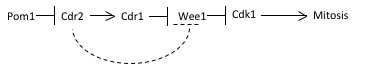
|
Wee1
Wee1 is a nuclear kinase belonging to the Ser/Thr family of protein kinases in the fission yeast ''Schizosaccharomyces pombe'' (''S. pombe'')Wee1has a molecular mass of 96 kDa and is a key regulator of cell cycle progression. It influences cell size by inhibiting the entry into mitosis, through inhibiting Cdk1. Wee1 has homologues in many other organisms, including mammals. Introduction The regulation of cell size is critical to ensure functionality of a cell. Besides environmental factors such as nutrients, growth factors and functional load, cell size is also controlled by a cellular cell size checkpoint. Wee1 is a component of this checkpoint. It is a kinase determining the timepoint of entry into mitosis, thus influencing the size of the daughter cells. Loss of Wee1 function will produce smaller than normal daughter cell, because cell division occurs prematurely. Its name is derived from the Scottish dialect word wee, meaning small - its discoverer Paul Nurse w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Size
Cell growth refers to an increase in the total mass of a cell, including both cytoplasmic, nuclear and organelle volume. Cell growth occurs when the overall rate of cellular biosynthesis (production of biomolecules or anabolism) is greater than the overall rate of cellular degradation (the destruction of biomolecules via the proteasome, lysosome or autophagy, or catabolism). Cell growth is not to be confused with cell division or the cell cycle, which are distinct processes that can occur alongside cell growth during the process of cell proliferation, where a cell, known as the mother cell, grows and divides to produce two daughter cells. Importantly, cell growth and cell division can also occur independently of one another. During early embryonic development ( cleavage of the zygote to form a morula and blastoderm), cell divisions occur repeatedly without cell growth. Conversely, some cells can grow without cell division or without any progression of the cell cycle, such as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wee1-like Protein Kinase
WEE1 homolog (''S. pombe''), also known as WEE1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''WEE1'' gene. Function This gene encodes a nuclear protein, which is a tyrosine kinase belonging to the Ser/Thr family of protein kinases. This protein catalyzes the inhibitory tyrosine phosphorylation of CDC2/cyclin B kinase, and appears to coordinate the transition between DNA replication and mitosis by protecting the nucleus from cytoplasmically activated CDC2 kinase. Interactions Wee1-like protein kinase has been shown to interact with YWHAB and PIN1 Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PIN1'' gene. Pin 1, or peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase (PPIase), isomerizes only phospho-Serine/Threonine-Proline motifs. The enzyme bi .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * EC 2.7.11 {{gene-11-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pom1
Pom1 is a polarity protein kinase in fission yeast, ''Schizosaccharomyces pombe'' (''S. pombe''), that localizes to cell ends and regulates cell division. As the cell lengthens, the level of Pom1 in the middle declines, which triggers mitosis.Bahler, J., and Pringle, J.R. “Pom1p, a fission yeast protein kinase that provides positional information for both polarized growth and cytokinesis.” Genes and Development 12, 1356-1370 (1998). The genebr>''pom1''codes for a protein 1087 amino acids long with the protein kinase domain likely located at the carboxyl terminus. Pom1 regulates a signaling pathway that includes Cdk1 and ultimately regulates mitotic entry.Moseley, J.B., Mayeux, A., Paoletti, A. and Nurse, P. “A spatial gradient coordinates cell size and mitotic entry in fission yeast.” Nature 459, 857-861 (2009). Cells with mutant pom1 form a septa and growth zone, but show a host of abnormalities including misplaced or misoriented septa, bi-polar growth replaced with r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Cycle Checkpoint
Cell cycle checkpoints are control mechanisms in the eukaryotic cell cycle which ensure its proper progression. Each checkpoint serves as a potential termination point along the cell cycle, during which the conditions of the cell are assessed, with progression through the various phases of the cell cycle occurring only when favorable conditions are met. There are many checkpoints in the cell cycle, but the three major ones are: the G1 checkpoint, also known as the Start or restriction checkpoint or Major Checkpoint; the G2/M checkpoint; and the metaphase-to-anaphase transition, also known as the spindle checkpoint. Progression through these checkpoints is largely determined by the activation of cyclin-dependent kinases by regulatory protein subunits called cyclins, different forms of which are produced at each stage of the cell cycle to control the specific events that occur therein. Background All living organisms are the products of repeated rounds of cell growth and divisio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizosaccharomyces Pombe
''Schizosaccharomyces pombe'', also called "fission yeast", is a species of yeast used in traditional brewing and as a model organism in molecular and cell biology. It is a unicellular eukaryote, whose cells are rod-shaped. Cells typically measure 3 to 4 micrometres in diameter and 7 to 14 micrometres in length. Its genome, which is approximately 14.1 million base pairs, is estimated to contain 4,970 protein-coding genes and at least 450 non-coding RNAs. These cells maintain their shape by growing exclusively through the cell tips and divide by medial fission to produce two daughter cells of equal size, which makes them a powerful tool in cell cycle research. Fission yeast was isolated in 1893 by Paul Lindner from East African millet beer. The species name ''pombe'' is the Swahili word for beer. It was first developed as an experimental model in the 1950s: by Urs Leupold for studying genetics, and by Murdoch Mitchison for studying the cell cycle. Paul Nurse, a fission yeast r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasensitivity
In molecular biology, ultrasensitivity describes an output response that is more sensitive to stimulus change than the hyperbolic Michaelis–Menten kinetics, Michaelis-Menten response. Ultrasensitivity is one of the biochemical switches in the cell cycle and has been implicated in a number of important cellular events, including exiting G2 cell cycle arrests in ''Xenopus laevis'' oocytes, a stage to which the cell or organism would not want to return. Ultrasensitivity is a cellular system which triggers entry into a different cellular state. Ultrasensitivity gives a small response to first input signal, but an increase in the input signal produces higher and higher levels of output. This acts to filter out noise, as small stimuli and threshold concentrations of the stimulus (input signal) is necessary for the trigger which allows the system to get activated quickly. Ultrasensitive responses are represented by sigmoidal graphs, which resemble cooperativity. The quantification of ult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cdk1
Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 also known as CDK1 or cell division cycle protein 2 homolog is a highly conserved protein that functions as a serine/threonine protein kinase, and is a key player in cell cycle regulation. It has been highly studied in the budding yeast '' S. cerevisiae'', and the fission yeast '' S. pombe'', where it is encoded by genes ''cdc28'' an''cdc2'' respectively. With its cyclin partners, Cdk1 forms complexes that phosphorylate a variety of target substrates (over 75 have been identified in budding yeast); phosphorylation of these proteins leads to cell cycle progression. Structure Cdk1 is a small protein (approximately 34 kilodaltons), and is highly conserved. The human homolog of Cdk1, ''CDK1'', shares approximately 63% amino-acid identity with its yeast homolog. Furthermore, human ''CDK1'' is capable of rescuing fission yeast carrying a ''cdc2'' mutation. Cdk1 is comprised mostly by the bare protein kinase motif, which other protein kinases share. Cdk1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maturation Promoting Factor
Maturation-promoting factor (abbreviated MPF, also called mitosis-promoting factor or M-Phase-promoting factor) is the cyclin-Cdk complex that was discovered first in frog eggs. It stimulates the mitotic and meiotic phases of the cell cycle. MPF promotes the entrance into mitosis (the M phase) from the G2 phase by phosphorylating multiple proteins needed during mitosis. MPF is activated at the end of G2 by a phosphatase, which removes an inhibitory phosphate group added earlier. The MPF is also called the M phase kinase because of its ability to phosphorylate target proteins at a specific point in the cell cycle and thus control their ability to function. Discovery In 1971, two independent teams of researchers (Yoshio Masui and Clement Markert, as well as Dennis Smith and Robert Ecker) found that frog oocytes arrested in G2 could be induced to enter M phase by microinjection of cytoplasm from oocytes that had been hormonally stimulated with progesterone. Because the entry of oo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA ( DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and subsequently the partitioning of its cytoplasm, chromosomes and other components into two daughter cells in a process called cell division. In cells with nuclei (eukaryotes, i.e., animal, plant, fungal, and protist cells), the cell cycle is divided into two main stages: interphase and the mitotic (M) phase (including mitosis and cytokinesis). During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, and replicates its DNA and some of its organelles. During the mitotic phase, the replicated chromosomes, organelles, and cytoplasm separate into two new daughter cells. To ensure the proper replication of cellular components and division, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints after each of the ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-terminus
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from N-terminus to C-terminus. The convention for writing peptide sequences is to put the C-terminal end on the right and write the sequence from N- to C-terminus. Chemistry Each amino acid has a carboxyl group and an amine group. Amino acids link to one another to form a chain by a dehydration reaction which joins the amine group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of the next. Thus polypeptide chains have an end with an unbound carboxyl group, the C-terminus, and an end with an unbound amine group, the N-terminus. Proteins are naturally synthesized starting from the N-terminus and ending at the C-terminus. Function C-terminal retention signals While the N-terminus of a protein often co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Protein phosphorylation often activates (or deactivates) many enzymes. Glucose Phosphorylation of sugars is often the first stage in their catabolism. Phosphorylation allows cells to accumulate sugars because the phosphate group prevents the molecules from diffusing back across their transporter. Phosphorylation of glucose is a key reaction in sugar metabolism. The chemical equation for the conversion of D-glucose to D-glucose-6-phosphate in the first step of glycolysis is given by :D-glucose + ATP → D-glucose-6-phosphate + ADP :ΔG° = −16.7 kJ/mol (° indicates measurement at standard condition) Hepatic cells are freely permeable to glucose, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CHEK1
Checkpoint kinase 1, commonly referred to as Chk1, is a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase that, in humans, is encoded by the ''CHEK1'' gene. Chk1 coordinates the DNA damage response (DDR) and cell cycle checkpoint response. Activation of Chk1 results in the initiation of cell cycle checkpoints, cell cycle arrest, DNA repair and cell death to prevent damaged cells from progressing through the cell cycle. Discovery In 1993, Beach and associates initially identified Chk1 as a serine/threonine kinase which regulates the G2/M phase transition in fission yeast. Constitutive expression of Chk1 in fission yeast was shown to induce cell cycle arrest. The same gene called Rad27 was identified in budding yeast by Carr and associates. In 1997, homologs were identified in more complex organisms including the fruit fly, human and mouse. Through these findings, it is apparent Chk1 is highly conserved from yeast to humans. Structure Human Chk1 is located on chromosome 11 on the cytogeni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |