|
Work-up (chemistry)
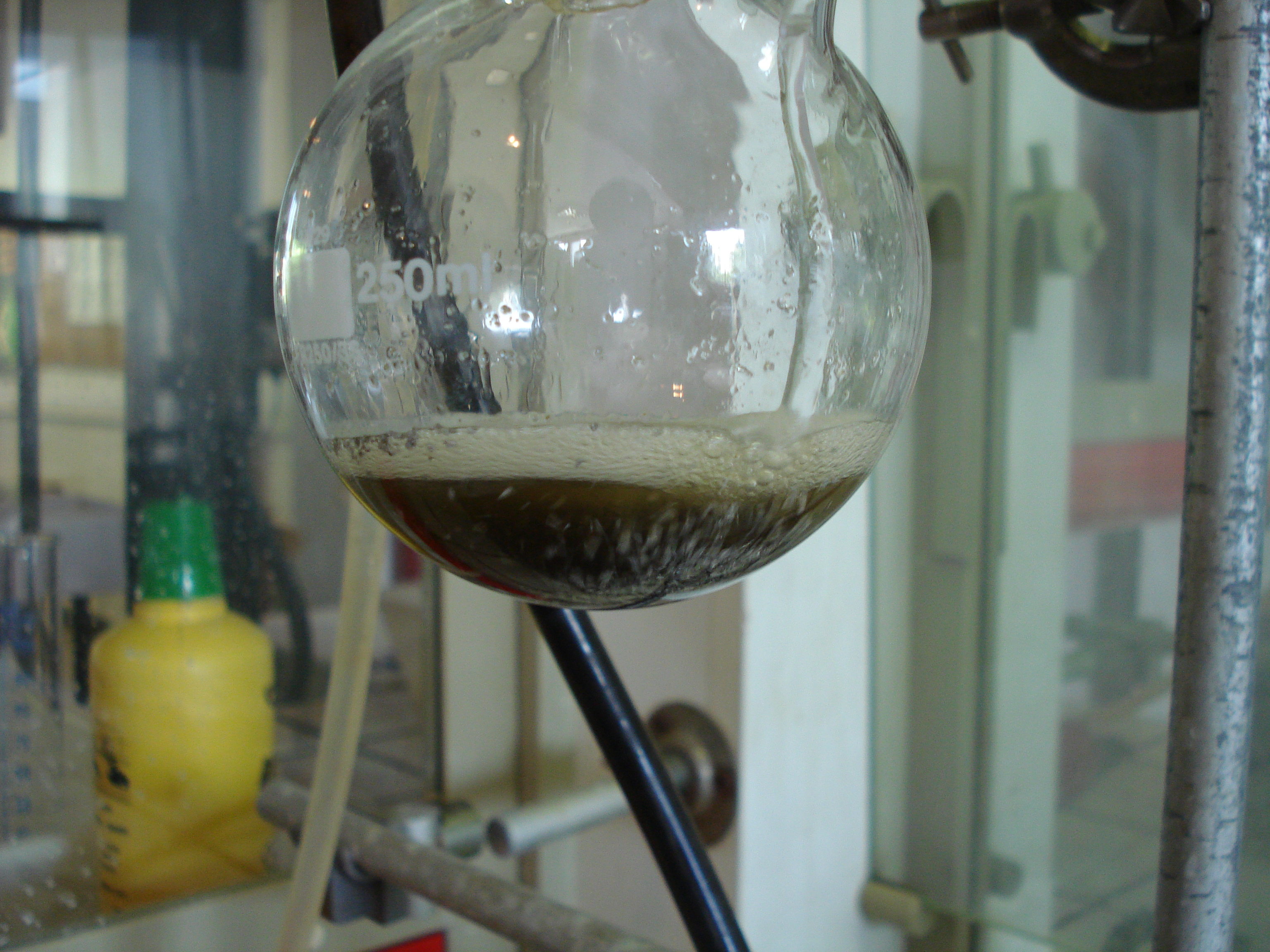
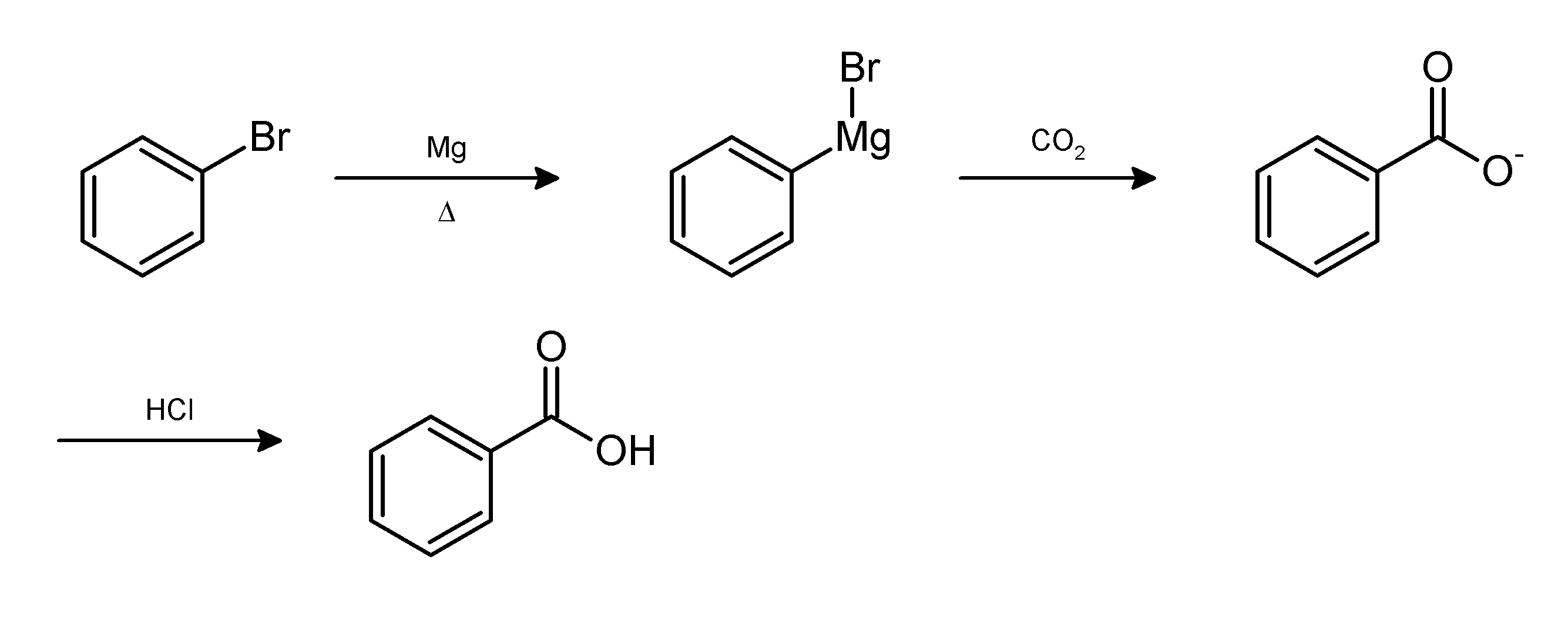
In chemistry, work-up refers to the series of manipulations required to isolate and purify the product(s) of a chemical reaction. Typically, these manipulations may include: * quenching a reaction to deactivate any unreacted reagents. * cooling the reaction mixture or adding an ''antisolvent'' to induce precipitation, and collecting or removing the solids by filtration, decantation, or centrifugation * removal of solvents by evaporation * separating the reaction mixture into organic and aqueous layers by liquid-liquid extraction * purification by chromatography, distillation or recrystallization For example, the Grignard reaction between phenylmagnesium bromide and carbon dioxide in the form of dry ice gives the conjugate base of benzoic acid. The desired product, benzoic acid, is obtained by the following work-up:{{cite book , title = Introduction to Organic Laboratory Techniques: A Small Scale Approach , author = Donald L. Pavia , year = 2004 , publisher = Thomson Brooks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science, scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the Chemical element, elements that make up matter to the chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during a Chemical reaction, reaction with other Chemical substance, substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both Basic research, basic and Applied science, applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth (botany), the formation of igneous rocks (geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded (ecology), the properties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recrystallization (chemistry)
In chemistry, recrystallization is a technique used to purify chemicals. By dissolving a mixture of a compound and impurities in an appropriate solvent, either the desired compound or impurities can be removed from the solution, leaving the other behind. It is named for the crystals often formed when the compound precipitates out. Alternatively, ''recrystallization'' can refer to the natural growth of larger ice crystals at the expense of smaller ones. Chemistry In chemistry, recrystallization is a procedure for purifying compounds. The most typical situation is that a desired "compound A" is contaminated by a small amount of "impurity B". There are various methods of purification that may be attempted (see Separation process), recrystallization being one of them. There are also different recrystallization techniques that can be used such as: Single-solvent recrystallization Typically, the mixture of "compound A" and "impurity B" is dissolved in the smallest amount of hot solv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buchner Funnel
Buchner is a German surname. Notable people with this surname include the following: * Andreas Buchner (1776–1854), German historian * Annemarie Buchner (1924-2014), German Olympian * August Buchner (1591–1661), German influential Baroque poet * Eduard Buchner (1860–1917), German chemist and zymologist * Edward Franklin Buchner (1868–1929), American psychologist * Ernst Buchner (curator) (1892–1962), German museum administrator * Hans Buchner (1483–1538, German organist and composer * Hans Ernst August Buchner (1850–1902), German bacteriologist * Johann Andreas Buchner (1783–1852), German pharmacologist * Ludwig Andreas Buchner (1813–1897), German pharmacologist * Paul Buchner Paul Buchner (June, 1531 - 13 November, 1607) was a German architect, geometer, carpenter, and screw maker from Nuremberg, Germany. Life Buchner grew up in Nuremberg and was an apprentice carpenter and screw maker, training under his cousin, ... (1531–1607), German architect, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decanted
Decantation is a process for the separation of mixtures of immiscible liquids or of a liquid and a solid mixture such as a suspension. The layer closer to the top of the container—the less dense of the two liquids, or the liquid from which the precipitate or sediment has settled out—is poured off, leaving the other component or the denser liquid of the mixture behind. An incomplete separation is witnessed during the separation of two immiscible liquids. To put it in a simple way, decantation is separating immiscible materials by transferring the top layer to another container. The process does not provide accurate or pure product. Processes Immiscible liquid separation Decantation can be used to separate immiscible liquids that have different densities. For example, when a mixture of water and oil is present in a beaker, after some time a distinct layer between the two liquids is formed, with the oil layer floating on top of the water layer. This separation can be done by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochloric Acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbolised by the chemical formula HA, to dissociate into a proton, H+, and an anion, A-. The dissociation of a strong acid in solution is effectively complete, except in its most concentrated solutions .... It is a component of the gastric acid in the digestive systems of most animal species, including humans. Hydrochloric acid is an important laboratory reagent and industrial chemical. History In the early tenth century, the Persian physician and alchemist Abu Bakr al-Razi ( 865–925, Latin: Rhazes) conducted experiments with sal ammoniac (ammonium chloride) and vitriol (hydrated sulfates of various metals), which he distilled together, thus producing the gas hydrogen chloride. In doing so, al-Razi may have stumbled upon a primitive method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grignard Reagent
A Grignard reagent or Grignard compound is a chemical compound with the general formula , where X is a halogen and R is an organic group, normally an alkyl or aryl. Two typical examples are methylmagnesium chloride and phenylmagnesium bromide . They are a subclass of the organomagnesium compounds. Grignard compounds are popular reagents in organic synthesis for creating new carbon-carbon bonds. For example, when reacted with another halogenated compound in the presence of a suitable catalyst, they typically yield and the magnesium halide as a byproduct; and the latter is insoluble in the solvents normally used. In this aspect, they are similar to organolithium reagents. Pure Grignard reagents are extremely reactive solids. They are normally handled as solutions in solvents such as diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran; which are relatively stable as long as water is excluded. In such a medium, a Grignard reagent is invariably present as a complex with the magnesium atom conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzoic Acid
Benzoic acid is a white (or colorless) solid organic compound with the formula , whose structure consists of a benzene ring () with a carboxyl () substituent. It is the simplest aromatic carboxylic acid. The name is derived from gum benzoin, which was for a long time its only source. Benzoic acid occurs naturally in many plants and serves as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of many secondary metabolites. Salts of benzoic acid are used as food preservatives. Benzoic acid is an important precursor for the industrial synthesis of many other organic substances. The salts and esters of benzoic acid are known as benzoates . History Benzoic acid was discovered in the sixteenth century. The dry distillation of gum benzoin was first described by Nostradamus (1556), and then by Alexius Pedemontanus (1560) and Blaise de Vigenère (1596). Justus von Liebig and Friedrich Wöhler determined the composition of benzoic acid. These latter also investigated how hippuric acid is related ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dry Ice
Dry ice is the solid form of carbon dioxide. It is commonly used for temporary refrigeration as CO2 does not have a liquid state at normal atmospheric pressure and sublimates directly from the solid state to the gas state. It is used primarily as a cooling agent, but is also used in fog machines at theatres for dramatic effects. Its advantages include lower temperature than that of water ice and not leaving any residue (other than incidental frost from moisture in the atmosphere). It is useful for preserving frozen foods (such as ice cream) where mechanical cooling is unavailable. Dry ice sublimates at at Earth atmospheric pressure. This extreme cold makes the solid dangerous to handle without protection from frostbite injury. While generally not very toxic, the outgassing from it can cause hypercapnia (abnormally elevated carbon dioxide levels in the blood) due to buildup in confined locations. Properties Dry ice is the solid form of carbon dioxide (CO2), a molecule co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. It is a trace gas in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.04% by volume (as of May 2022), having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm. Burning fossil fuels is the primary cause of these increased CO2 concentrations and also the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for policy makersiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, ice caps, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylmagnesium Bromide
Phenylmagnesium bromide, with the simplified formula , is a magnesium-containing organometallic compound. It is commercially available as a solution in diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran (THF). Phenylmagnesium bromide is a Grignard reagent. It is often used as a synthetic equivalent for the phenyl "Ph−" synthon. Preparation Phenylmagnesium bromide is commercially available as solutions of diethyl ether or THF. Laboratory preparation involves treating bromobenzene with magnesium metal, usually in the form of turnings. A small amount of iodine may be used to activate the magnesium to initiate the reaction. Coordinating solvents such as ether or THF, are required to solvate (complex) the magnesium(II) center. The solvent must be aprotic since alcohols and water contain an acidic proton and thus react with phenylmagnesium bromide to give benzene. Carbonyl-containing solvents, such as acetone and ethyl acetate, are also incompatible with the reagent. Structure Although phenylmagn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grignard Reaction
The Grignard reaction () is an organometallic chemical reaction in which alkyl, allyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides ( Grignard reagent) is added to a carbonyl group in an aldehyde or ketone. This reaction is important for the formation of carbon–carbon bonds. The reaction of an organic halide with magnesium is ''not'' a Grignard reaction, but provides a Grignard reagent. : Grignard reactions and reagents were discovered by and are named after the French chemist François Auguste Victor Grignard (University of Nancy, France), who published it in 1900 and was awarded the 1912 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work. Reaction mechanism Because carbon is more electronegative than magnesium, the carbon attached to magnesium functions as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon atom that is present within the polar bond of a carbonyl group. The addition of the Grignard reagent to the carbonyl typically proceeds through a six-membered ring transition state. Based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |