|
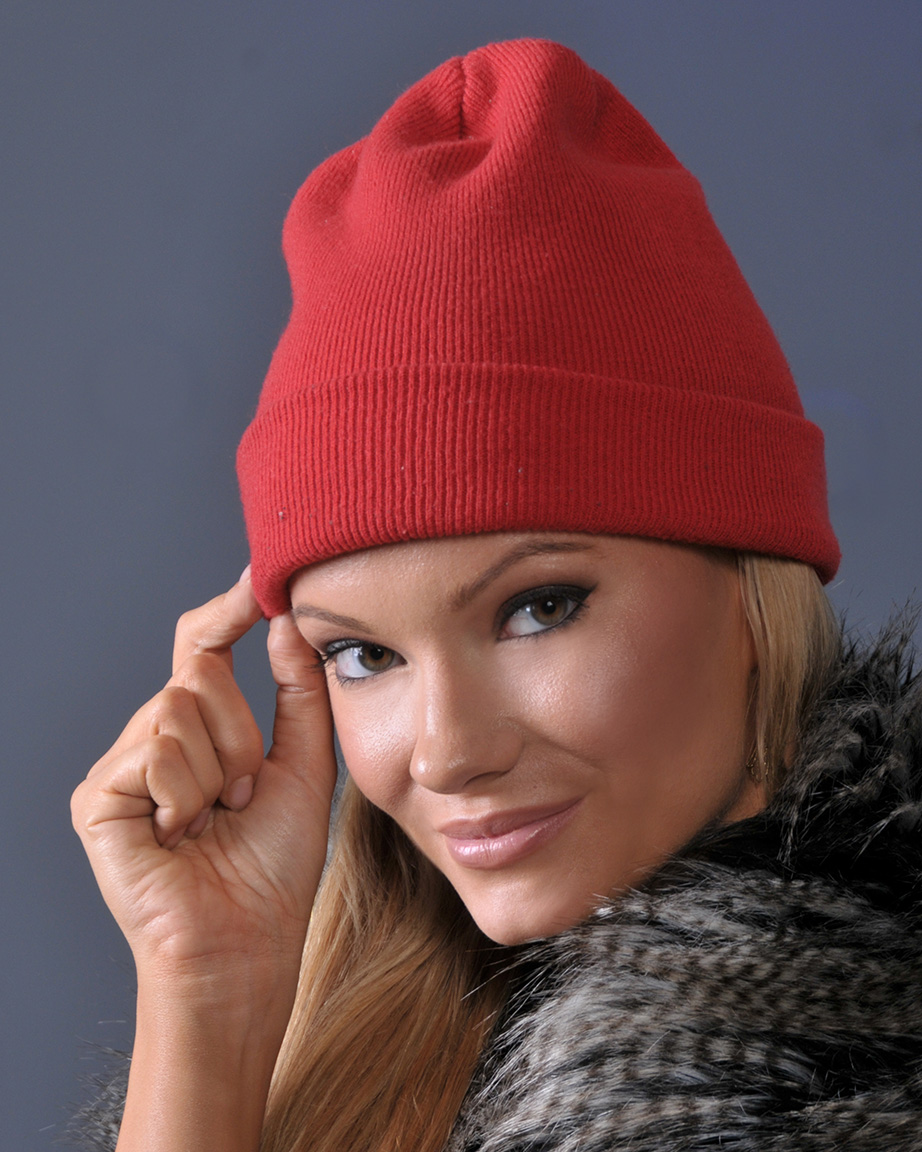
Watch Cap
A knit cap is a piece of knitted headwear designed to provide warmth in cold weather. It usually has a simple tapered shape, although more elaborate variants exist. Historically made of wool, it is now often made of synthetic fibers. Found all over the world where the climate demands warm clothing, knit caps are known by a variety of local names. In American English this type of hat is known as a ''beanie'' or a "watch cap,", while in Canadian English, a knit cap is known as a ', ', or ' (pronounced ). Construction Most knit caps are tapered at the top. The stretch of the knitting itself hugs the head, keeping the cap secure. They are sometimes topped with a pom-pom or loose tassels. Knit caps may have a folded brim, or none, and may be worn tightly fitting the head or loose on top. A South American tradition from the Andes Mountains is for the cap to have ear flaps, with strings for tying under the chin. A special type of cap called a balaclava folds down over the head wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woman Wearing A Knit Cap-2014
A woman is an adult female human. Prior to adulthood, a female human is referred to as a girl (a female child or Adolescence, adolescent). The plural ''women'' is sometimes used in certain phrases such as "women's rights" to denote female humans regardless of age. Typically, women inherit a pair of X chromosomes, one from each parent, and are capable of pregnancy and giving childbirth, birth from puberty until menopause. More generally, sex differentiation of the female fetus is governed by the lack of a present, or functioning, SRY-gene on either one of the respective sex chromosomes. Female anatomy is distinguished from male anatomy by the female reproductive system, which includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and vulva. A fully developed woman generally has a wider pelvis, broader hips, and larger breasts than an adult man. Women have significantly less facial and other body hair, have a higher body fat composition, and are on average shorter and less muscu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knitting
Knitting is a method by which yarn is manipulated to create a textile, or fabric. It is used to create many types of garments. Knitting may be done by hand or by machine. Knitting creates stitches: loops of yarn in a row, either flat or in ''the round'' (tubular). There are usually many ''active stitches'' on the knitting needle at one time. Knitted fabric consists of a number of consecutive rows of connected loops that intermesh with the next and previous rows. As each row is formed, each newly created loop is pulled through one or more loops from the prior row and placed on the ''gaining needle so'' that the loops from the prior row can be pulled off the other needle without unraveling. Differences in yarn (varying in fibre type, ''weight'', uniformity and ''twist''), needle size, and stitch type allow for a variety of knitted fabrics with different properties, including color, texture, thickness, heat retention, water resistance, and integrity. A small sample of kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia. Geopolitical causes of the war included the decline of the Ottoman Empire, the expansion of the Russian Empire in the preceding Russo-Turkish Wars, and the British and French preference to preserve the Ottoman Empire to maintain the balance of power in the Concert of Europe. The flashpoint was a disagreement over the rights of Christian minorities in Palestine, then part of the Ottoman Empire, with the French promoting the rights of Roman Catholics, and Russia promoting those of the Eastern Orthodox Church. The churches worked out their differences with the Ottomans and came to an agreement, but both the French Emperor Napoleon III and the Russian Tsar Nicholas I refused to back down. Nicholas issued an ultimatum that demanded the Orthodox subjects of the Ottoman Empire be placed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Templar
, colors = White mantle with a red cross , colors_label = Attire , march = , mascot = Two knights riding a single horse , equipment = , equipment_label = , battles = The Crusades, including: , anniversaries = , decorations = , battle_honours = , commander1 = Hugues de Payens , commander1_label = First Grand Master , commander2 = Jacques de Molay , commander2_label = Last Grand Master , commander3 = , commander3_label = , notable_commanders = The Poor Fellow-Soldiers of Christ and of the Temple of Solomon ( la, Pauperes commilitones Christi Templique Salomonici), also known as the Order of Solomon's Temple, the Knights Templar, or simply the Templars, was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uhlan
Uhlans (; ; ; ; ) were a type of light cavalry, primarily armed with a lance. While first appearing in the cavalry of Lithuania and then Poland, Uhlans were quickly adopted by the mounted forces of other countries, including France, Russia, Prussia, Saxony and Austria-Hungary. Uhlans traditionally wore a double-breasted short-tailed jacket with a coloured 'plastron' panel at the front, a coloured sash, and a square-topped Polish lancer cap (, also called ). This cap or cavalry helmet was derived from a traditional design of Polish cap, formalised and stylised for military use. Their lances were traditionally topped with a small, swallow-tailed flag ('' pennon'') just below the spearhead. Etymology There are several suggested etymologies for the word uhlan. In the Turkic languages, ''oğlan'' means ''young man'' or ''boy''. It is probable that this entered Polish via Tatar or Turkish and was styled as ''ułan''. The Polish spelling was then adopted by German, French and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts established by England between the late 16th and early 18th centuries. At its height it was the largest empire in history and, for over a century, was the foremost global power. By 1913, the British Empire held sway over 412 million people, of the world population at the time, and by 1920, it covered , of the Earth's total land area. As a result, its constitutional, legal, linguistic, and cultural legacy is widespread. At the peak of its power, it was described as "the empire on which the sun never sets", as the Sun was always shining on at least one of its territories. During the Age of Discovery in the 15th and 16th centuries, Portugal and Spain pioneered European exploration of the globe, and in the process established large overse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Lexico, Oxford Dictionaries, "English language, English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in England, or, more broadly, to the collective dialects of English throughout the British Isles taken as a single umbrella variety, for instance additionally incorporating Scottish English, Welsh English, and Ulster English, Northern Irish English. Tom McArthur (linguist), Tom McArthur in the ''Oxford Guide to World English'' acknowledges that British English shares "all the ambiguities and tensions [with] the word 'British people, British' and as a result can be used and interpreted in two ways, more broadly or more narrowly, within a range of blurring and ambiguity". Variations exist in formal (both written and spoken) English in the United Kingdom. For example, the adjective ''wee'' is almost exclusively used in parts of Scotland, North E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Pennsylvania English
Western Pennsylvania English, known more narrowly as Pittsburgh English or popularly as Pittsburghese, is a dialect of American English native primarily to the western half of Pennsylvania, centered on the city of Pittsburgh, but potentially appearing in some speakers as far north as Erie County, as far west as Youngstown, Ohio, and as far south as Clarksburg, West Virginia. Commonly associated with the white working class of Pittsburgh, users of the dialect are colloquially known as "Yinzers". Overview Scots-Irish, Pennsylvania Dutch, Polish, Ukrainian and Croatian immigrants to the area all provided certain loanwords to the dialect (see "Vocabulary" below). Many of the sounds and words found in the dialect are popularly thought to be unique to Pittsburgh, but that is a misconception since the dialect resides throughout the greater part of western Pennsylvania and the surrounding areas. Central Pennsylvania, currently an intersection of several dialect regions, was identif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standing Watch
Watchkeeping or watchstanding is the assignment of sailors to specific roles on a ship to operate it continuously. These assignments, also known at sea as ''watches'', are constantly active as they are considered essential to the safe operation of the vessel and also allow the ship to respond to emergencies and other situations quickly. These watches are divided into work periods to ensure that the roles are always occupied at all times, while those members of the crew who are assigned to work during a watch are known as ''watchkeepers''. On a typical seafaring vessel, be it naval or merchant, personnel "keep a watch" in various locations and duties across the ship, such as the bridge and engine room. Typical bridge watchkeepers include a lookout and a deck officer who is responsible for the safe navigation of the ship; whereas in the engine room, an engine officer ensures that running machinery continues to operate within tolerances. Types of watches A wide variety of types of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Military
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. The armed forces consists of six service branches: the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and Coast Guard. The president of the United States is the commander-in-chief of the armed forces and forms military policy with the Department of Defense (DoD) and Department of Homeland Security (DHS), both federal executive departments, acting as the principal organs by which military policy is carried out. All six armed services are among the eight uniformed services of the United States. From their inception during the American Revolutionary War, the U.S. Armed Forces have played a decisive role in the history of the United States. They helped forge a sense of national unity and identity through victories in the First Barbary War and the Second Barbary War. They played a critical role in the American Civil War, keeping the Confederacy from seceding from the republic and preserving the unio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
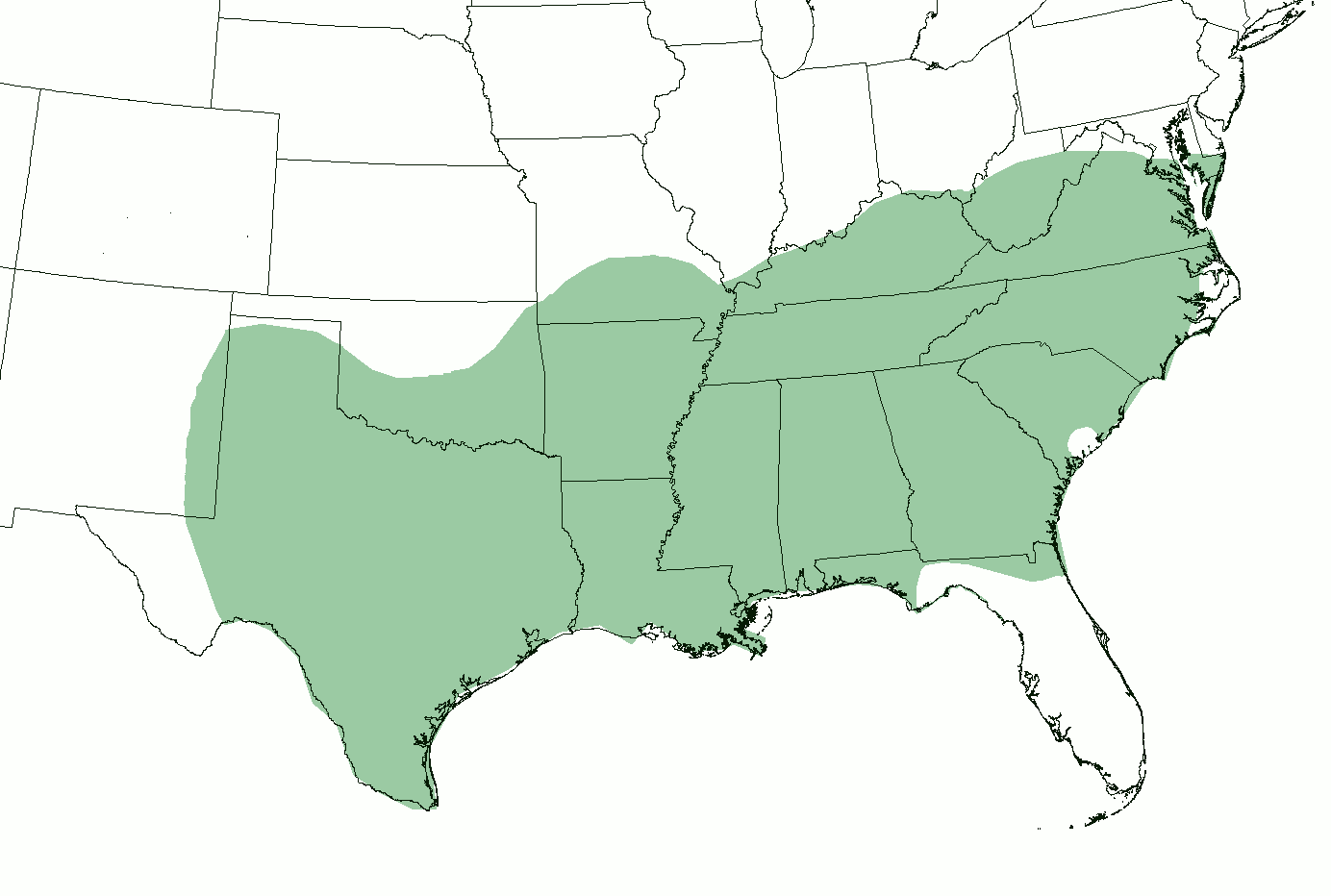
Southern American English
Southern American English or Southern U.S. English is a regional dialect or collection of dialects of American English spoken throughout the Southern United States, though concentrated increasingly in more rural areas, and spoken primarily by White Southerners. In terms of accent, its most innovative forms include southern varieties of Appalachian English and certain varieties of Texan English. Popularly known in the United States as a Southern accent or simply Southern, Southern American English now comprises the largest American regional accent group by number of speakers. Formal, much more recent terms within American linguistics include Southern White Vernacular English and Rural White Southern English. History and geography A diversity of earlier Southern dialects once existed: a consequence of the mix of English speakers from the British Isles (including largely Southern English and Scots-Irish immigrants) who migrated to the American South in the 17th and 18th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twill
Twill is a type of textile weave with a pattern of diagonal parallel ribs. It is one of three fundamental types of textile weaves along with plain weave and satin. It is made by passing the weft thread over one or more warp threads then under two or more warp threads and so on, with a "step," or offset, between rows to create the characteristic diagonal pattern. Because of this structure, twill generally drapes well. Classification Twill weaves can be classified from four points of view: # According to the stepping: #* ''Warp-way'': 3/1 warp way twill, etc. #* ''Weft-way'': 2/3 weft way twill, etc. # According to the direction of twill lines on the face of the fabric: #* ''S-twill'', or ''left-hand twill weave'': 2/1 S, etc. #* ''Z-twill'', or ''right-hand twill weave'': 3/2 Z, etc. # According to the face yarn (warp or weft): #* ''Warp face twill weave'': 4/2 S, etc. #* ''Weft face twill weave'': 1/3 Z, etc. #* ''Double face'' twill weave'': 3/3 Z, etc. # According to the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


.jpg)