|
Watch Glass
A watch glass is a circular concave piece of glass used in chemistry as a surface to evaporate a liquid, to hold solids while being weighed, for heating a small amount of substance and as a cover for a beaker (glassware), beaker. A larger watchglass may be referred to as a clockglass. The latter use is generally applied to prevent dust or other particles entering the beaker; the watch glass does not completely seal the beaker, so gas exchanges still occur. When used as an evaporation surface, a watch glass allows closer observation of Precipitation (chemistry), precipitates or crystallization, and can be placed on a surface of contrasting color to improve the visibility overall. Watch glasses are also sometimes used to cover a glass of whisky, to concentrate the aromas in the glass, and to prevent spills when the whisky is swirled. Watch glasses are named so because they are similar to the glass used for the front of old-fashioned pocket watches. In reference to this, large watch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watch Glass
A watch glass is a circular concave piece of glass used in chemistry as a surface to evaporate a liquid, to hold solids while being weighed, for heating a small amount of substance and as a cover for a beaker (glassware), beaker. A larger watchglass may be referred to as a clockglass. The latter use is generally applied to prevent dust or other particles entering the beaker; the watch glass does not completely seal the beaker, so gas exchanges still occur. When used as an evaporation surface, a watch glass allows closer observation of Precipitation (chemistry), precipitates or crystallization, and can be placed on a surface of contrasting color to improve the visibility overall. Watch glasses are also sometimes used to cover a glass of whisky, to concentrate the aromas in the glass, and to prevent spills when the whisky is swirled. Watch glasses are named so because they are similar to the glass used for the front of old-fashioned pocket watches. In reference to this, large watch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesium Fluoride
Caesium fluoride or cesium fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula CsF and it is a hygroscopic white salt. Caesium fluoride can be used in organic synthesis as a source of the fluoride anion. Caesium also has the highest electropositivity of all non-radioactive elements and fluorine has the highest electronegativity of all known elements. Synthesis and properties Caesium fluoride can be prepared by the reaction of caesium hydroxide (CsOH) with hydrofluoric acid (HF) and the resulting salt can then be purified by recrystallization. The reaction is shown below: :CsOH + HF → CsF + H2O Using the same reaction, another way to create caesium fluoride is to treat caesium carbonate (Cs2CO3) with hydrofluoric acid and again, the resulting salt can then be purified by recrystallization. The reaction is shown below: :Cs2CO3 + 2 HF → 2 CsF + H2O + CO2 CsF is more soluble than sodium fluoride or potassium fluoride in organic solvents. It is available in its anhydrous for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laboratory Watch Glasses Of Different Sizes 2
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratory services are provided in a variety of settings: physicians' offices, clinics, hospitals, and regional and national referral centers. Overview The organisation and contents of laboratories are determined by the differing requirements of the specialists working within. A physics laboratory might contain a particle accelerator or vacuum chamber, while a metallurgy laboratory could have apparatus for casting or refining metals or for testing their strength. A chemist or biologist might use a wet laboratory, while a psychologist's laboratory might be a room with one-way mirrors and hidden cameras in which to observe behavior. In some laboratories, such as those commonly used by computer scientists, computers (sometimes supercomputers) are used for either simulations or the analysis of data. Scienti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification. The word ''crystal'' derives from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning both "ice" and "rock crystal", from (), "icy cold, frost". Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third category of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sapphire
Sapphire is a precious gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum, consisting of aluminium oxide () with trace amounts of elements such as iron, titanium, chromium, vanadium, or magnesium. The name sapphire is derived via the Latin "sapphirus" from the Greek "sappheiros", which referred to Lapis lazuli, lapis lazuli. It is typically blue, but natural "fancy" sapphires also occur in yellow, purple, orange, and green colors; "parti sapphires" show two or more colors. Red corundum stones also occur, but are called ruby, rubies rather than sapphires. Pink-colored corundum may be classified either as ruby or sapphire depending on locale. Commonly, natural sapphires are cut and polished into gemstones and worn in jewellery, jewelry. They also may be created synthetically in laboratories for industrial or decorative purposes in large boule (crystal), crystal boules. Because of the remarkable hardness of sapphires 9 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, Mohs scale (the third hardest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nanometer, nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 Hertz, PHz) to 400 nm (750 Hertz, THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack the energy to ionization, ionize atoms, it can cause chemical reactions and causes many substances to glow or fluorescence, fluoresce. Consequently, the chemical and biological effects of UV are greater than simple heating effects, and many practical applications of UV radiation derive from its interactions with organic molecules. Short-wave ultraviolet light damages DNA and sterilizes surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Shock
Thermal shock is a type of rapidly transient mechanical load. By definition, it is a mechanical load caused by a rapid change of temperature of a certain point. It can be also extended to the case of a thermal gradient, which makes different parts of an object expand by different amounts. This differential expansion can be more directly understood in terms of strain, than in terms of stress, as it is shown in the following. At some point, this stress can exceed the tensile strength of the material, causing a crack to form. If nothing stops this crack from propagating through the material, it will cause the object's structure to fail. Failure due to thermal shock can be prevented by: # Reducing the thermal gradient seen by the object, by changing its temperature more slowly or increasing the material's thermal conductivity # Reducing the material's coefficient of thermal expansion # Increasing its strength # Introducing built-in compressive stress, as for example in tempered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
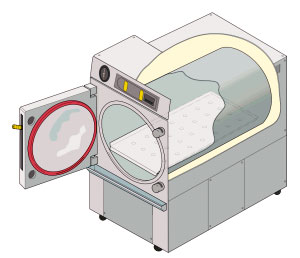
Autoclave
An autoclave is a machine used to carry out industrial and scientific processes requiring elevated temperature and pressure in relation to ambient pressure and/or temperature. Autoclaves are used before surgical procedures to perform sterilization and in the chemical industry to cure coatings and vulcanize rubber and for hydrothermal synthesis. Industrial autoclaves are used in industrial applications, especially in the manufacturing of composites. Many autoclaves are used to sterilize equipment and supplies by subjecting them to pressurized saturated steam at for around 30-60 minutes at a pressure of 15 psi (103 kPa or 1.02 atm) depending on the size of the load and the contents. The autoclave was invented by Charles Chamberland in 1879, although a precursor known as the steam digester was created by Denis Papin in 1679. The name comes from Greek ''auto-'', ultimately meaning self, and Latin ''clavis'' meaning key, thus a self-locking device. Uses Sterilization autoclav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sterilization (microbiology)
Sterilization refers to any process that removes, kills, or deactivates all forms of life (particularly microorganisms such as fungi, bacteria, spores, and unicellular eukaryotic organisms) and other biological agents such as prions present in or on a specific surface, object, or fluid. Sterilization can be achieved through various means, including heat, chemicals, irradiation, high pressure, and filtration. Sterilization is distinct from disinfection, sanitization, and pasteurization, in that those methods reduce rather than eliminate all forms of life and biological agents present. After sterilization, an object is referred to as being sterile or aseptic. Applications Foods One of the first steps toward modernized sterilization was made by Nicolas Appert, who discovered that application of heat over a suitable period slowed the decay of foods and various liquids, preserving them for safe consumption for a longer time than was typical. Canning of foods is an extension of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laboratory
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratory services are provided in a variety of settings: physicians' offices, clinics, hospitals, and regional and national referral centers. Overview The organisation and contents of laboratories are determined by the differing requirements of the specialists working within. A physics laboratory might contain a particle accelerator or vacuum chamber, while a metallurgy laboratory could have apparatus for casting or refining metals or for testing their strength. A chemist or biologist might use a wet laboratory, while a psychologist's laboratory might be a room with one-way mirrors and hidden cameras in which to observe behavior. In some laboratories, such as those commonly used by computer scientists, computers (sometimes supercomputers) are used for either simulations or the analysis of data. Scient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Funnel
A funnel is a tube or pipe that is wide at the top and narrow at the bottom, used for guiding liquid or powder into a small opening. Funnels are usually made of stainless steel, aluminium, glass, or plastic. The material used in its construction should be sturdy enough to withstand the weight of the substance being transferred, and it should not react with the substance. For this reason, stainless steel or glass are useful in transferring diesel, while plastic funnels are useful in the kitchen. Sometimes disposable paper funnels are used in cases where it would be difficult to adequately clean the funnel afterwards (for example, in adding motor oil into a car). Dropper funnels, also called dropping funnels or tap funnels, have a tap to allow the controlled release of a liquid. A flat funnel, made of polypropylene, utilises living hinges and flexible walls to fold flat. The term "funnel" may refer to the chimney or smokestack on a steam locomotive and commonly refers to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beaker (glassware)
In laboratory equipment, a beaker is generally a cylindrical container with a flat bottom.Oxford English Dictionary 1989 edition Most also have a small spout (or "beak") to aid pouring, as shown in the picture. Beakers are available in a wide range of sizes, from one milliliter up to several liters. A beaker is distinguished from a flask by having straight rather than sloping sides. The exception to this definition is a slightly conical-sided beaker called a Philips beaker. The beaker shape in general drinkware is similar. Beakers are commonly made of glass (today usually borosilicate glass Borosilicate glass is a type of glass with silica and boron trioxide as the main glass-forming constituents. Borosilicate glasses are known for having very low coefficients of thermal expansion (≈3 × 10−6 K−1 at 20 °C), ma ...), but can also be in metal (such as stainless steel or aluminum) or certain plastics (notably polythene, polypropylene, PTFE). A common use fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |