|
Wh-fronting
In linguistics, wh-movement (also known as wh-fronting, wh-extraction, or wh-raising) is the formation of syntactic dependencies involving interrogative words. An example in English is the dependency formed between ''what'' and the object position of ''doing'' in "What are you doing?". Interrogative forms are sometimes known within English linguistics as ''interrogative word, wh-words'', such as ''what, when, where, who'', and ''why'', but also include other interrogative words, such as ''how''. This dependency has been used as a diagnostic tool in syntactic studies as it can be observed to interact with other grammatical constraints. In languages with wh-syntactic movement, movement, sentences or clauses with a wh-word show a non-canonical word order that places the wh-word (or phrase containing the wh-word) at or near the front of the sentence or clause ("''Whom'' are you thinking about?") instead of the canonical position later in the sentence ("I am thinking about ''you''"). Lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constituent (linguistics)
In syntactic analysis, a constituent is a word or a group of words that function as a single unit within a hierarchical structure. The constituent structure of sentences is identified using ''tests for constituents''. These tests apply to a portion of a sentence, and the results provide evidence about the constituent structure of the sentence. Many constituents are phrases. A phrase is a sequence of one or more words (in some theories two or more) built around a head lexical item and working as a unit within a sentence. A word sequence is shown to be a phrase/constituent if it exhibits one or more of the behaviors discussed below. The analysis of constituent structure is associated mainly with phrase structure grammars, although dependency grammars also allow sentence structure to be broken down into constituent parts. Tests for constituents in English Tests for constituents are diagnostics used to identify sentence structure. There are numerous tests for constituents that are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
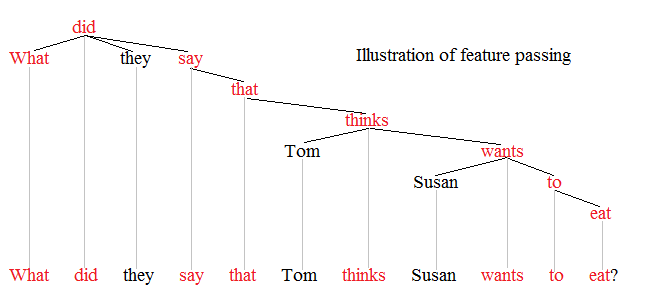
Syntactic Movement
Syntactic movement is the means by which some theories of syntax address discontinuities. Movement was first postulated by structuralist linguists who expressed it in terms of ''discontinuous constituents'' or ''displacement''. Some constituents appear to have been displaced from the position in which they receive important features of interpretation. The concept of movement is controversial and is associated with so-called ''transformational'' or ''derivational'' theories of syntax (such as transformational grammar, government and binding theory, minimalist program). Representational theories (such as head-driven phrase structure grammar, lexical functional grammar, construction grammar, and most dependency grammars), in contrast, reject the notion of movement and often instead address discontinuities with other mechanisms including graph reentrancies, feature passing, and type shifters. Illustration Movement is the traditional means of explaining discontinuities such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
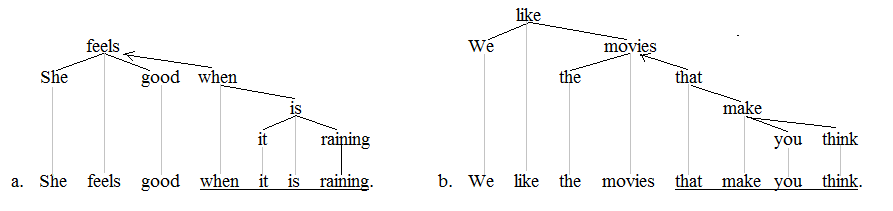
Discontinuity (linguistics)
In linguistics, a discontinuity occurs when a given word or phrase is separated from another word or phrase that it modifies in such a manner that a direct connection cannot be established between the two without incurring crossing lines in the Parse tree, tree structure. The terminology that is employed to denote discontinuities varies depending on the theory of syntax at hand. The terms ''discontinuous constituent'', ''displacement'', ''long distance dependency'', ''unbounded dependency'', and ''projectivity violation'' are largely synonymous with the term ''discontinuity''. There are various types of discontinuities, the most prominent and widely studied of these being topicalization, wh-fronting, scrambling (linguistics), scrambling, and extraposition. Natural languages vary with respect to the types of discontinuities that they permit. The fixed word order of English allows for relatively few discontinuities compared to, for instance, the Slavic languages, which are much more p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages), phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language, and analogous systems of sign languages), and pragmatics (how the context of use contributes to meaning). Subdisciplines such as biolinguistics (the study of the biological variables and evolution of language) and psycholinguistics (the study of psychological factors in human language) bridge many of these divisions. Linguistics encompasses Outline of linguistics, many branches and subfields that span both theoretical and practical applications. Theoretical linguistics is concerned with understanding the universal grammar, universal and Philosophy of language#Nature of language, fundamental nature of language and developing a general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preposition Stranding
Preposition stranding or p-stranding is the syntax, syntactic construction in which a so-called ''stranded'', ''hanging'', or ''dangling'' preposition occurs somewhere other than immediately before its corresponding object (grammar), object; for example, at the end of a sentence. The term ''preposition stranding'' was coined in 1964, predated by stranded preposition in 1949. Linguists had previously identified such a construction as a sentence-terminal preposition or as a preposition at the end. Preposition stranding is found in English and other Germanic languages, as well as in Vata and Gbadi (languages in the Niger–Congo languages, Niger–Congo family), and certain dialects of French language, French spoken in North America. P-stranding occurs in various syntactic contexts, including passive voice, wh-movement, ''wh-''movement, and sluicing. ''Wh-''movement and P-stranding Wh-movement, ''Wh-''movement—which involves ''wh-''words like ''who'', ''what'', ''when'', ''where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix Clause
In language, a clause is a Constituent (linguistics), constituent or Phrase (grammar), phrase that comprises a semantic predicand (expressed or not) and a semantic Predicate (grammar), predicate. A typical clause consists of a subject (grammar), subject and a syntactic Predicate (grammar), predicate, the latter typically a verb phrase composed of a verb with or without any object (grammar), objects and other Grammatical modifier, modifiers. However, the subject is sometimes unexpressed if it is easily deducible from the context, especially in null-subject languages but also in other languages, including instances of the imperative mood in English grammar, English. A complete simple sentence contains a single clause with a finite verb. Complex sentences contain at least one clause subordinated (dependent clause, ''dependent'') to an ''independent clause'' (one that could stand alone as a simple sentence), which may be co-ordinated with other independents with or without dependents. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relative Clause
A relative clause is a clause that modifies a noun or noun phrase and uses some grammatical device to indicate that one of the arguments in the relative clause refers to the noun or noun phrase. For example, in the sentence ''I met a man who wasn't too sure of himself'', the Dependent clause, subordinate clause ''who wasn't too sure of himself'' is a relative clause since it modifies the noun ''man'' and uses the pronoun ''who'' to indicate that the same "MAN" is referred to in the subordinate clause (in this case as its subject (grammar), subject). In many languages, relative clauses are introduced by a special class of pronouns called ''relative pronouns'', such as ''who'' in the example just given. In other languages, relative clauses may be marked in different ways: they may be introduced by a special class of conjunctions called ''relativizers'', the main verb of the relative clause may appear in a special morphological variant, or a relative clause may be indicated by word o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pied-piping
In linguistics, pied-piping is a phenomenon of syntax whereby a given focused expression brings along an encompassing phrase with it when it is moved. The term was introduced by John Robert Ross in 1967. It references the legend of the Pied Piper of Hamelin, where a piper lures rats and children away from their town. In syntactic pied-piping, a focused expression (such as an interrogative word) pulls its host phrase with it when it moves to its new position in the sentence. Metaphorically, the focused expression is the piper, and the host phrase is the material being pied-piped. Pied-piping is an aspect of syntactic discontinuities and has to do with constituents that can or cannot be discontinuous. Pied-piping is most visible in cases of ''wh''-fronting of information questions and relative clauses, but it is not limited to ''wh''-fronting. It can also occur with almost any type of discontinuity, including extraposition, scrambling, and topicalization. Most, if not all, la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John R
John R. (born John Richbourg, August 20, 1910 – February 15, 1986) was an American radio disc jockey who attained fame in the 1950s and 1960s for playing rhythm and blues music on Nashville radio station WLAC. He was also a notable record producer and artist manager. Richbourg was arguably the most popular and charismatic of the four announcers at WLAC who showcased popular African-American music in nightly programs from the late 1940s to the early 1970s. (The other three were Gene Nobles, Herman Grizzard, and Bill "Hoss" Allen.) Later rock music disc jockeys, such as Alan Freed and Wolfman Jack, mimicked Richbourg's practice of using speech that simulated African-American street language of the mid-twentieth century. Richbourg's highly stylized approach to on-air presentation of both music and advertising earned him popularity, but it also created identity confusion. Because Richbourg and fellow disc jockey Allen used African-American speech patterns, many listeners thought t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistic Island (syntactic island), a construction
{{disambiguation ...
Linguistic island may refer to: * Language island (language enclave), an area * Island (linguistics) In linguistics, wh-movement (also known as wh-fronting, wh-extraction, or wh-raising) is the formation of syntactic dependencies involving interrogative words. An example in English is the dependency formed between ''what'' and the object position ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistic Prescription
Linguistic prescription is the establishment of rules defining publicly preferred Usage (language), usage of language, including rules of spelling, pronunciation, vocabulary, grammar, etc. Linguistic prescriptivism may aim to establish a standard language, teach what a particular society or sector of a society perceives as a correct or proper form, or advise on effective and stylistically apt communication. If usage preferences are conservative, prescription might appear resistant to language change; if radical, it may produce neologisms. Such prescriptions may be motivated by consistency (making a language simpler or more logical); rhetorical effectiveness; tradition; aesthetics or personal preferences; linguistic purism or nationalism (i.e. removing foreign influences); or to avoid causing offense (etiquette or political correctness). Prescriptive approaches to language are often contrasted with the Linguistic description, descriptive approach of Linguistics, academic linguistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
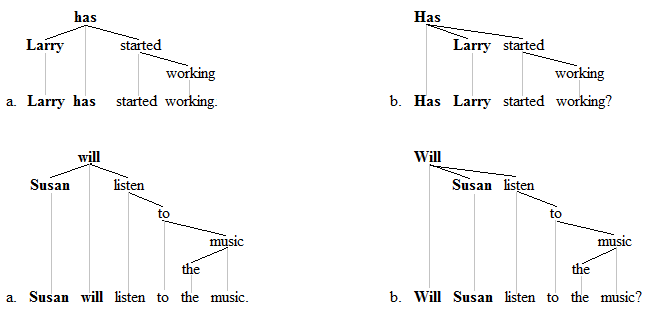
Subject–auxiliary Inversion
Subject–auxiliary inversion (SAI; also called subject–operator inversion) is a frequently occurring type of inversion (linguistics), inversion in the English language whereby a finite auxiliary verb – taken here to include finite forms of the copula (linguistics), copula ''be'' – appears to "invert" (change places) with the subject (grammar), subject. The word order is therefore Aux-S (auxiliary–subject), which is the opposite of the canonical SV (Subject–verb–object word order, subject–verb) order of declarative clauses in English. The most frequent use of subject–auxiliary inversion in English is in the formation of questions, although it also has other uses, including the formation of condition clauses, and in the syntax of sentences beginning with negative expressions (negative inversion). In certain types of English sentences, inversion is also possible with verbs other than auxiliaries; these are described in the article on the subject–verb inversion in En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |