|
Wine Capsule
A wine bottle is a bottle, generally a glass bottle, that is used for holding wine. Some wines are fermented in the bottle while others are bottled only after fermentation. Recently the bottle has become a standard unit of volume to describe sales in the wine industry, measuring . Wine bottles are produced, however, in a variety of volumes and shapes. Wine bottles are traditionally sealed with a cork, but screw-top caps are becoming popular, and there are several other methods used to seal a bottle. Sizes Many traditional wine bottle sizes are named for Biblical kings and historical figures. The chart below lists the sizes of various wine bottles in multiples relating to a standard bottle of wine, which is (six 125 mL servings). The "wineglassful"—an official unit of the apothecaries' system of weights—is much smaller at . Most champagne houses are unable to carry out secondary fermentation in bottles larger than a magnum due to the difficulty in riddling large, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wine Bottle
A wine bottle is a bottle, generally a glass bottle, that is used for holding wine. Some wines are fermented in the bottle while others are bottled only after fermentation. Recently the bottle has become a standard unit of volume to describe sales in the wine industry, measuring . Wine bottles are produced, however, in a variety of volumes and shapes. Wine bottles are traditionally sealed with a cork, but screw-top caps are becoming popular, and there are several other methods used to seal a bottle. Sizes Many traditional wine bottle sizes are named for Biblical kings and historical figures. The chart below lists the sizes of various wine bottles in multiples relating to a standard bottle of wine, which is (six 125 mL servings). The "wineglassful"—an official unit of the apothecaries' system of weights—is much smaller at . Most champagne houses are unable to carry out secondary fermentation in bottles larger than a magnum due to the difficulty in riddling large, heav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
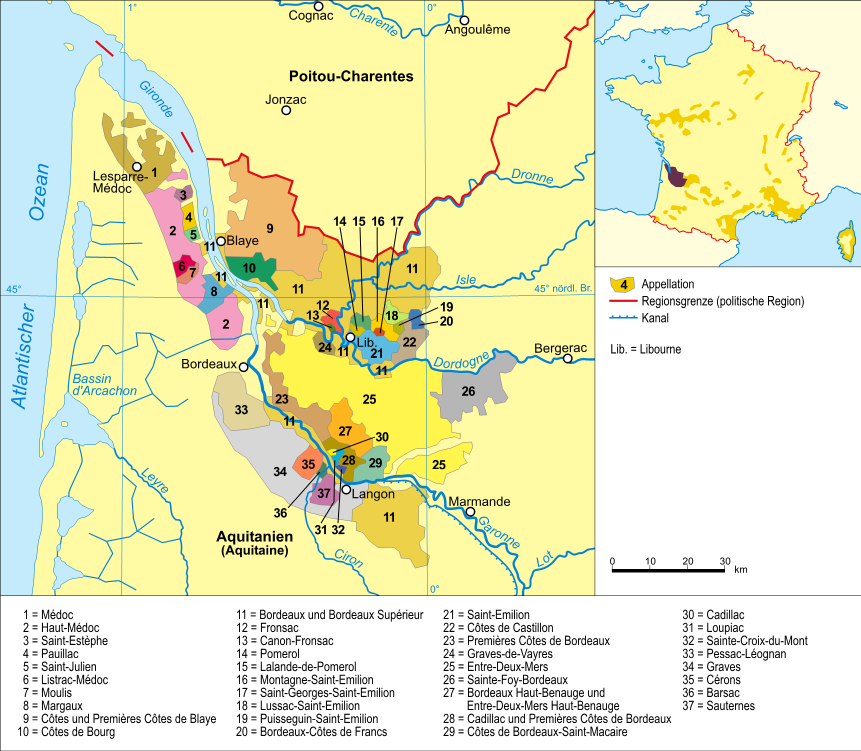
Bordeaux Wine
Bordeaux wine ( oc, vin de Bordèu, french: vin de Bordeaux) is produced in the Bordeaux region of southwest France, around the city of Bordeaux, on the Garonne River. To the north of the city the Dordogne River joins the Garonne forming the broad estuary called the Gironde; the Gironde department, with a total vineyard area of over 120,000 hectares, is the largest wine growing area in France. Average vintages produce over 700 million bottles of wine, ranging from large quantities of everyday table wine, to some of the most expensive and prestigious wines in the world. The vast majority of wine produced in Bordeaux is red (sometimes called "claret" in Britain), with sweet white wines (most notably Sauternes), dry whites, and (in much smaller quantities) rosé and sparkling wines (Crémant de Bordeaux) collectively making up the remainder. Bordeaux wine is made by more than 8,500 producers or ''châteaux''. There are 54 appellations of Bordeaux wine. History Viticulture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babylon
''Bābili(m)'' * sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠 * arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel'' * syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel'' * grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn'' * he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel'' * peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru'' * elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babili'' *Kassite: ''Karanduniash'', ''Karduniash'' , image = Street in Babylon.jpg , image_size=250px , alt = A partial view of the ruins of Babylon , caption = A partial view of the ruins of Babylon , map_type = Near East#West Asia#Iraq , relief = yes , map_alt = Babylon lies in the center of Iraq , coordinates = , location = Hillah, Babil Governorate, Iraq , region = Mesopotamia , type = Settlement , part_of = Babylonia , length = , width = , area = , height = , builder = , material = , built = , abandoned = , epochs = , cultures = Sumerian, Akkadian, Amorite, Kassite, Assyrian, Chaldean, Achaemenid, Hellenistic, Parthian, Sasanian, Muslim , dependency_of = , occupants = , event = , excavations = , archaeologists = Hormuzd Rassam, Robe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biblical Magi
The biblical Magi from Middle Persian ''moɣ''(''mard'') from Old Persian ''magu-'' 'Zoroastrian clergyman' ( or ; singular: ), also referred to as the (Three) Wise Men or (Three) Kings, also the Three Magi were distinguished foreigners in the Gospel of Matthew and Christian tradition. They are said to have visited Jesus after his birth, bearing gifts of gold, frankincense and myrrh. They are regular figures in traditional accounts of the nativity celebrations of Christmas and are an important part of Christian tradition. The Gospel of Matthew is the only one of the four canonical gospels to mention the Magi. has it that they came "from the east" to worship the "king of the Jews". The gospel never mentions the number of Magi. Still, most western Christian denominations have traditionally assumed them to have been three in number, based on the statement that they brought three gifts. In Eastern Christianity, especially the Syriac churches, the Magi often number twelve. Their i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shalmaneser V
Shalmaneser V (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning "Salmānu is foremost"; Biblical Hebrew: ) was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of his father Tiglath-Pileser III in 727 BC to his deposition and death in 722 BC. Though Shalmaneser V's brief reign is poorly known from contemporary sources, he remains known for the conquest of Samaria and the fall of the Kingdom of Israel, though the conclusion of that campaign is sometimes attributed to his successor, Sargon II, instead. Shalmaneser V is known to have campaigned extensively in the lands west of the Assyrian heartland, warring not only against the Israelites, but also against the Phoenician city-states and against kingdoms in Anatolia. Though he successfully annexed some lands to the Assyrian Empire, his campaigns resulted in long and drawn-out sieges lasting several years, some being unresolved at the end of his reign. The circumstances of his deposition and death are not clear, though they were likely violen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)