|
Wiring
Electrical wiring is an electrical installation of cabling and associated devices such as switches, distribution boards, sockets, and light fittings in a structure. Wiring is subject to safety standards for design and installation. Allowable wire and electrical cable, cable types and sizes are specified according to the circuit operating voltage and electric current capability, with further restrictions on the environmental conditions, such as ambient temperature range, moisture levels, and exposure to sunlight and chemicals. Associated circuit protection, control, and distribution devices within a building's wiring system are subject to voltage, current, and functional specifications. Wiring safety codes vary by locality, country, or region. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) is attempting to harmonise wiring standards among member countries, but significant variations in design and installation requirements still exist. Wiring codes of practice and regulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BS 7671
British Standard BS 7671 "Requirements for Electrical Installations. IET Wiring Regulations", informally called in the UK electrical community "The Regs", is the national standard in the United Kingdom for electrical installation and the safety of electrical wiring in domestic, commercial, industrial, and other buildings, also in special installations and locations, such as marinas or caravan parks and medical locations In general, BS 7671 applies to circuits supplied at nominal voltages (Uo) up to and including 1000 volts AC or 1500 volts DC. The standard therefore covers the Extra Low Voltage (ELV) range (0-50V AC, 0-125V DC), and the Low Voltage (LV) range (50-1000V AC, 125-1500V DC). The frequencies covered for AC are 50 Hz, 60 Hz, and 400 Hz, used in the UK for houses, offices, and commerce. It did not become a recognized British Standard until the publication of the 16th edition in 1992. The standard takes account of the technical substance of agreements re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Electrical Code (US)
The National Electrical Code (NEC), or NFPA 70, is a regionally adoptable standard for the safe installation of electrical wiring and equipment in the United States. It is part of the National Fire Code series published by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), a private trade association. Despite the use of the term "national", it is not a federal law. It is typically adopted by states and municipalities in an effort to standardize their enforcement of safe electrical practices. In some cases, the NEC is amended, altered and may even be rejected in lieu of regional regulations as voted on by local governing bodies. The "authority having jurisdiction" inspects for compliance with these standards. The NEC should not be confused with the National Electrical Safety Code (NESC) published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). The NESC is used for electric power and communication utility systems including overhead lines, underground lines and powe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Electrical Code
The National Electrical Code (NEC), or NFPA 70, is a regionally adoptable standard for the safe installation of electrical wiring and equipment in the United States. It is part of the National Fire Code series published by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), a private trade association. Despite the use of the term "national", it is not a Law of the United States, federal law. It is typically adopted by U.S. state, states and municipalities in an effort to standardize their enforcement of safe electrical practices. In some cases, the NEC is amended, altered and may even be rejected in lieu of regional regulations as voted on by local governing bodies. The "authority having jurisdiction" inspects for compliance with these standards. The NEC should not be confused with the National Electrical Safety Code (NESC) published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). The NESC is used for electric power and communication utility systems including overh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Code
{{Electrical Wiring Sidebar An electrical code is a set of regulations for the design and installation of electrical wiring in a building. The intention of a code is to provide standards to ensure electrical wiring systems that are safe for people and property. Such wiring is subject to rigorous safety standards for design and installation. Wires and electrical cables are specified according to the circuit operating voltage and electric current capability, with further restrictions on the environmental conditions, such as ambient temperature range, moisture levels, and exposure to sunlight and chemicals. Associated circuit protection, control and distribution devices within a building's wiring system are subject to voltage, current and functional specification. To ensure both wiring and associated devices are designed, selected and installed so that they are safe for use, they are subject to wiring safety codes or regulations, which vary by locality, country or region. The Int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microgeneration
Microgeneration is the small-scale production of heat or electric power from a "low carbon source," as an alternative or supplement to traditional centralized grid-connected power. Microgeneration technologies include small-scale wind turbines, micro hydro, solar PV systems, microbial fuel cells, ground source heat pumps, and micro combined heat and power installations. These technologies are often combined to form a hybrid power solution that can offer superior performance and lower cost than a system based on one generator. History In the United States, Microgeneration had its roots in the 1973 oil crisis and the Yom Kippur War which prompted innovation. on June 20, 1979, 32 solar panels were installed at the White House. The solar cells were dismantled 7 years later during the Reagan administration. The use of Solar water heating dates back before 1900 with "the first practical solar cell being developed by Bell Labs in 1954." The "University of Delaware is credited wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photovoltaic System
A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and convert sunlight into electricity, a solar inverter to convert the output from direct current, direct to alternating current, as well as photovoltaic mounting system, mounting, solar cable, cabling, and other electrical accessories to set up a working system. It may also use a solar tracking system to improve the system's overall performance and include an rechargeable battery, integrated battery. PV systems convert light directly into electricity, and are not to be confused with other solar technologies, such as concentrated solar power or Solar thermal energy, solar thermal, used for heating and cooling. A solar array only encompasses the ensemble of solar panels, the visible part of the PV system, and does not include all the other hardw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Cable
An electrical cable is an assembly of one or more wires running side by side or bundled, which is used to carry electric current. One or more electrical cables and their corresponding connectors may be formed into a ''cable assembly'', which is not necessarily suitable for connecting two devices but can be a partial product (e.g. to be soldered onto a printed circuit board with a connector mounted to the housing). Cable assemblies can also take the form of a cable tree or cable harness, used to connect many terminals together. Etymology The original meaning of ''cable'' in the electrical wiring sense was for submarine telegraph cables that were armoured with iron or steel wires. Early attempts to lay submarine cables without armouring failed because they were too easily damaged. The armouring in these early days (mid-19th century) was implemented in separate factories to the factories making the cable cores. These companies were specialists in manufacturing wire rope of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEC 60446
The international standard IEC 60446 ''Basic and safety principles for man-machine interface, marking and identification - Identification of equipment terminals, conductor terminations and conductors'' was a standard published by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) that defined basic safety principles for identifying electrical conductors by colours or numerals, for example in electricity distribution wiring. The standard has been withdrawn; the fourth edition (IEC 60446:2007) was merged in 2010 into the fifth edition of IEC 60445 along with the fourth edition, IEC 60445:2006. Permitted colours The standard permits the following colours for identifying conductors: : black, brown, red, orange, yellow, green, blue, violet, grey, white, pink, and turquoise. (The colours green and yellow on their own are only permitted where confusion with the colouring of the green/yellow protective conductor is unlikely. Combinations of the above colours are permitted, but green ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEC 60364
IEC 60364 ''Electrical Installations for Buildings'' is the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)'s international standard on ''electrical installations of buildings''. This standard is an attempt to harmonize national wiring standards in an IEC standard and is published in the European Union by CENELEC as "HD 60364". The latest versions of many European wiring regulations (e.g., BS 7671 in the UK) follow the section structure of IEC 60364 very closely, but contain additional language to cater for historic national practice and to simplify field use and determination of compliance by electricians and inspectors. National codes and site guides are meant to attain the common objectives of IEC 60364, and provide rules in a form that allows for guidance of persons installing and inspecting electrical systems. The standard has several parts: * Part 1: Fundamental principles, assessment of general characteristics, definitions * Part 4: Protection for safety ** Section 41: Pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Electrical Code
The Canadian Electrical Code, CE Code, or CSA C22.1 is a standard published by the Canadian Standards Association pertaining to the installation and maintenance of electrical equipment in Canada. The first edition of the Canadian Electrical Code was published in 1927. The current (25th) edition was published in April of 2021. Code revisions are now scheduled on a three-year cycle. The Code is produced by a large body of volunteers from industry and various levels of government. The Code uses a prescriptive model, outlining in detail the wiring methods that are acceptable. In the current edition, the Code recognizes that other methods can be used to assure safe installations, but these methods must be acceptable to the authority enforcing the Code in a particular jurisdiction. The Canadian Electrical Code serves as the basis for wiring regulations across Canada. Generally, legislation adopts the Code by reference, usually with a schedule of changes that amend the Code for local c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
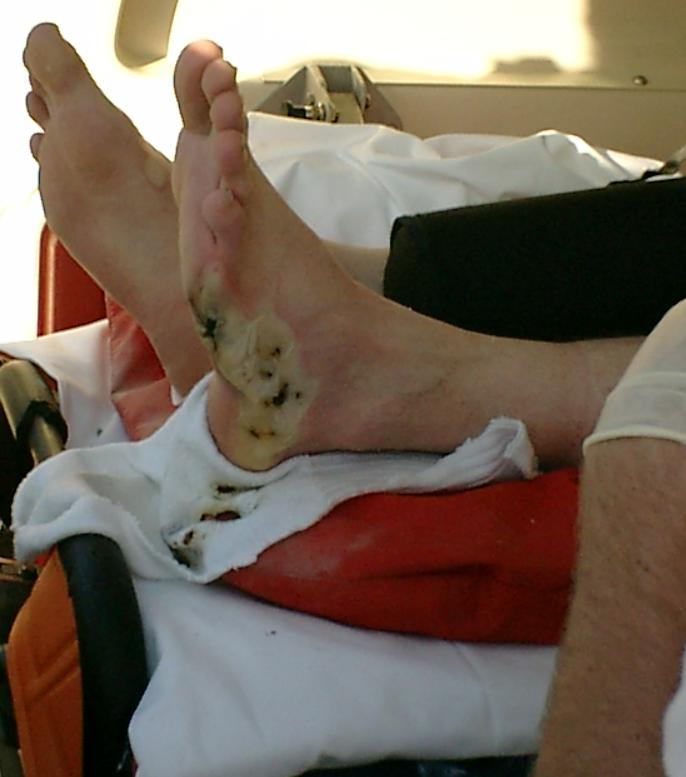
Electrical Shock
Electrical injury is a physiological reaction caused by electric current passing through the body. The injury depends on the density of the current, tissue resistance and duration of contact. Very small currents may be imperceptible or produce a light tingling sensation. A shock caused by low and otherwise harmless current could startle an individual and cause injury due to jerking away or falling. Stronger currents may cause some degree of discomfort or pain, while more intense currents may induce involuntary muscle contractions, preventing the person from breaking free of the source of electricity. Still larger currents result in tissue damage and may trigger ventricular fibrillation or cardiac arrest. Consequences of injury from electricity may include amputations, bone fractures and orthopedic and musculoskeletal injuries. If death results from an electric shock the cause of death is generally referred to as electrocution. Electric injury occurs upon contact of a body part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase (electricity)
A polyphase system is a means of distributing alternating-current (AC) electrical power where the power transfer is constant during each electrical cycle. AC phase refers to the phase offset value (in degrees) between AC in multiple conducting wires; ''phases'' may also refer to the corresponding terminals and conductors, as in color codes. Polyphase systems have three or more energized electrical conductors carrying alternating currents with a defined phase between the voltage waves in each conductor; for three-phase voltage, the phase angle is 120° or 2π/3 radians (although early systems used 4 wire two-phase). Polyphase systems are particularly useful for transmitting power to electric motors which rely on alternating current to rotate. The most common example is the three-phase power system used for industrial applications and for power transmission. Compared to a single-phase, two-wire system, a three-phase three-wire system transmits three times as much power for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |