|
Wood Carving
Wood carving is a form of woodworking by means of a cutting tool (knife) in one hand or a chisel by two hands or with one hand on a chisel and one hand on a mallet, resulting in a wooden figure or figurine, or in the sculptural ornamentation of a wooden object. The phrase may also refer to the finished product, from individual sculptures to hand-worked mouldings composing part of a tracery. The making of sculpture in wood has been extremely widely practised, but doesn't survive undamaged as well as the other main materials like stone and bronze, as it is vulnerable to decay, insect damage, and fire. Therefore, it forms an important hidden element in the art history of many cultures. Outdoor wood sculptures do not last long in most parts of the world, so it is still unknown how the totem pole tradition developed. Many of the most important sculptures of China and Japan, in particular, are in wood, and so are the great majority of African sculpture and that of Oceania an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early Early may refer to: History * The beginning or oldest part of a defined historical period, as opposed to middle or late periods, e.g.: ** Early Christianity ** Early modern Europe Places in the United States * Early, Iowa * Early, Texas * Early ..., High Middle Ages, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
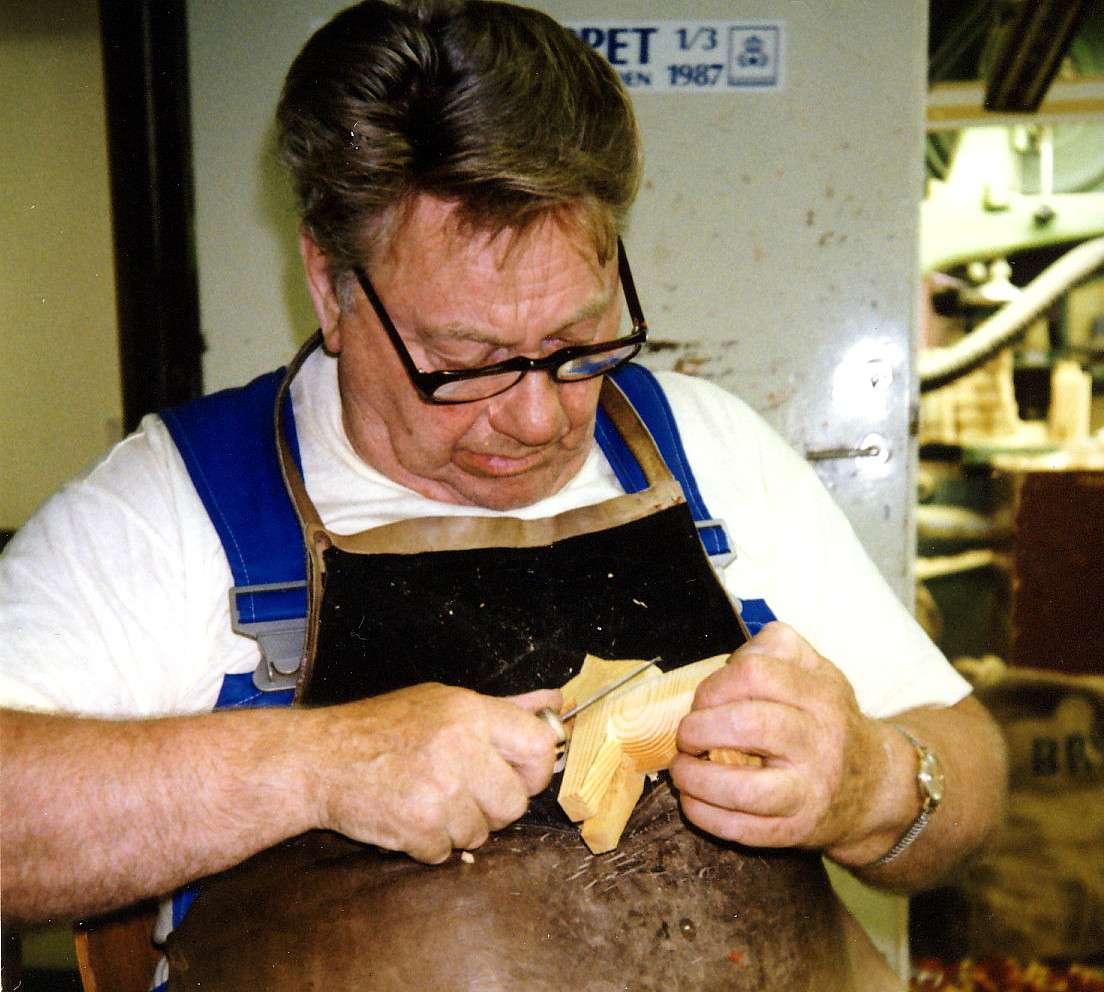
Whittling
Whittling may refer either to the art of carving shapes out of raw wood using a knife or a time-occupying, non-artistic (contrast wood carving for artistic process) process of repeatedly shaving slivers from a piece of wood. It is used by many as a pastime, or as a way to make artistic creations. Background of whittling Casual whittling is typically performed with a light, small-bladed knife, usually a pocket knife. Specialized whittling knives, with fixed single blades, are preferred for sculpting artistic work. They have thick handles which are easier to grip for long periods and have better leverage, allowing more precise control and pressure. Occasionally the terms "whittling" and "carving" are used interchangeably, but they are different arts. Carving employs the use of chisels, gouges, with or without a mallet, and often powered equipment such as lathes. Whittling, however, involves only the use of a knife. In industrialized areas of the world, whittling is mainly a hobb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treen (wooden)
Treen (literally "of a tree") is a generic name for small handmade functional household objects made of wood. Treen is distinct from furniture, such as chairs, and cabinetry, as well as clocks and cupboards. Before the late 17th century, when silver, pewter, and ceramics were introduced for tableware, most small household items, boxes and tableware were carved from wood. Today, treen is highly collectable for its patina and tactile appeal. Anything from wooden plates and bowls, snuff boxes and needle cases, spoons and stay busks to shoehorns and chopping boards can be classed as treen. Domestic and agricultural wooden tools are also usually classed with treen. Before the advent of cheap metal wares in industrialized societies, and later plastic, wood played a much greater part as the raw material for common objects. Turning and carving were the key manufacturing techniques. The selection of wood species was important, and close-grained native hardwoods such as box, beech and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lovespoon
A lovespoon is a wooden spoon decoratively carved that was traditionally presented as a gift of romantic intent. The spoon is normally decorated with symbols of love, and was intended to reflect the skill of the carver. Due to the intricate designs, lovespoons are no longer used as functioning spoons and are now decorative craft items. Origins The lovespoon is a traditional craft that dates back to the seventeenth century. Over generations, decorative carvings were added to the spoon and it lost its original practical use and became a treasured decorative item to be hung on a wall. The earliest known dated lovespoon from Wales, displayed in the St Fagans National History Museum near Cardiff, is from 1667, although the tradition is believed to date back long before that. The earliest dated lovespoon worldwide originates from Germany, and is dated as 1664. Symbols The lovespoon was given to a young woman by her suitor. It was important for the girl's father to see that the young m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scandinavian Flat-plane Style Of Woodcarving
The Scandinavian flat-plane style of woodcarving is a style of figure carving. The figures are carved in large flat planes, created primarily using a carving knife. Tool marks are left in the carving and very little (if any) rounding or sanding upright=1.35, Sheets of sandpaper with different grit sizes (40 (coarse), 80, 150, 240, 600 (fine)). Sandpaper and glasspaper are names used for a type of coated abrasive that consists of sheets of paper or cloth with abrasive material glued ... is done. Emil Janel, a Swedish-born American artist, was considered by many to be one of the best of this genre. A common example of the style is the Dalecarlian horse, whose distinctive shape is due to this manner of carving. References * Woodcarving {{decorative-art-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
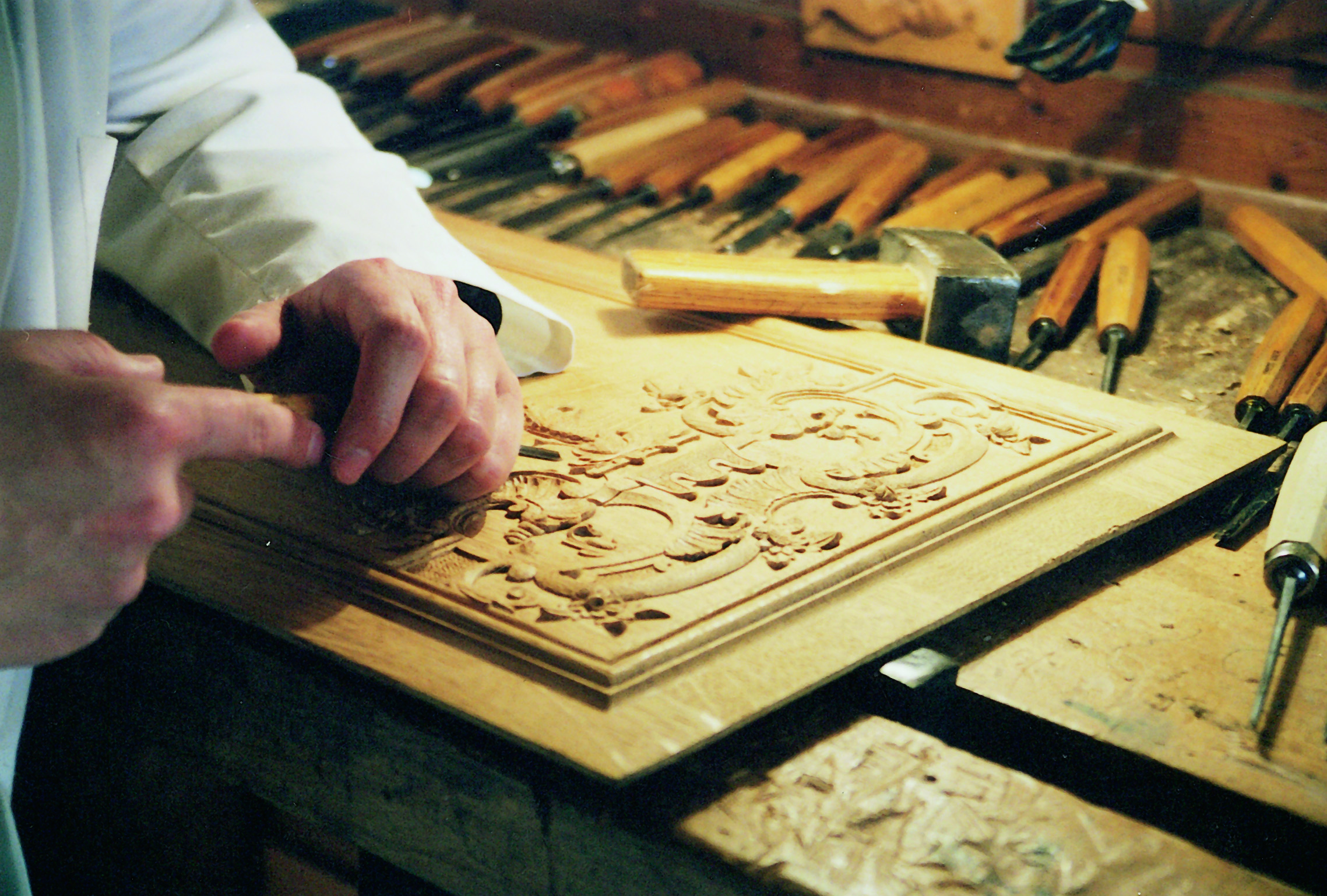
Relief Carving
In wood carving relief carving is a type in which figures or patterns are carved in a flat panel of wood; the same term is also used for carving in stone, ivory carving and various other materials. The figures project only slightly from the background rather than standing freely. Depending on the degree of projection, reliefs may also be classified as high or medium relief. Relief carving can be described as "carving pictures in wood". The process of relief carving involves removing wood from a flat wood panel in such a way that an object appears to rise out of the wood. Relief carving begins with a design idea, usually put to paper in the form of a master pattern which is then transferred to the wood surface. Most relief carving is done with hand tools, chisels and gouges, which often require a mallet to drive them through the wood. As wood is removed from the panel around the objects traced onto it from the pattern, the objects themselves stand up from the background wood. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chip Carving
Chip carving or chip-carving, ''kerbschnitt'' in German, is a style of carving in which knives or chisels are used to remove small chips of the material from a flat surface in a single piece. The style became important in Migration Period metalwork, mainly animal style jewellery, where the faceted surfaces created caught the light to give a glinting appearance. This was very probably a transfer to metalworking of a technique already used in woodcarving, but no wooden examples have survived. Famous Anglo-Saxon examples include the jewellery from Sutton Hoo and the Tassilo Chalice, though the style originated in mainland Europe. In later British and Irish metalwork, the same style was imitated using casting, which is often called imitation chip-carving, or sometimes just chip carving (authors are not always careful to distinguish the two), a term also sometimes applied to pottery decorated in a similar way. Woodwork In modern wood carving, the style is also called spoon carving. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larch
Larches are deciduous conifers in the genus ''Larix'', of the family Pinaceae (subfamily Laricoideae). Growing from tall, they are native to much of the cooler temperate northern hemisphere, on lowlands in the north and high on mountains further south. Larches are among the dominant plants in the boreal forests of Siberia and Canada. Although they are conifers, larches are deciduous trees that lose their needles in the autumn. Etymology The English name Larch ultimately derives from the Latin "larigna," named after the ancient settlement of Larignum. The story of its naming was preserved by Vitruvius: It is worth while to know how this wood was discovered. The divine Caesar, being with his army in the neighbourhood of the Alps, and having ordered the towns to furnish supplies, the inhabitants of a fortified stronghold there, called Larignum, trusting in the natural strength of their defences, refused to obey his command. So the general ordered his forces to the assault. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
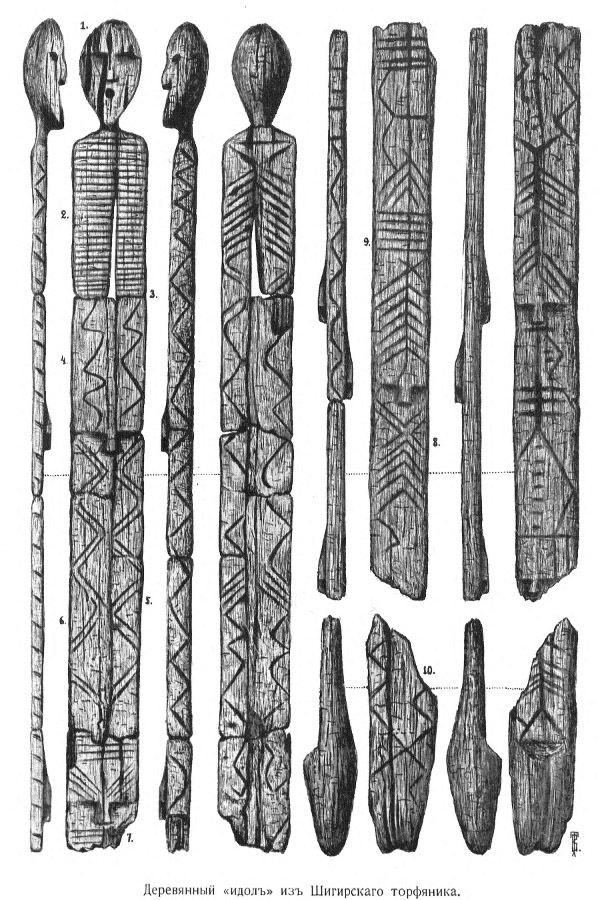
Shigir Idol
The Shigir Sculpture, or Shigir Idol (russian: Шигирский идол), is the oldest known wooden sculpture in the world, made during the Mesolithic period, shortly after the end of the last Ice Age. The wood it was carved from is approximately 12,000 years old. It is displayed in the Sverdlovsk Regional Museum of Local Lore in Yekaterinburg, Russia. Discovery The sculpture was discovered on January 24, 1890 at a depth of in the peat bog of Shigir, on the eastern slope of the Middle Urals, near the village of Kalata (modern Kirovgrad) and approximately from Yekaterinburg. Investigations in this area had begun 40 years earlier, after the discovery of a variety of prehistoric objects in an open-cast gold mine. It was extracted in ten parts. Professor D. I. Lobanov combined the main fragments to reconstitute a sculpture high. In 1914, archaeologist proposed a variant of this reconstruction by integrating the unused fragments. His reconstruction suggested that the orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iconography
Iconography, as a branch of art history, studies the identification, description and interpretation of the content of images: the subjects depicted, the particular compositions and details used to do so, and other elements that are distinct from artistic style. The word ''iconography'' comes from the Greek ("image") and ("to write" or ''to draw''). A secondary meaning (based on a non-standard translation of the Greek and Russian equivalent terms) is the production or study of the religious images, called "icons", in the Byzantine and Orthodox Christian tradition (see Icon). This usage is mostly found in works translated from languages such as Greek or Russian, with the correct term being "icon painting". In art history, "an iconography" may also mean a particular depiction of a subject in terms of the content of the image, such as the number of figures used, their placing and gestures. The term is also used in many academic fields other than art history, for example semioti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin. Its eighteen integral regions (five of which are overseas) span a combined area of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |