|
Water Dredge
A water eductor or water dredge is an eductor-jet pump-based tool used by underwater archaeology, underwater archaeologists to remove sediments from an underwater archaeological site. airlift (dredging device), Airlifts may be used for the same purpose. It consists of a large bore straight tube to which is attached a hose pipe through which clean water is pumped. The Bernoulli's principle, Bernoulli effect from the flow of pumped water causes suction at the mouth of the dredge. Water and sediment are sucked from the excavation site and released from the far end of the tube. The tube can be made of any rigid material such as steel or plastic. The diameter of the tube depends on the power available from the pump and whether delicate work is required. In the hands of a trained archaeologist, the water dredge performs the same function as a wheelbarrow on land. It is used to carry away sediments, not to dig holes. The archaeologist dislodges the material using a trowel, brush or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eductor-jet Pump
A vacuum ejector, or simply ejector is a type of vacuum pump, which produces vacuum by means of the Venturi effect. In an ejector, a working fluid (liquid or gaseous) flows through a jet nozzle into a tube that first narrows and then expands in cross-sectional area. The fluid leaving the jet is flowing at a high velocity which due to Bernoulli's principle results in it having low pressure, thus generating a vacuum. The outer tube then narrows into a mixing section where the high velocity working fluid mixes with the fluid that is drawn in by the vacuum, imparting enough velocity for it to be ejected, the tube then typically expands in order to decrease the velocity of the ejected stream, allowing the pressure to smoothly increase to the external pressure. The strength of the vacuum produced depends on the velocity and shape of the fluid jet and the shape of the constriction and mixing sections, but if a liquid is used as the working fluid the strength of the vacuum produced is l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artifact (archaeology)
An artifact, or artefact (see American and British English spelling differences), is a general term for an item made or given shape by humans, such as a tool or a work of art, especially an object of archaeological interest. In archaeology, the word has become a term of particular nuance and is defined as an object recovered by archaeological endeavor, which may be a cultural artifact having cultural interest. Artifact is the general term used in archaeology, while in museums the equivalent general term is normally "object", and in art history perhaps artwork or a more specific term such as "carving". The same item may be called all or any of these in different contexts, and more specific terms will be used when talking about individual objects, or groups of similar ones. Artifacts exist in many different forms and can sometimes be confused with ecofacts and features; all three of these can sometimes be found together at archaeological sites. They can also exist in different t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maritime Archaeology
Maritime archaeology (also known as marine archaeology) is a discipline within archaeology as a whole that specifically studies human interaction with the sea, lakes and rivers through the study of associated physical remains, be they vessels, shore-side facilities, port-related structures, cargoes, human remains and submerged landscapes. A specialty within maritime archaeology is nautical archaeology, which studies ship construction and use. As with archaeology as a whole, maritime archaeology can be practised within the historical, industrial, or prehistoric periods. An associated discipline, and again one that lies within archaeology itself, is underwater archaeology, which studies the past through any submerged remains be they of maritime interest or not. An example from the prehistoric era would be the remains of submerged settlements or deposits now lying under water despite having been dry land when sea levels were lower. The study of submerged aircraft lost in lakes, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Geographic Magazine
''National Geographic'' (formerly the ''National Geographic Magazine'', sometimes branded as NAT GEO) is a popular American monthly magazine published by National Geographic Partners. Known for its photojournalism, it is one of the most widely read magazines of all time. The magazine was founded in 1888 as a scholarly journal, nine months after the establishment of the society, but is now a popular magazine. In 1905, it began including pictures, a style for which it became well-known. Its first color photos appeared in the 1910s. During the Cold War, the magazine committed itself to present a balanced view of the physical and human geography of countries beyond the Iron Curtain. Later, the magazine became outspoken on environmental issues. Since 2019, controlling interest has been held by The Walt Disney Company. Topics of features generally concern geography, history, nature, science, and world culture. The magazine is well known for its distinctive appearance: a thick squar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Lift
Gas lift or bubble pumps use the artificial lift technique of raising a fluid such as water or oil by introducing bubbles of compressed air, water vapor or other vaporous bubbles into the outlet tube. This has the effect of reducing the hydrostatic pressure in the outlet tube vs. the hydrostatic pressure at the inlet side of the tube. Devices using this type of lift mechanism: *Coffee percolators and electric drip coffeemakers use vaporized water to lift hot water *Airlift pumps uses compressed air to lift water *Pulser pumps use a subterranean chamber of air for an airlift pump * Suction dredges use an airlift pump to vacuum mud, sand and debris *Mist lift pumps uses vaporized water to lift seawater in Ocean thermal energy conversion Petroleum industry uses In the United States, gas lift is used in 10% of the oil wells that have insufficient reservoir pressure to produce the well. In the petroleum industry, the process involves injecting gas through the tubing-casing annulus. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspirator (pump)
A vacuum ejector, or simply ejector is a type of vacuum pump, which produces vacuum by means of the Venturi effect. In an ejector, a working fluid (liquid or gaseous) flows through a jet nozzle into a tube that first narrows and then expands in cross-sectional area. The fluid leaving the jet is flowing at a high velocity which due to Bernoulli's principle results in it having low pressure, thus generating a vacuum. The outer tube then narrows into a mixing section where the high velocity working fluid mixes with the fluid that is drawn in by the vacuum, imparting enough velocity for it to be ejected, the tube then typically expands in order to decrease the velocity of the ejected stream, allowing the pressure to smoothly increase to the external pressure. The strength of the vacuum produced depends on the velocity and shape of the fluid jet and the shape of the constriction and mixing sections, but if a liquid is used as the working fluid the strength of the vacuum produced is l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airlift Pump
An airlift pump is a pump that has low suction and moderate discharge of liquid and entrained solids. The pump injects compressed air at the bottom of the discharge pipe which is immersed in the liquid. The compressed air mixes with the liquid causing the air-water mixture to be less dense than the rest of the liquid around it and therefore is displaced upwards through the discharge pipe by the surrounding liquid of higher density. Solids may be entrained in the flow and if small enough to fit through the pipe, will be discharged with the rest of the flow at a shallower depth or above the surface. Airlift pumps are widely used in aquaculture to pump, circulate and aerate water in closed, recirculating systems and ponds. Other applications include dredging, underwater archaeology, salvage operations and collection of scientific specimens. Principle The only energy required is provided by compressed air. This air is usually compressed by a compressor or a blower. The air is injec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venturi Tube
The Venturi effect is the reduction in fluid pressure that results when a fluid flows through a constricted section (or choke) of a pipe. The Venturi effect is named after its discoverer, the 18th century Italian physicist, Giovanni Battista Venturi. Background In inviscid fluid dynamics, an incompressible fluid's velocity must ''increase'' as it passes through a constriction in accord with the principle of mass continuity, while its static pressure must ''decrease'' in accord with the principle of conservation of mechanical energy (Bernoulli's principle). Thus, any gain in kinetic energy a fluid may attain by its increased velocity through a constriction is balanced by a drop in pressure. By measuring pressure, the flow rate can be determined, as in various flow measurement devices such as Venturi meters, Venturi nozzles and orifice plates. Referring to the adjacent diagram, using Bernoulli's equation in the special case of steady, incompressible, inviscid flows (such as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
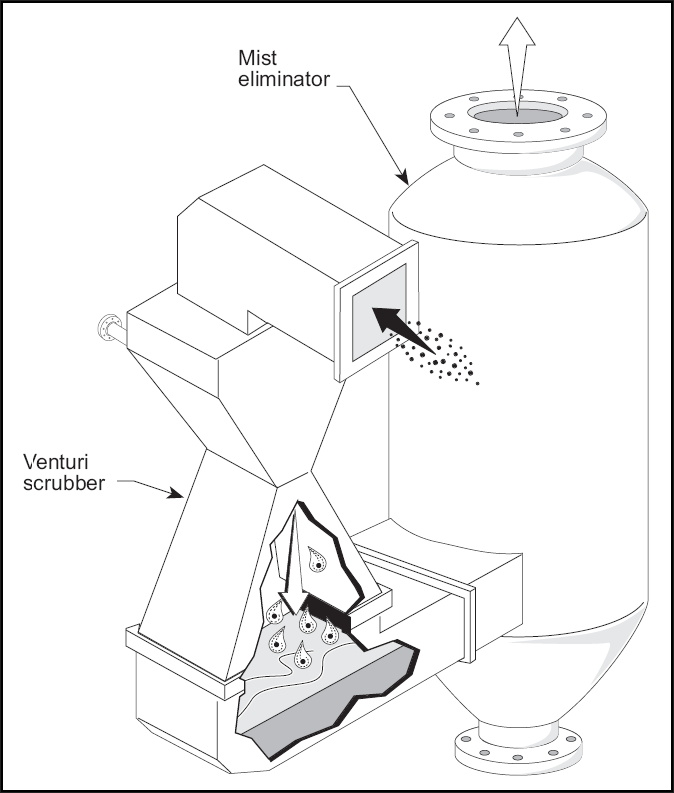
Wet Scrubber
The term wet scrubber describes a variety of devices that remove pollutants from a furnace flue gas or from other gas streams. In a wet scrubber, the polluted gas stream is brought into contact with the scrubbing liquid, by spraying it with the liquid, by forcing it through a pool of liquid, or by some other contact method, so as to remove the pollutants. Design The design of wet scrubbers or any air pollution control device depends on the industrial process conditions and the nature of the air pollutants involved. Inlet gas characteristics and dust properties (if particles are present) are of primary importance. Scrubbers can be designed to collect particulate matter and/or gaseous pollutants. The versatility of wet scrubbers allow them to be built in numerous configurations, all designed to provide good contact between the liquid and polluted gas stream. Wet scrubbers remove dust particles by ''capturing'' them in liquid droplets. The droplets are then collected, the liq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratigraphy
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock (geology), rock layers (Stratum, strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary rock, sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks. Stratigraphy has three related subfields: lithostratigraphy (lithologic stratigraphy), biostratigraphy (biologic stratigraphy), and chronostratigraphy (stratigraphy by age). Historical development Catholic priest Nicholas Steno established the theoretical basis for stratigraphy when he introduced the law of superposition, the principle of original horizontality and the principle of lateral continuity in a 1669 work on the fossilization of organic remains in layers of sediment. The first practical large-scale application of stratigraphy was by William Smith (geologist), William Smith in the 1790s and early 19th century. Known as the "Father of English geology", Smith recognized the significance of Stratum, strata or rock layering and the importance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underwater Archaeology
Underwater archaeology is archaeology practiced underwater. As with all other branches of archaeology, it evolved from its roots in pre-history and in the classical era to include sites from the historical and industrial eras. Its acceptance has been a relatively late development due to the difficulties of accessing and working underwater sites, and because the application of archaeology to underwater sites initially emerged from the skills and tools developed by shipwreck salvagers. As a result, underwater archaeology initially struggled to establish itself as actual archaeological research. This changed when universities began teaching the subject and a theoretical and practical base for the sub-discipline was firmly established in the late 1980’s. Underwater archaeology now has a number of branches including, maritime archaeology: the scientifically based study of past human life, behaviours and cultures and their activities in, on, around and (lately) under the sea, estuarie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feature (archaeology)
In archaeological excavation, a feature is a collection of one or more contexts representing some human non-portable activity, such as a hearth or wall. Features serve as an indication that the area in which they are found has been interfered with in the past, usually by humans. Features are distinguished from artifacts in that they cannot be separated from their location without changing their form. Artifacts are portable, while features are non-portable. Artifacts and features can both be made from any available material, with the primary distinction being portability. Features and artifacts differ from ecofacts. Ecofacts are natural remains, such as plants and animals. Types Features are categorized by the time period, as either historic or prehistoric. Prehistoric archaeology refers to the time in history before human life was recorded or documented, while historic archaeology refers to the time period where there was a documented human past. In relation to site stra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |