|
Whip-lash Squid
The Mastigoteuthidae, also known as whip-lash squid, are a family of small deep-sea squid. Approximately 20 known species in six genera are represented, with members found in both the mesopelagic and bathypelagic zone of most oceans. Originally described by Verill in 1881, it was later lowered by Chun (1920) to a subfamily (Mastigoteuthinae) of the Chiroteuthidae. However, Roper et al. (1969) raised it back to the family level, and this has not been changed since. The taxonomy of this family is extremely unstable, and there have been at times one genus (Young, Lindgren, & Vecchione, 2008), two genera and four subgenera(Salcedo-Vargas & Okutani, 1994), two genera and several 'groups' (Salcedo-Vargas, 1997), five genera (Braid, McBride, & Bolstad, 2014) and one species with an uncertain placement, or six genera (Young, Vecchione, & Braid, 2014). Description Mastigoteuthids range in size from quite small species in the genus '' Mastigoteuthis'', to relatively gigantic sizes in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastigoteuthis Flammea
''Mastigoteuthis flammea'' (flaming whiplash squid) is a species of whip-lash squid The Mastigoteuthidae, also known as whip-lash squid, are a family of small deep-sea squid. Approximately 20 known species in six genera are represented, with members found in both the mesopelagic and bathypelagic zone of most oceans. Originally d .... Image:Mastigoteuthis flammea2.jpg, Ventral views of funnel locking apparatuses (left: 27 mm ML, right: 35 mm ML) Image:Mastigoteuthis flammea3.jpg, Dorsal view of nuchal cartilage References * Chun, C. 1910. Die Cephalopoden. Oegopsida. ''Wissenschaftliche Ergebnisse der Deutschen Tiefsee Expedition auf dem Dampfer "Valdivia" 1898-1899'' 18(1): 1-401. External links Tree of Life web project: ''Mastigoteuthis flammea'' Mastigoteuthis Molluscs described in 1908 Taxa named by Carl Chun {{squid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiroteuthidae
The Chiroteuthidae are a family of deep-sea squid, generally small to medium in size, rather soft and gelatinous, and slow moving. They are found in most temperate and tropical oceans, but are known primarily from the North Atlantic, North Pacific, and Indo-Pacific. The family is represented by approximately 12 species and four subspecies in four genera, two of which are monotypic. They are sometimes known collectively as whip-lash squid, but this common name is also applied to the Mastigoteuthidae, which are sometimes treated as a subfamily (Mastigoteuthinae) of Chiroteuthidae. The monotypic genus '' Grimalditeuthis'' was once (and may still be) given its own family, Grimalditeuthidae. Generally speaking, chiroteuthids are not well represented by described specimens, because they are so often damaged during capture. Description The Chiroteuthidae are most notable for their unique paralarval stage, known as the doratopsis stage. Although morphology varies greatly withi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans ( Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benthos
Benthos (), also known as benthon, is the community of organisms that live on, in, or near the bottom of a sea, river, lake, or stream, also known as the benthic zone.Benthos from the Census of Antarctic Marine Life website This community lives in or near marine or freshwater sedimentary environments, from tidal pools along the , out to the continental shelf, and then down to the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnoteuthis Magna
''Magnoteuthis'' is a genus of whip-lash squid containing at least three species. Some teuthologists consider '' Idioteuthis'' or '' Mastigoteuthis'' synonymous with this taxon In biology, a taxon ( back-formation from '' taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular n ..., but it is genetically and morphologically distinct. Species *Genus ''Magnoteuthis'' **'' Magnoteuthis magna'' (Joubin, 1913) **'' Magnoteuthis microlucens'' (Young, Lindgren & Vecchione, 2008) **'' Magnoteuthis osheai'' Braid & Bolstad, 2015 References External links Squid Cephalopod genera {{squid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastigopsis Hjorti
''Mastigopsis'' is a genus of whip-lash squid containing one single species, ''Mastigopsis hjorti''. Some teuthologists consider ''Idioteuthis'' synonymous with this taxon; however, genetic results indicate that this genus is not closely related with ''Idioteuthis'' but actually closer to ''Magnoteuthis''. Description ''Mastigopsis hjorti'' is similar to '' Idioteuthis cordiformis'' in that it has large fins, skin tubercles, no pocket between the bridles and the large dividing, protective membranes on the tentacular clubs but the main difference is that this species has photophores on its eyes. The suckers on the tentacular club are all of similar size, except for those nearest the tip. The funnel has a locking-apparatus which has an oval, slightly curved depression and towards the posterior its sides protrude having no cartilaginous fleshy projections. The fins are large and measure around 90% of the length of the mantle. The mantle, head, funnel and the aboral surface of the ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastigoteuthis Inermis
''Mastigoteuthis inermis'' is a species of whip-lash squid The Mastigoteuthidae, also known as whip-lash squid, are a family of small deep-sea squid. Approximately 20 known species in six genera are represented, with members found in both the mesopelagic and bathypelagic zone of most oceans. Originally d .... Richard E. Young and Michael Vecchione consider it to be a junior synonym of the widely distributed '' M. magna''. References *Rancurel, P. 1972. ''Mastigoteuthis inermis'' espèce nouvelle de Chiroteuthidae du Golfe de Guinée (Cephalopoda - Oegopsida). ''Bulletin de la Société Zoologique de France'' 97(1): 25-34. External links Tree of Life web project: ''Mastigoteuthis inermis'' Mastigoteuthis Molluscs described in 1972 {{Squid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatophore
Chromatophores are cells that produce color, of which many types are pigment-containing cells, or groups of cells, found in a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopods. Mammals and birds, in contrast, have a class of cells called melanocytes for coloration. Chromatophores are largely responsible for generating skin and eye colour in ectothermic animals and are generated in the neural crest during embryonic development. Mature chromatophores are grouped into subclasses based on their colour (more properly " hue") under white light: xanthophores (yellow), erythrophores (red), iridophores (reflective / iridescent), leucophores (white), melanophores (black/brown), and cyanophores (blue). While most chromatophores contain pigments that absorb specific wavelengths of light, the color of leucophores and iridophores is produced by their respective scattering and optical interference properties. Some species can rapidly change colour throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioluminescence
Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by living organisms. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms including some bioluminescent bacteria, and terrestrial arthropods such as fireflies. In some animals, the light is bacteriogenic, produced by symbiotic bacteria such as those from the genus '' Vibrio''; in others, it is autogenic, produced by the animals themselves. In a general sense, the principal chemical reaction in bioluminescence involves a light-emitting molecule and an enzyme, generally called luciferin and luciferase, respectively. Because these are generic names, luciferins and luciferases are often distinguished by the species or group, e.g. firefly luciferin. In all characterized cases, the enzyme catalyzes the oxidation of the luciferin. In some species, the luciferase requires other cofactors, such as calcium or magnesium ions, and so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photophore
A photophore is a glandular organ that appears as luminous spots on various marine animals, including fish and cephalopods. The organ can be simple, or as complex as the human eye; equipped with lenses, shutters, color filters and reflectors, however unlike an eye it is optimized to produce light, not absorb it. The bioluminescence can variously be produced from compounds during the digestion of prey, from specialized mitochondrial cells in the organism called photocytes ("light producing" cells), or, similarly, associated with symbiotic bacteria in the organism that are cultured. The character of photophores is important in the identification of deep sea fishes. Photophores on fish are used for attracting food or for camouflage from predators by counter-illumination. Photophores are found on some cephalopods including the firefly squid, which can create impressive light displays, as well as numerous other deep sea organisms such as the pocket shark Mollisquama mississippie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventouse Calmar
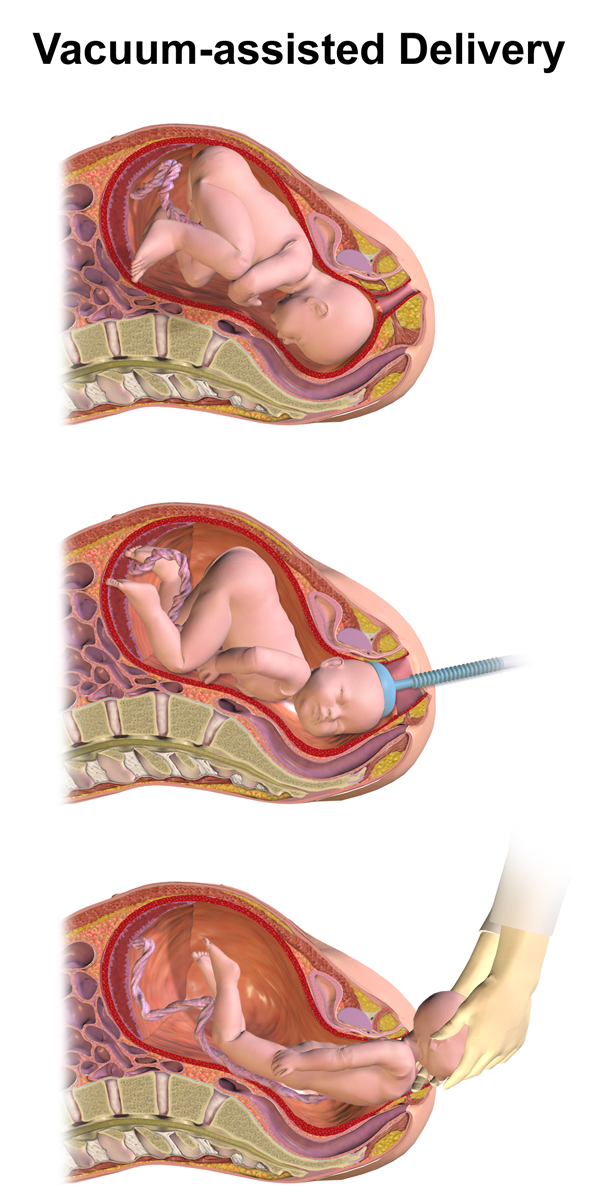
Vacuum extraction (VE), also known as ventouse, is a method to assist delivery of a baby using a vacuum device. It is used in the second stage of labor if it has not progressed adequately. It may be an alternative to a forceps delivery and caesarean section. It cannot be used when the baby is in the breech position or for premature births. The use of VE is generally safe, but it can occasionally have negative effects on either the mother or the child. The term comes from the French word for "suction cup". Medical uses There are several indications to use a vacuum extraction to aid delivery: * Maternal exhaustion * Prolonged second stage of labor * Foetal distress in the second stage of labor, generally indicated by changes in the foetal heart-rate (usually measured on a CTG) * Maternal illness where prolonged "bearing down" or pushing efforts would be risky (e.g. cardiac conditions, blood pressure, aneurysm, glaucoma). If these conditions are known about before the birth, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalopod Arm
All cephalopods possess flexible limbs extending from their heads and surrounding their beaks. These appendages, which function as muscular hydrostats, have been variously termed arms, legs or tentacles. Description In the scientific literature, a cephalopod ''arm'' is often treated as distinct from a ''tentacle'', though the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, often with the latter acting as an umbrella term for cephalopod limbs. Generally, arms have suckers along most of their length, as opposed to tentacles, which have suckers only near their ends.Young, R.E., M. Vecchione & K.M. Mangold 1999Cephalopoda Glossary Tree of Life web project. Barring a few exceptions, octopuses have eight arms and no tentacles, while squid and cuttlefish have eight arms (or two "legs" and six "arms") and two tentacles.Norman, M. 2000. ''Cephalopods: A World Guide''. ConchBooks, Hackenheim. p. 15. "There is some confusion around the terms ''arms'' versus ''tentacles''. The numerous li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)