|
Wreckage Of San José
The 1651 wreckage of ''San José'' and the subsequent killings and looting carried out by indigenous Cuncos was a defining event in Colonial Chile that contributed to Spanish-Cunco tensions that led to the Battle of Río Bueno and the Mapuche uprising of 1655. Background The Spanish city of Valdivia had been reestablished by the Spanish in 1645 following a 1643 Dutch attempt to establish a settlement in the location. More than a city the Spanish settlement of Valdivia was by 1651 a military garrison tasked with constructing the Valdivian Fort System in case the Dutch or any other naval power would attempt to take Valdivia again. This garrison was financed by the Real Situado, an annual payment of silver to strengthen the military of war-torn Chile. As Valdivia was surrounded by hostile Mapuche territory the only access to the Spanish settlement was by sea. In January 1651 the Spanish and Mapuches had celebrated the Parliament of Boroa renewing the fragile peace that had been est ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cunco People
Cuncos or Juncos is a poorly known subgroup of Huilliche people native to coastal areas of southern Chile and the nearby inland. Mostly a historic term, Cuncos are chiefly known for their long-running conflict with the Spanish during the colonial era of Chilean history. Cuncos cultivated maize, potatoes and quinoa and raised chilihueques.Urbina 2009, p. 44. Their economy was complemented by travels during spring and summer to the coast where they gathered shellfish and hunted sea lions. They were said to live in large rukas.Alcamán 1997, p. 32. Cuncos were organized in small local chiefdoms forming a complex system intermarried families or clans with local allegiance.Alcamán 1997, p. 47. Ethnicity and identity The details of the identity of the Cuncos is not fully clear. José Bengoa defines "Cunco" as a category of indigenous Mapuche-Huilliche people in southern Chile used by the Spanish in colonial times.Bengoa 2000, p. 122. The Spanish referred to them as ''indios cunco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diego De Rosales
Diego de Rosales (Madrid, 1601 - Santiago, 1677) was a Spanish chronicler and author of ''Historia General del Reino de Chile''. He studied in his hometown, where he also joined the Society of Jesus. He came to Chile in the year 1629, without having taken his last vows still being sent to the residence that the Jesuits had in Arauco. He served as an Army chaplain in the Arauco War during the government of Don Francisco Laso de la Vega and, in 1640, was ordained a priest in Santiago. During this time, he acquired his knowledge of the language and customs of the Mapuche. He was close to the governors Francisco López de Zúñiga and Martín de Mujica y Buitrón, accompanying them and participating in the parliaments held in 1641 and 1647 during the Arauco War. In 1650, Governor Antonio de Acuña Cabrera tasked him to conduct a journey to the Pehuenche tribes east of Villarica and later to Lake Nahuelhuapi. During the Mapuche uprising of 1655, he was in Boroa, long besi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shipwrecks
A shipwreck is the wreckage of a ship that is located either beached on land or sunken to the bottom of a body of water. Shipwrecking may be intentional or unintentional. Angela Croome reported in January 1999 that there were approximately three million shipwrecks worldwide (an estimate rapidly endorsed by UNESCO and other organizations). When a ship's crew has died or abandoned the ship, and the ship has remained adrift but unsunk, they are instead referred to as ghost ships. Types Historic wrecks are attractive to maritime archaeologists because they preserve historical information: for example, studying the wreck of revealed information about seafaring, warfare, and life in the 16th century. Military wrecks, caused by a skirmish at sea, are studied to find details about the historic event; they reveal much about the battle that occurred. Discoveries of treasure ships, often from the period of European colonisation, which sank in remote locations leaving few livin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maritime Incidents In Chile
Maritime may refer to: Geography * Maritime Alps, a mountain range in the southwestern part of the Alps * Maritime Region, a region in Togo * Maritime Southeast Asia * The Maritimes, the Canadian provinces of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Prince Edward Island * Maritime County, former county of Poland, existing from 1927 to 1939, and from 1945 to 1951 * Neustadt District, Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia, known from 1939 to 1942 as ''Maritime District'', a former district of Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia, Nazi Germany, from 1939 to 1945 * The Maritime Republics, thalassocratic city-states on the Italian peninsula during the Middle Ages Museums * Maritime Museum (Belize) * Maritime Museum (Macau), China * Maritime Museum (Malaysia) * Maritime Museum (Stockholm), Sweden Music * ''Maritime'' (album), a 2005 album by Minotaur Shock * Maritime (band), an American indie pop group * "The Maritimes" (song), a song on the 2005 album ''Boy-Cott-In the Industry'' by Classified * "Maritime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pehuén Editores
''Araucaria araucana'' (commonly called the monkey puzzle tree, monkey tail tree, piñonero, pewen or Chilean pine) is an evergreen tree growing to a trunk diameter of 1–1.5 m (3–5 ft) and a height of 30–40 m (100–130 ft). It is native to central and southern Chile and western Argentina. ''Araucaria araucana'' is the hardiest species in the conifer genus '' Araucaria''. Because of the prevalence of similar species in ancient prehistory, it is sometimes called a living fossil. It is also the national tree of Chile. Its conservation status was changed to Endangered by the IUCN in 2013 due to the dwindling population caused by logging, forest fires, and grazing. Description The leaves are thick, tough, and scale-like, triangular, long, broad at the base, and with sharp edges and tips. According to Lusk, the leaves have an average lifespan of 24 years and so cover most of the tree except for the older branches. It is usually dioecious, with the male a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concepción, Chile
Concepción (; originally: ''Concepción de la Madre Santísima de la Luz'', "Conception of the Blessed Mother of Light") is a city and commune in central Chile, and the geographical and demographic core of the Greater Concepción metropolitan area, one of the three major conurbations in the country. It has a significant impact on domestic trade being part of the most heavily industrialized region in the country. It is the seat of the Concepción Province and capital of the Bío Bío Region. It sits about 500 km south of the nation's capital, Santiago. The city was first settled in the Bay of Concepción, in the zone that would later become the commune of Penco, now part of the Concepción conurbation. The city's demonym, , comes from the place of its original foundation. The city center and historic district is located in the Valle de la Mocha (La Mocha Valley), where it relocated after serious damages left by an earthquake in 1751. The origin of Concepción dates back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cacique
A ''cacique'' (Latin American ; ; feminine form: ''cacica'') was a tribal chieftain of the Taíno people, the indigenous inhabitants at European contact of the Bahamas, the Greater Antilles, and the northern Lesser Antilles. The term is a Spanish transliteration of the Taíno word ''kasike''. Cacique was initially translated as "king" or "prince" for the Spanish. In the colonial era the conquistadors and the administrators who followed them used the word generically, to refer to any leader of practically any indigenous group they encountered in the Western Hemisphere. In Hispanic and Lusophone countries, the term also has come to mean a political boss, similar to ''caudillo,'' exercising power in a system of ''caciquismo''. Spanish colonial-era caciques The Taíno word ''kasike'' descends from the Taíno word ''kassiquan'', which means "to keep house". In 1555 the word first entered the English language, defined as "prince". In Taíno culture, the ''kasike'' rank was her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
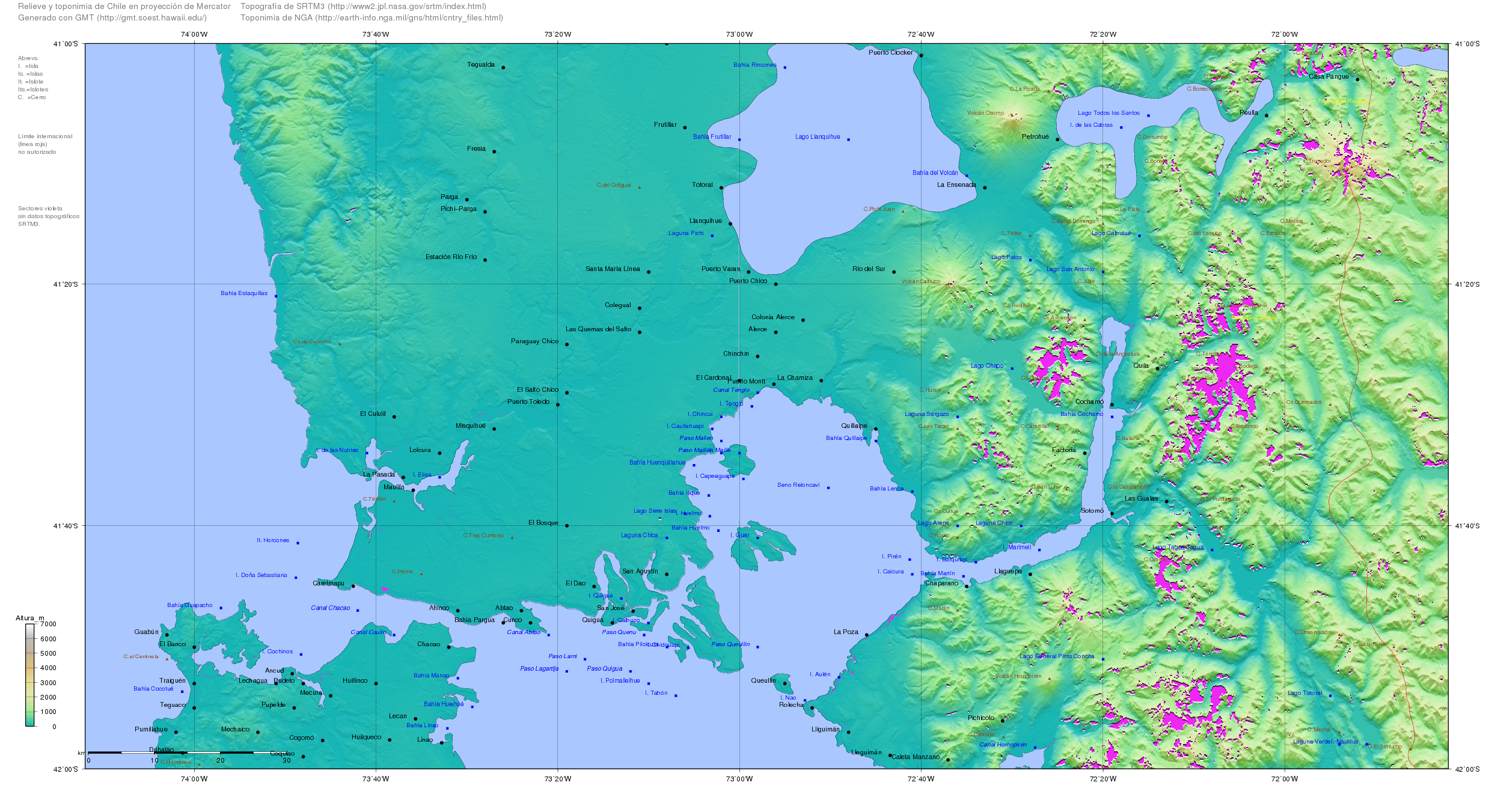
Osorno, Chile
Osorno (Mapuche: Chauracavi) is a city and commune in southern Chile and capital of Osorno Province in the Los Lagos Region. It had a population of 145,475, as of the 2002 census. It is located south of the national capital of Santiago, north of the regional capital of Puerto Montt and west of the Argentine city of San Carlos de Bariloche, connected via International Route 215 through the Cardenal Antonio Samoré Pass. It is a gateway for land access to the far south regions of Aysén and Magallanes, which would otherwise be accessible only by sea or air from the rest of the country. Located at the confluence of Rahue and Damas River, Osorno is the main service centre of agriculture and cattle farming in the northern Los Lagos Region. The city's cultural heritage is shaped by Huilliche, Spanish, and German influences. History Prehistory The city of Osorno is built upon river terraces formed during the last of Earth's geological periods —the Quaternary. 130,000 years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Ignacio De La Carrera Yturgoyen
Juan Ignacio de la Carrera Yturgoyen (31 July 1620 – 27 March 1682) was a Spanish soldier known for his career in colonial administration of Chile and for being the original patriarch of the Carrera family, a family that had outstanding public participation during the nineteenth century, especially during the Independence of Chile. He was born in Alegria de Oria, Gipuzkoa, Basque Country, Spain and died in Santiago, Chile. He married Catalina de Elguea y Cáceres (granddaughter of the Judeo-converso Diego Garcia de Caceres), with whom he had ten children, including Miguel de la Carrera, ancestor of the Carrera family, and Mariana de la Carrera Elguea common trunk on the Montt family tree. He also had three illegitimate children. Career Juan Ignacio arrived in Chile and landed in the city of Concepción del Nuevo Extremo on April 4, 1639. During his political career he held the following roles: *Mayor of Santiago in 1655 during the Great Uprising *Field Master of the Royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bueno River
Bueno River (Spanish: ''Río Bueno'') is a river in southern Chile. It originates in Ranco Lake and like most of Chile rivers it drains into the Pacific Ocean at the southern boundary of the Valdivian Coastal Reserve. Its lower flow forms the border between Osorno Province and Ranco Province. Traditionally it marks also the northern boundary of the indigenous Huilliche territory known as Futahuillimapu. The river passes through Río Bueno commune and city that takes name from the river. The major tributaries of the Bueno River are the Pilmaiquén River and the Rahue River, joining the river from the south. The former is the outlet of Puyehue Lake and the latter is the outlet of Rupanco Lake. Starting upstream the following settlements lie along the river: Puerto Nuevo at the source, Río Bueno, Trumao, Llancacura, and La Barra at the outflow in the ocean. The original Huilliche name for the river was ''Huenuleufu'', a combination of ''huenu'' "upper" and ''leufü'' "river ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diego Barros Arana
Diego Jacinto Agustín Barros Arana (; August 16, 1830 – November 4, 1907) was a Chilean professor, legislator, minister and diplomat. He is considered the most important Chilean historian of the 19th century. His main work ''General History of Chile'' ( es, Historia General de Chile) is a 15-volume work that spanned over 300 years of the nation's history. Barros Arana was of Basque descent. He also was an educator and a . He was director of the Instituto Nacional, a public high school, and of the . Works * * * * * * * * * * ** * * * * * List of works ...
|
Huilliche People
The Huilliche , Huiliche or Huilliche-Mapuche are the southern partiality of the Mapuche macroethnic group of Chile. Located in the Zona Sur, they inhabit both Futahuillimapu ("great land of the south") and, as the Cunco subgroup, the north half of Chiloé Island. The Huilliche are the principal indigenous people of those regions.Villalobos ''et al''. 1974, p. 49. According to Ricardo E. Latcham the term Huilliche started to be used in Spanish after the second founding of Valdivia in 1645, adopting the usage of the Mapuches of Araucanía for the southern Mapuche tribes. Huilliche means 'southerners' (Mapudungun ''willi'' 'south' and ''che'' 'people'.) A genetic study showed significant affinities between Huilliches and indigenous peoples east of the Andes, which suggests but does not prove a partial origin in present-day Argentina. During the 16th, 17th, and 18th centuries, the mainland Huilliche were generally successful at resisting Spanish encroachment. However, after the H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)