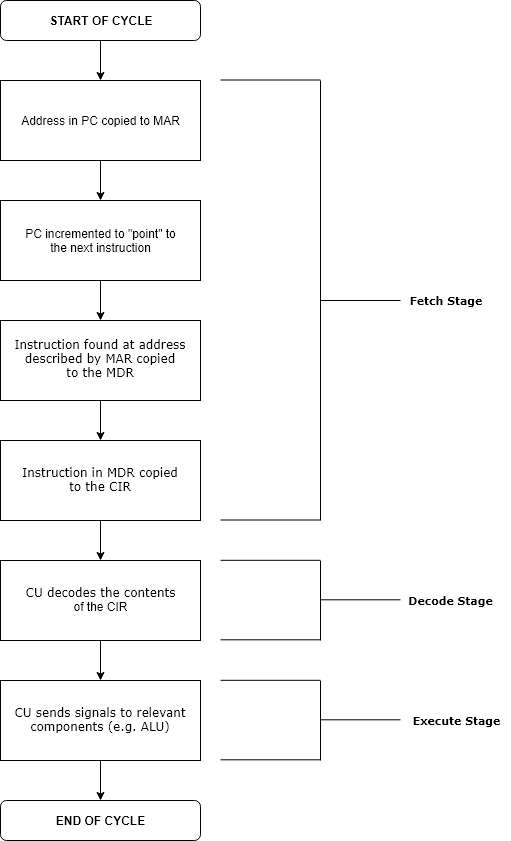
Runtime (program Lifecycle Phase)
Execution in computer engineering, computer and software engineering is the process by which a computer or virtual machine interprets and acts on the instructions of a computer program. Each instruction of a program is a description of a particular action which must be carried out, in order for a specific problem to be solved. Execution involves repeatedly following a "Instruction cycle, fetch–decode–execute" cycle for each instruction done by the control unit. As the executing machine follows the instructions, specific effects are produced in accordance with the Formal semantics of programming languages, semantics of those instructions. Programs for a computer may be executed in a Batch processing, batch process without human interaction or a User (computing), user may type Command (computing), commands in an Session (computer science), interactive session of an Interpreter (computing), interpreter. In this case, the "commands" are simply program instructions, whose executio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |