|
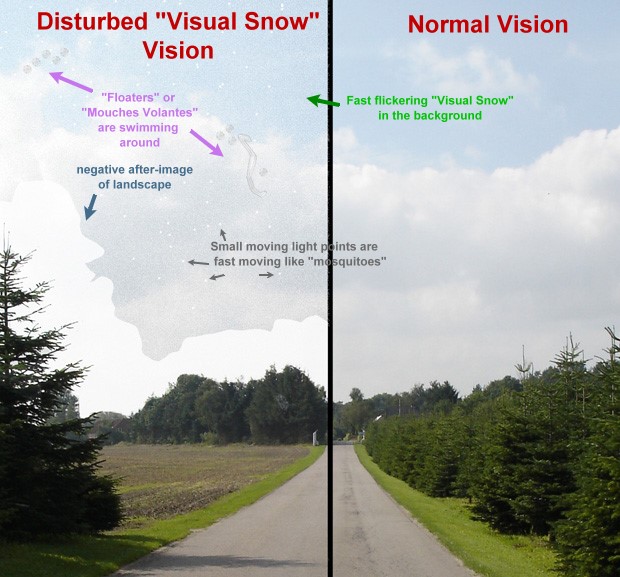
Visual Snow
Visual snow syndrome (VSS) is an uncommon neurological condition in which the primary symptom is that affected individuals see persistent flickering white, black, transparent, or coloured dots across the whole visual field. Other common symptoms are palinopsia, enhanced entoptic phenomena, photophobia, and headaches. The condition is typically always present and has no known cure, as viable treatments are still under research. Migraine and tinnitus are common comorbidities and are both associated with a more severe presentation of the syndrome. The cause of the syndrome is unclear. The underlying mechanism is believed to involve excessive excitability of neurons in the right lingual gyrus and left anterior lobe of cerebellum. Another hypothesis proposes that visual snow syndrome could be a type of thalamocortical dysrhythmia and may involve the thalamic reticular nucleus (TRN). A failure of inhibitory action from the TRN to the thalamus may be the underlying cause for inabilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurology
Neurology (from el, wikt:νεῦρον, νεῦρον (neûron), "string, nerve" and the suffix wikt:-logia, -logia, "study of") is the branch of specialty (medicine), medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the brain, the spinal cord and the peripheral nerves. Neurological practice relies heavily on the field of neuroscience, the scientific study of the nervous system. A neurologist is a physician specializing in neurology and trained to investigate, diagnose and treat neurological disorders. Neurologists treat a myriad of neurologic conditions, including stroke, seizures, movement disorders such as Parkinson's disease, autoimmune neurologic disorders such as multiple sclerosis, headache disorders like migraine and dementias such as Alzheimer's disease. Neurologists may also be involved in clinical research, clinical trials, and basic research, basic or translational research. While neurology is a nonsurgical sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persistent Aura Without Infarction
Persistent aura without infarction (PAWOI) is a rare and seemingly benign condition, first described in case reports in 1982 as "prolonged/persistent migraine aura status", and in 2000 as "migraine aura status", that is not yet fully understood. PAWOI is said to possibly be a factor involved in a variety of neurological symptoms, including visual snow, loss of vision, increased afterimages, tinnitus, and others. The pathogenesis of PAWOI is unknown. It is not clear which medical examinations are useful in diagnosing PAWOI. At present, PAWOI is usually diagnosed solely based on the patient's current and past symptoms. It is possible that an "overactive brain" or a chemical imbalance underlies the disorder. Various medications have been tried as treatment, notably acetazolamide, valproate, lamotrigine, topiramate, and furosemide Furosemide is a loop diuretic medication used to treat fluid build-up due to heart failure, liver scarring, or kidney disease. It may also be used for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Disorder
Central nervous system diseases, also known as central nervous system disorders, are a group of neurological disorders that affect the structure or function of the brain or spinal cord, which collectively form the central nervous system (CNS). These disorders may be caused by such things as infection, injury, blood clots, age related degeneration, cancer, autoimmune disfunction, and birth defects. The symptoms vary widely, as do the treatments. Central nervous system tumors are the most common forms of pediatric cancer. Brain tumors are the most frequent and have the highest mortality. Some disorders, such as substance addiction, autism, and ADHD may be regarded as CNS disorders, though the classifications are not without dispute. Signs and symptoms Every disease has different signs and symptoms. Some of them are persistent headache; pain in the face, back, arms, or legs; an inability to concentrate; loss of feeling; memory loss; loss of muscle strength; tremors; seizures; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Lobe Of Cerebellum
The anterior lobe of cerebellum is the portion of the cerebellum responsible for mediating unconscious proprioception. Inputs into the anterior lobe of the cerebellum are mainly from the spinal cord. It is sometimes equated to the "paleocerebellum". Clinical significance Anterior lobe syndrome When a person gets most of their calories from alcohol (chronic alcoholism) the anterior lobe can deteriorate due to malnutrition. This is known as anterior lobe syndrome, and it causes unsteady gait. Additional images File:Anterior lobe of cerebellum -- animation.gif, Animation. Anterior lobe shown in red. File:Anterior lobe of cerebellum --- animation.gif, Close up animation. Anterior lobe shown in red. File:Cerebellar lobes by Sanjoy Sanyal.webm, Dissection video (1 min 20 s). Demonstrating the three cerebellar lobes. References External links * NIF Search - Anterior Lobe of the Cerebellumvia the Neuroscience Information Framework The Neuroscience Information Framework is a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingual Gyrus
The lingual gyrus, also known as the ''medial'' occipitotemporal gyrus, is a brain structure that is linked to processing vision, especially related to letters. It is thought to also play a role in analysis of logical conditions (i.e., logical order of events) and encoding visual memories. It is named after its shape, which is somewhat similar to a tongue. Contrary to the name, the region has little to do with speech. It is believed that a hypermetabolism of the lingual gyrus is associated with visual snow. Location The lingual gyrus of the occipital lobe lies between the calcarine sulcus and the posterior part of the collateral sulcus; behind, it reaches the occipital pole; in front, it is continued on to the tentorial surface of the temporal lobe, and joins the parahippocampal gyrus. Function Role in vision This region is believed to play an important role in vision and dreaming. Visual memory dysfunction and visuo-limbic disconnection have been shown in cases where the lingu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinnitus
Tinnitus is the perception of sound when no corresponding external sound is present. Nearly everyone experiences a faint "normal tinnitus" in a completely quiet room; but it is of concern only if it is bothersome, interferes with normal hearing, or is associated with other problems. While often described as a ringing, it may also sound like a clicking, buzzing, hissing or roaring. It may be soft or loud, low- or high- pitched, and may seem to come from one or both ears or from the head itself. In some people, it may interfere with concentration, and in some cases is associated with anxiety and depression. Tinnitus is usually associated with a degree of hearing loss and decreased comprehension of speech in noisy environments. It is common, affecting about 10–15% of people. Most, however, tolerate it well, and it is a significant problem in only 1–2% of all people. It can trigger a fight-or-flight response, as the brain may perceive it as dangerous and important. The word ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headache
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches. Headaches can occur as a result of many conditions. There are a number of different classification systems for headaches. The most well-recognized is that of the International Headache Society, which classifies it into more than 150 types of primary and secondary headaches. Causes of headaches may include dehydration; fatigue; sleep deprivation; stress; the effects of medications (overuse) and recreational drugs, including withdrawal; viral infections; loud noises; head injury; rapid ingestion of a very cold food or beverage; and dental or sinus issues (such as sinusitis). Treatment of a headache depends on the underlying cause, but commonly involves pain medication (especially in case of migraine or cluster headache). A headache is one of the most commonly experienced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photophobia
Photophobia is a medical symptom of abnormal intolerance to visual perception of light. As a medical symptom photophobia is not a morbid fear or phobia, but an experience of discomfort or pain to the eyes due to light exposure or by presence of actual physical sensitivity of the eyes, though the term is sometimes additionally applied to abnormal or irrational fear of light such as heliophobia. The term ''photophobia'' comes from the Greek language, Greek φῶς (''phōs''), meaning "light", and φόβος (''phóbos''), meaning "fear". Causes Patients may develop photophobia as a result of several different medical conditions, related to the human eye, eye, the nervous system, genetic, or other causes. Photophobia may manifest itself in an increased response to light starting at any step in the visual system, such as: *Too much light entering the eye. Too much light can enter the eye if it is damaged, such as with corneal abrasion and retinal damage, or if its pupil(s) is unabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entoptic Phenomenon
Entoptic phenomena () are visual effects whose source is within the human eye itself. (Occasionally, these are called entopic phenomena, which is probably a typographical mistake.) In Helmholtz's words: "Under suitable conditions light falling on the eye may render visible certain objects within the eye itself. These perceptions are called ''entoptical''." Overview Entoptic images have a physical basis in the image cast upon the retina. Hence, they are different from optical illusions, which are caused by the visual system and characterized by a visual percept that (loosely said) appears to differ from reality. Because entoptic images are caused by phenomena within the observer's own eye, they share one feature with optical illusions and hallucinations: the observer cannot share a direct and specific view of the phenomenon with others. Helmholtz commented on entoptic phenomena which could be seen easily by some observers, but could not be seen at all by others. This variance is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palinopsia
Palinopsia (Greek: ''palin'' for "again" and ''opsia'' for "seeing") is the persistent recurrence of a visual image after the stimulus has been removed. Palinopsia is not a diagnosis; it is a diverse group of pathological visual symptoms with a wide variety of causes. Visual perseveration is synonymous with palinopsia. In 2014, Gersztenkorn and Lee comprehensively reviewed all cases of palinopsia in the literature and subdivided it into two clinically relevant groups: illusory palinopsia and hallucinatory palinopsia. Hallucinatory palinopsia, usually due to seizures or posterior cortical lesions, describes afterimages that are formed, long-lasting, and high resolution. Illusory palinopsia, usually due to migraines, head trauma, prescription drugs, visual snow or hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD), describes afterimages that are affected by ambient light and motion and are unformed, indistinct, or low resolution. Presentation People with palinopsia frequently repor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Field
The visual field is the "spatial array of visual sensations available to observation in introspectionist psychological experiments". Or simply, visual field can be defined as the entire area that can be seen when an eye is fixed straight at a point. The equivalent concept for optical instruments and image sensors is the field of view (FOV). In optometry, ophthalmology, and neurology, a visual field test is used to determine whether the visual field is affected by diseases that cause local scotoma or a more extensive loss of vision or a reduction in sensitivity (increase in threshold). Normal limits The normal (monocular) human visual field extends to approximately 60 degrees nasally (toward the nose, or inward) from the vertical meridian in each eye, to 107 degrees temporally (away from the nose, or outwards) from the vertical meridian, and approximately 70 degrees above and 80 below the horizontal meridian. The binocular visual field is the superimposition of the two monocular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noise (video)
Noise, commonly known as static, white noise, static noise, or snow, in analog video and television, is a random dot pixel pattern of static displayed when no transmission signal is obtained by the antenna receiver of television sets and other display devices. Description The random pixel pattern is superimposed on the picture or the television screen, being visible as a random flicker of "dots", "snow" or "fuzzy zig-zags" in some television sets, is the result of electronic noise and radiated electromagnetic noise accidentally picked up by the antenna like air or cable. This effect is most commonly seen with analog TV sets, blank VHS tapes, or other display devices. There are many sources of electromagnetic noise which cause the characteristic display patterns of static. Atmospheric sources of noise are the most ubiquitous, and include electromagnetic signals prompted by cosmic microwave background radiation In Big Bang cosmology the cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMB ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |