|
Woolly Hair
Woolly hair is a difficult to brush hair, usually present since birth and typically most severe in childhood. It has extreme curls and kinks and occurs in non-black people. The hairs come together to form tight locks, unlike in afro-textured hair, where the hairs remain individual. Woolly hair can be generalised over the whole scalp, when it tends to run in families, or it may involve just part of the scalp as in woolly hair nevus. The presence of woolly hair may indicate other problems such as with the heart in Naxos–Carvajal syndrome. Diagnosis is suspected by its general appearance and confirmed by scanning electron microscopy. The condition is rare. Alfred Milne Gossage coined the term ''woolly hair'' in 1908. Edgar Anderson distinguished woolly hair from afro-textured hair in 1936. Discovery Alfred Milne Gossage coined the term ''woolly hair'' to describe the sign in 18 members in three or four generations of a European family in Lowestoft, England, in 1908. He tho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naxos Syndrome
__notoc__ Naxos disease (also known as "diffuse non-epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma with woolly hair and cardiomyopathy" or "diffuse palmoplantar keratoderma with woolly hair and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy", first described on the island of Naxos by Nikos Protonotarios) is a cutaneous condition characterized by a palmoplantar keratoderma. The prevalence of the syndrome is up to 1 in every 1000 people in the Greek islands. It has been associated with mutations in the genes encoding the proteins desmoplakin, plakoglobin, desmocollin-2, and SRC-interacting protein (SIP). Naxos disease has the same cutaneous phenotype as the Carvajal syndrome. Symptoms Between 80 and 99% of those with Naxos disease will display some of the following symptoms: * Disease of the heart muscle * Thickening of palms and soles * Sudden increased heart rate * Dizzy spells * Kinked hair See also * Olmsted syndrome * List of cutaneous conditions * List of conditions caused ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Dominant And Recessive
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes is collectively known as atDNA or auDNA. For example, humans have a diploid genome that usually contains 22 pairs of autosomes and one allosome pair (46 chromosomes total). The autosome pairs are labeled with numbers (1–22 in humans) roughly in order of their sizes in base pairs, while allosomes are labelled with their letters. By contrast, the allosome pair consists of two X chromosomes in females or one X and one Y chromosome in males. Unusual combinations of XYY, XXY, XXX, XXXX, XXXXX or XXYY, among other Salome combinations, are known to occur and usually cause developmental abnormalities. Autosomes still contain sexual determination genes even though they are not sex chromosomes. For example, the SRY gene on the Y chromosome e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichorrhexis Nodosa
Trichorrhexis nodosa is a defect in the hair shaft characterized by thickening or weak points (nodes) that cause the hair to break off easily.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. .Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. . This group of conditions contributes to the appearance of hair loss, lack of growth, and damaged-looking hair. Symptoms Among the symptoms (and signs) for this condition are the following: * lack of apparent hair growth * hair appears patchy * hair breaks easily close to scalp * hair may have thickenings or nodes in the shaft * ends of hair thinned or split * whitish discoloration of hair tips * hair breaks easily at tips Complications This condition is not dangerous but may affect self-esteem. Causes Trichorrhexis may have a genetic basis but appears to be precipitated by environmental factors. Among Cauca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pili Torti
Pili torti (singular pilus tortus; also known as "twisted hairs") is characterized by short and brittle hairs that appear flattened and twisted when viewed through a microscope.Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. .James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. . This phenotype is noted in Menkes disease and Lichen planopilaris. Pili torti can also occur after use of retinoids, such as isotretinoin Isotretinoin, also known as 13-''cis''-retinoic acid and sold under the brand name Accutane among others, is a medication primarily used to treat severe acne. It is also used to prevent certain skin cancers ( squamous-cell carcinoma), and in t .... See also * List of cutaneous conditions * Crandall syndrome References External links Conditions of the skin appendages Human hair Hair diseases {{skin-appendage-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
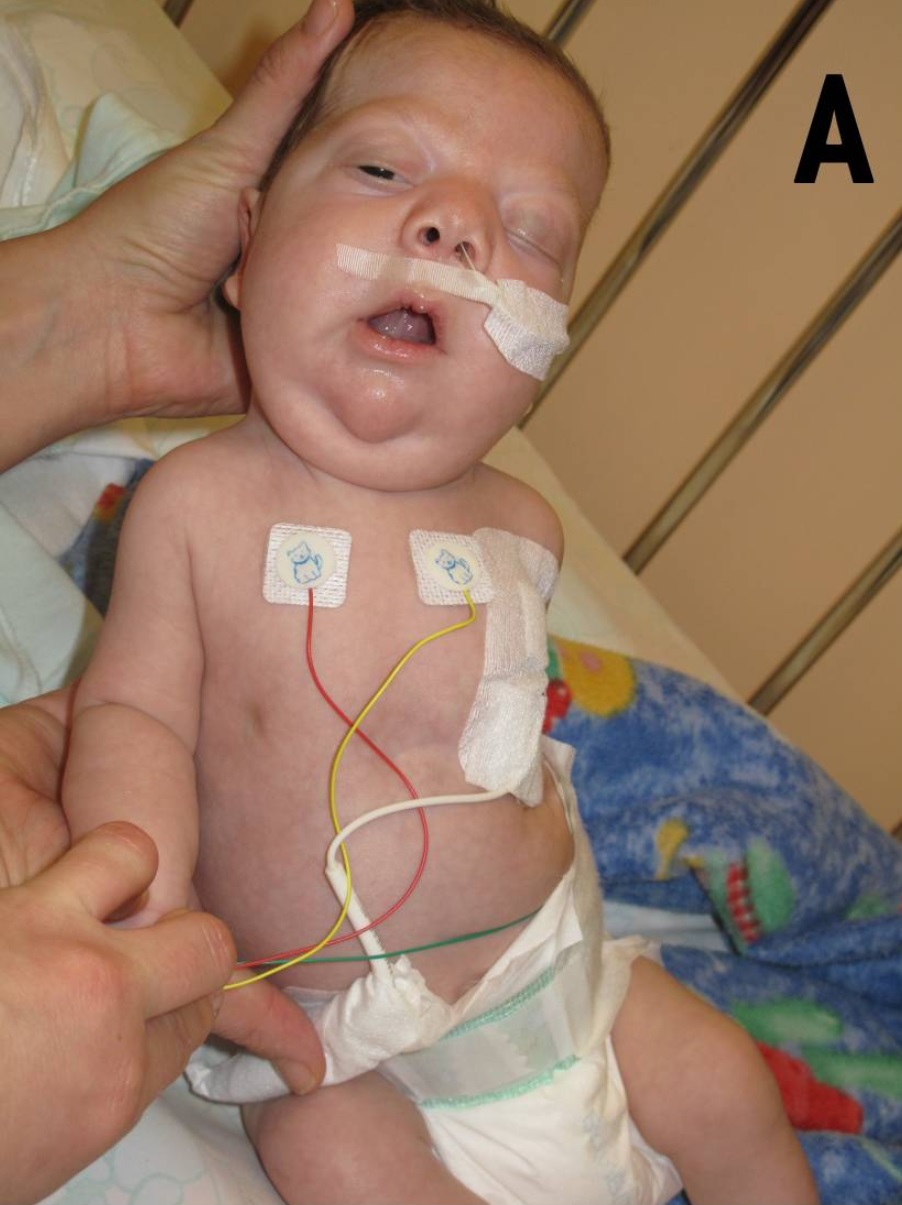
Cardiofaciocutaneous Syndrome
Cardiofaciocutaneous (CFC) syndrome is an extremely rare genetic disorder, and is one of the RASopathies. It was first described in 1986. It is characterized by the following: *Distinctive facial appearance *Unusually sparse, brittle, curly scalp hair *A range of skin abnormalities from dermatitis to thick, scaly skin over the entire body (generalized ichthyosis) *Heart malformations in over 75% of patients (congenital or appearing later), especially an obstruction of the normal flow of blood from the lower right ventricle of the heart to the lungs (valvar pulmonary stenosis) *Growth delays *Feeding problems associated with severe gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) *Foot abnormalities (extra toe or fusion of two or more toes) *Intellectual disability *Failure to thrive Presentation Head Individuals with the disorder usually have distinctive malformations of the craniofacial area including an unusually large head (macrocephaly), prominent forehead, and abnormal narrowing of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noonan Syndrome
Noonan syndrome (NS) is a genetic disorder that may present with mildly unusual facial features, short height, congenital heart disease, bleeding problems, and skeletal malformations. Facial features include widely spaced eyes, light-colored eyes, low-set ears, a short neck, and a small lower jaw. Heart problems may include pulmonary valve stenosis. The breast bone may either protrude or be sunken, while the spine may be abnormally curved. Intelligence in the syndrome is often normal. Complications of NS can include leukemia. A number of genetic mutations can result in Noonan syndrome. The condition may be inherited from a person's parents as an autosomal dominant condition or occur as a new mutation. Noonan syndrome is a type of RASopathy, the underlying mechanism for which involves overactivation within the RAS/MAPK cell signaling pathway. The diagnosis may be suspected based on symptoms, medical imaging, and blood tests. Confirmation may be achieved with genetic tes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persistent Pupillary Membrane
Persistent pupillary membrane (PPM) is a condition of the eye involving remnants of a fetal membrane that persist as strands of tissue crossing the pupil. The pupillary membrane in mammals exists in the fetus as a source of blood supply for the lens. It normally atrophies from the time of birth to the age of four to eight weeks. PPM occurs when this atrophy is incomplete. It generally does not cause any symptoms. The strands can connect to the cornea or lens, but most commonly to other parts of the iris. Attachment to the cornea can cause small corneal opacities, while attachment to the lens can cause small cataracts. Using topical atropine to dilate the pupil may help break down PPMs. In dogs, PPM is inherited in the Basenji but can occur in other breeds such as the Pembroke Welsh Corgi, Chow Chow, Mastiff, and English Cocker Spaniel. It can also be observed in cats, horses, and cattle Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterochromia Iridum
Heterochromia is a variation in coloration. The term is most often used to describe color differences of the iris, but can also be applied to color variation of hair or skin. Heterochromia is determined by the production, delivery, and concentration of melanin (a pigment). It may be inherited, or caused by genetic mosaicism, chimerism, disease, or injury. It occurs in humans and certain breeds of domesticated animals. Heterochromia of the eye is called heterochromia iridum or heterochromia iridis. It can be complete or sectoral. In complete heterochromia, one iris is a different color from the other. In sectoral heterochromia, part of one iris is a different color from its remainder. In central heterochromia, there is a ring around the pupil or possibly spikes of different colors radiating from the pupil. Though multiple causes have been posited, the scientific consensus is that a lack of genetic diversity is the primary reason behind heterochromia, at least in domestic anima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Verrucous Epidermal Nevus
Linear verrucous epidermal nevus is a skin lesion characterized by a verrucous skin-colored, dirty-gray or brown papule.Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. .James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. . Generally, multiple papules present simultaneously, and coalesce to form a serpiginous plaque. When this nevus covers a diffuse or extensive portion of the body's surface area, it may be referred to as a systematized epidermal nevus, when it involved only one-half of the body it is called a nevus unius lateris. See also * Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus * Epidermis (skin), Epidermis * Skin lesion * List of cutaneous conditions References External links Epidermal nevi, neoplasms, and cysts {{Epidermal-growth-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypopigmentation
Hypopigmentation is characterized specifically as an area of skin becoming lighter than the baseline skin color, but not completely devoid of pigment. This is not to be confused with depigmentation, which is characterized as the absence of all pigment. It is caused by melanocyte or melanin depletion, or a decrease in the amino acid tyrosine, which is used by melanocytes to make melanin. Some common genetic causes include mutations in the tyrosinase gene or OCA2 gene. As melanin pigments tend to be in the skin, eye, and hair, these are the commonly affected areas in those with hypopigmentation. Hypopigmentation is common and approximately one in twenty have at least one hypopigmented macule. Hypopigmentation can be upsetting to some, especially those with darker skin whose hypopigmentation marks are seen more visibly. Most causes of hypopigmentation are not serious and can be easily treated. Presentation Associated conditions It is seen in: * Albinism * Idiopathic guttate hypom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RASopathy
The RASopathies are developmental syndromes caused by germline mutations (or in rare cases by somatic mosaicism) in genes that alter the Ras subfamily and mitogen-activated protein kinases that control signal transduction, including: * Capillary malformation-AV malformation syndrome * Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome * Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome * Hereditary gingival fibromatosis type 1 * Neurofibromatosis type 1 * Noonan syndrome * Costello syndrome, Noonan-like * Legius syndrome, Noonan-like * Noonan syndrome with multiple lentigines, formerly called LEOPARD syndrome Noonan syndrome with multiple lentigines (NSML) which is part of a group called Ras/MAPK pathway syndromes, is a rare autosomal dominant, multisystem disease caused by a mutation in the protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 11 gene (''PT ..., Noonan-like * SYNGAP1-related intellectual disability References {{Medicine, state=collapsed Autosomal dominant disorders Congenital vascular defects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosaic (genetics)
Mosaicism or genetic mosaicism is a condition in multicellular organisms in which a single organism possesses more than one genetic line as the result of genetic mutation. This means that various genetic lines resulted from a single fertilized egg. Genetic mosaics may often be confused with chimerism, in which two or more genotypes arise in one individual similarly to mosaicism. In chimerism, though, the two genotypes arise from the fusion of more than one fertilized zygote in the early stages of embryonic development, rather than from a mutation or chromosome loss. Genetic mosaicism can result from many different mechanisms including chromosome nondisjunction, anaphase lag, and endoreplication. Anaphase lagging is the most common way by which mosaicism arises in the preimplantation embryo. Mosaicism can also result from a mutation in one cell during development, in which case the mutation will be passed on only to its daughter cells (and will be present only in certain adult ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |