|
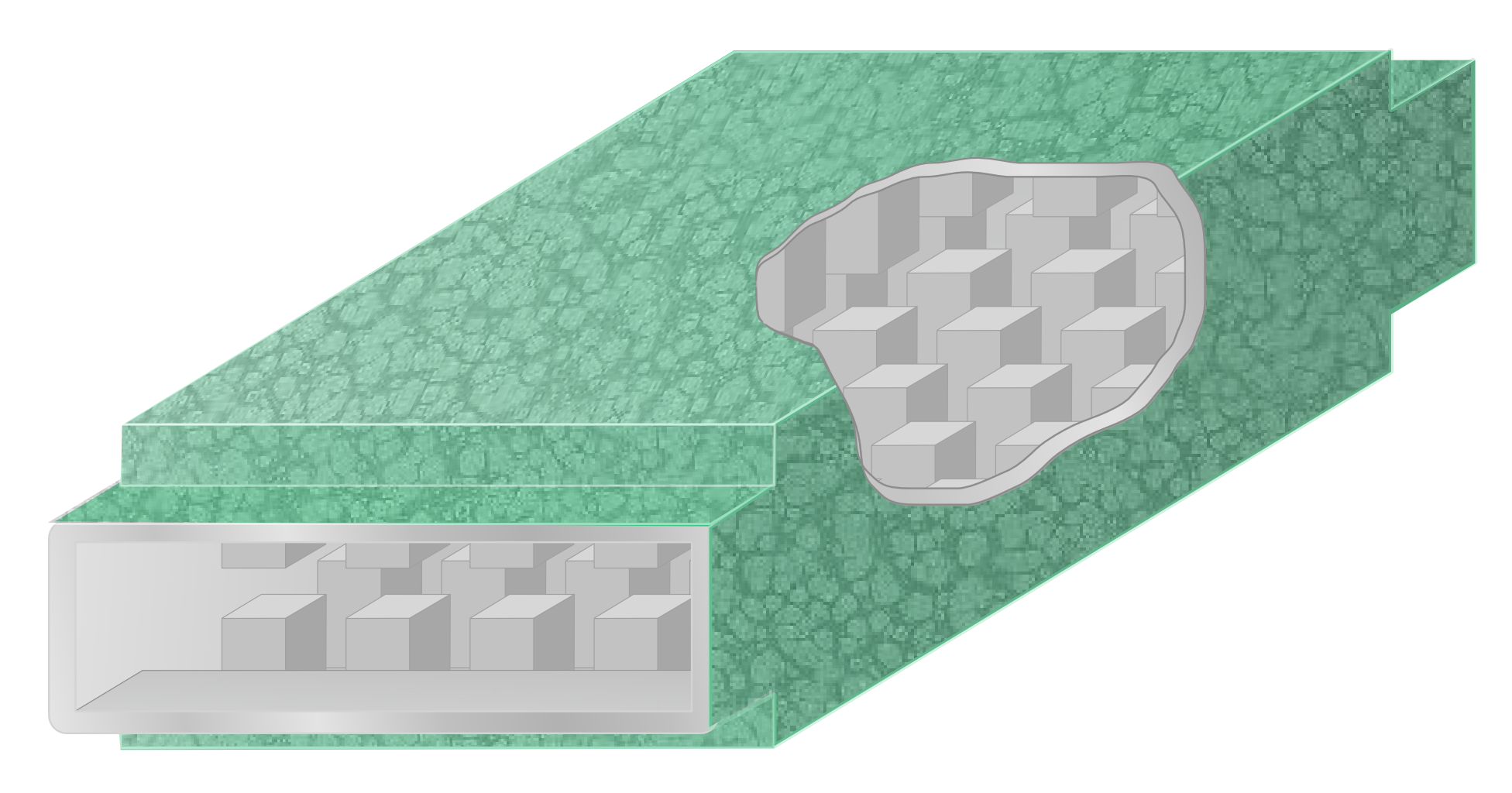
Waffle-iron Filter
A waffle-iron filter is a type of waveguide filter used at microwave frequencies for signal filtering. It is a variation of the corrugated-waveguide filter but with longitudinal slots cut through the corrugations resulting in an internal structure that has the appearance of a waffle-iron. Waffle-iron filters are particularly suitable where both a wide passband, and a wide stopband free of spurious transmission modes, are required. They also have a high power-handling capability. Applications include suppressing the harmonic output of transmitters and the design of wide-band diplexers. They are also used in industrial microwave manufacturing processes to prevent the escape of microwave radiation from the microwave chamber. Filters with an analogous design are now appearing in photonics, but, due to the higher frequency, at a much smaller scale. This small size allows them to be incorporated into integrated circuits. Design techniques for waffle-iron filters include i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waffle-iron Filter
A waffle-iron filter is a type of waveguide filter used at microwave frequencies for signal filtering. It is a variation of the corrugated-waveguide filter but with longitudinal slots cut through the corrugations resulting in an internal structure that has the appearance of a waffle-iron. Waffle-iron filters are particularly suitable where both a wide passband, and a wide stopband free of spurious transmission modes, are required. They also have a high power-handling capability. Applications include suppressing the harmonic output of transmitters and the design of wide-band diplexers. They are also used in industrial microwave manufacturing processes to prevent the escape of microwave radiation from the microwave chamber. Filters with an analogous design are now appearing in photonics, but, due to the higher frequency, at a much smaller scale. This small size allows them to be incorporated into integrated circuits. Design techniques for waffle-iron filters include i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-pass Filter
A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a selected cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The exact frequency response of the filter depends on the filter design. The filter is sometimes called a high-cut filter, or treble-cut filter in audio applications. A low-pass filter is the complement of a high-pass filter. In optics, high-pass and low-pass may have different meanings, depending on whether referring to frequency or wavelength of light, since these variables are inversely related. High-pass frequency filters would act as low-pass wavelength filters, and vice versa. For this reason it is a good practice to refer to wavelength filters as ''short-pass'' and ''long-pass'' to avoid confusion, which would correspond to ''high-pass'' and ''low-pass'' frequencies. Low-pass filters exist in many different forms, including electronic circuits such as a hiss filter used in audio, anti-ali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumped Element
The lumped-element model (also called lumped-parameter model, or lumped-component model) simplifies the description of the behaviour of spatially distributed physical systems, such as electrical circuits, into a topology consisting of discrete entities that approximate the behaviour of the distributed system under certain assumptions. It is useful in electrical systems (including electronics), mechanical multibody systems, heat transfer, acoustics, etc. This may be contrasted to distributed parameter systems or models in which the behaviour is distributed spatially and cannot be considered as localized into discrete entities. Mathematically speaking, the simplification reduces the state space of the system to a finite dimension, and the partial differential equations (PDEs) of the continuous (infinite-dimensional) time and space model of the physical system into ordinary differential equations (ODEs) with a finite number of parameters. Electrical systems Lumped-matter disci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waffle-iron Round Teeth
A waffle iron or waffle maker is a utensil or appliance used to cook waffles. It comprises two metal plates with a connecting hinge, molded to create the honeycomb pattern found on waffles. The iron is heated and either batter is poured or dough is placed between the plates, which are then closed together to bake breakfast delicacies with a sweet dessert flavor, very similar to pancakes but lighter and sweeter. The appearance is much harder to achieve than a pancake; hence the waffle iron. Varieties Traditional waffle irons are attached to tongs with wooden handles and held over an open flame, or set on a stove. Most modern waffle irons are self-contained tabletop electrical appliances, heated by an electric heating element controlled by an internal thermostat. Electric irons come with either removable or non-removable plates. Professional waffle makers are usually made of uncoated cast iron whereas domestic models, particularly cast aluminum ones, are often teflon coated. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choke (electronics)
In electronics, a choke is an inductor used to block higher-frequency alternating currents while passing direct current (DC) and lower-frequencies alternating current (AC) in an electrical circuit. A choke usually consists of a coil of insulated wire often wound on a magnetic core, although some consist of a doughnut-shaped "bead" of ferrite material strung on a wire. The choke's impedance increases with frequency. Its low electrical resistance passes both AC and DC with little power loss, but its reactance limits the amount of AC passed. The name comes from blocking—"choking"—high frequencies while passing low frequencies. It is a functional name; the name "choke" is used if an inductor is used for blocking or decoupling higher frequencies, but the component is simply called an "inductor" if used in electronic filters or tuned circuits. Inductors designed for use as chokes are usually distinguished by not having low-loss construction (high Q factor) required in inductor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulcanisation
Vulcanization (British: Vulcanisation) is a range of processes for hardening rubbers. The term originally referred exclusively to the treatment of natural rubber with sulfur, which remains the most common practice. It has also grown to include the hardening of other (synthetic) rubbers via various means. Examples include silicone rubber via room temperature vulcanizing and chloroprene rubber (neoprene) using metal oxides. Vulcanization can be defined as the curing of elastomers, with the terms 'vulcanization' and 'curing' sometimes used interchangeably in this context. It works by forming cross-links between sections of polymer chain which results in increased rigidity and durability, as well as other changes in the mechanical and electrical properties of the material. Vulcanization, in common with the curing of other thermosetting polymers, is generally irreversible. The word vulcanization is derived from Vulcan, the Roman god of fire and forge. History Rubber—latex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rendering (food Processing)
Rendering is a process that converts waste animal tissue into stable, usable materials. Rendering can refer to any processing of animal products into more useful materials, or, more narrowly, to the rendering of whole animal fatty tissue into purified fats like lard or tallow. Rendering can be carried out on an industrial, farm, or kitchen scale. It can also be applied to non-animal products that are rendered down to pulp. In animal products, the majority of tissue processed comes from slaughterhouses, with the most common animal sources are beef, pork, mutton, and poultry. The rendering process simultaneously dries the material and separates the fat from the bone and protein, yielding a fat commodity and a protein meal. The occupation of renderer has been described as dangerous and dirty. Description A rendering process converts waste animal tissue into stable, usable materials. Rendering can refer to any processing of animal products into more useful materials, or, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Station
A ground station, Earth station, or Earth terminal is a terrestrial radio station designed for extraplanetary telecommunication with spacecraft (constituting part of the ground segment of the spacecraft system), or reception of radio waves from astronomical radio sources. Ground stations may be located either on the surface of the Earth, or in its atmosphere. Earth stations communicate with spacecraft by transmitting and receiving radio waves in the super high frequency (SHF) or extremely high frequency (EHF) bands (e.g. microwaves). When a ground station successfully transmits radio waves to a spacecraft (or vice versa), it establishes a telecommunications link. A principal telecommunications device of the ground station is the parabolic antenna. Ground stations may have either a fixed or itinerant position. Article 1 § III of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) Radio Regulations describes various types of stationary and mobile ground stations, and thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antenna (radio)
In radio engineering, an antenna or aerial is the interface between radio waves propagating through space and electric currents moving in metal conductors, used with a transmitter or receiver. In transmission, a radio transmitter supplies an electric current to the antenna's terminals, and the antenna radiates the energy from the current as electromagnetic waves (radio waves). In reception, an antenna intercepts some of the power of a radio wave in order to produce an electric current at its terminals, that is applied to a receiver to be amplified. Antennas are essential components of all radio equipment. An antenna is an array of conductors ( elements), electrically connected to the receiver or transmitter. Antennas can be designed to transmit and receive radio waves in all horizontal directions equally ( omnidirectional antennas), or preferentially in a particular direction ( directional, or high-gain, or “beam” antennas). An antenna may include components not conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impedance Matching
In electronics, impedance matching is the practice of designing or adjusting the input impedance or output impedance of an electrical device for a desired value. Often, the desired value is selected to maximize power transfer or minimize signal reflection. For example, impedance matching typically is used to improve power transfer from a radio transmitter via the interconnecting transmission line to the antenna. Signals on a transmission line will be transmitted without reflections if the transmission line is terminated with a matching impedance. Techniques of impedance matching include transformers, adjustable networks of lumped resistance, capacitance and inductance, or properly proportioned transmission lines. Practical impedance-matching devices will generally provide best results over a specified frequency band. The concept of impedance matching is widespread in electrical engineering, but is relevant in other applications in which a form of energy, not necessa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotropic
Isotropy is uniformity in all orientations; it is derived . Precise definitions depend on the subject area. Exceptions, or inequalities, are frequently indicated by the prefix ' or ', hence '' anisotropy''. ''Anisotropy'' is also used to describe situations where properties vary systematically, dependent on direction. Isotropic radiation has the same intensity regardless of the direction of measurement, and an isotropic field exerts the same action regardless of how the test particle is oriented. Mathematics Within mathematics, ''isotropy'' has a few different meanings: ; Isotropic manifolds: A manifold is isotropic if the geometry on the manifold is the same regardless of direction. A similar concept is homogeneity. ; Isotropic quadratic form: A quadratic form ''q'' is said to be isotropic if there is a non-zero vector ''v'' such that ; such a ''v'' is an isotropic vector or null vector. In complex geometry, a line through the origin in the direction of an isotropic vect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transverse Mode
A transverse mode of electromagnetic radiation is a particular electromagnetic field pattern of the radiation in the plane perpendicular (i.e., transverse) to the radiation's propagation direction. Transverse modes occur in radio waves and microwaves confined to a waveguide, and also in light waves in an optical fiber and in a laser's optical resonator. Transverse modes occur because of boundary conditions imposed on the wave by the waveguide. For example, a radio wave in a hollow metal waveguide must have zero tangential electric field An electric field (sometimes E-field) is the physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles and exerts force on all other charged particles in the field, either attracting or repelling them. It also refers to the physical field fo ... amplitude at the walls of the waveguide, so the transverse pattern of the electric field of waves is restricted to those that fit between the walls. For this reason, the modes supported by a wav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |