|
Vaso-occlusive Crisis
A vaso-occlusive crisis is a common painful complication of sickle cell anemia in adolescents and adults. It is a form of sickle cell crisis. Sickle cell anemia – most common in those of African, Hispanic, and Mediterranean origin – leads to sickle cell crisis when the circulation of blood vessels is obstructed by sickled red blood cells, causing ischemic injuries. The most common complaint is of pain, and recurrent episodes may cause irreversible organ damage. One of the most severe forms is the acute chest syndrome which occurs as a result of infarction of the lung parenchyma. This can rapidly result in death. Other types of vaso-occlusive crisis in sickle cell anemia include dactylitis, priapism, abdominal pain, and jaundice. Diagnosis Diagnosis of vaso-occlusive crisis is based on clinical manifestations, complete blood count with white blood cell differential, platelet count, reticulocyte count, and comprehensive metabolic panel with liver and kidney function tests. Ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angiology
Angiology (from Greek , ''angeīon'', "vessel"; and , ''-logia'') is the medical specialty dedicated to studying the circulatory system and of the lymphatic system, i.e., arteries, veins and lymphatic vessels. In the UK, this field is more often termed ''angiology'', and in the United States the term vascular medicine is more frequent. The field of vascular medicine (angiology) is the field that deals with preventing, diagnosing and treating vascular and blood vessel related diseases. Overview Arterial diseases include the aorta (aneurysms/dissection) and arteries supplying the legs, hands, kidneys, brain, intestines. It also covers arterial thrombosis and embolism; vasculitides; and vasospastic disorders. Naturally, it deals with preventing cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack and stroke. Venous diseases include venous thrombosis, chronic venous insufficiency, and varicose veins. Lymphatic diseases include primary and secondary forms of lymphedema. It also inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Blood Cell Differential
A white blood cell differential is a medical laboratory test that provides information about the types and amounts of white blood cells in a person's blood. The test, which is usually ordered as part of a complete blood count (CBC), measures the amounts of the five normal white blood cell typesneutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils and basophilsas well as abnormal cell types if they are present. These results are reported as percentages and absolute values, and compared against reference ranges to determine whether the values are normal, low, or high. Changes in the amounts of white blood cells can aid in the diagnosis of many health conditions, including viral, bacterial, and parasitic infections and blood disorders such as leukemia. White blood cell differentials may be performed by an automated analyzera machine designed to run laboratory tests – or manually, by examining blood smears under a microscope. The test was performed manually until white blood c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbaric Oxygen
Hyperbaric medicine is medical treatment in which an ambient pressure greater than sea level atmospheric pressure is a necessary component. The treatment comprises hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), the medical use of oxygen at an ambient pressure higher than atmospheric pressure, and therapeutic recompression for decompression illness, intended to reduce the injurious effects of systemic gas bubbles by physically reducing their size and providing improved conditions for elimination of bubbles and excess dissolved gas. The equipment required for hyperbaric oxygen treatment consists of a pressure chamber, which may be of rigid or flexible construction, and a means of delivering 100% oxygen. Operation is performed to a predetermined schedule by trained personnel who monitor the patient and may adjust the schedule as required. HBOT found early use in the treatment of decompression sickness, and has also shown great effectiveness in treating conditions such as gas gangrene and carbon mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artemisinin
Artemisinin () and its semisynthetic derivatives are a group of drugs used in the treatment of malaria due to '' Plasmodium falciparum''. It was discovered in 1972 by Tu Youyou, who shared the 2015 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for her discovery. Artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) are now standard treatment worldwide for ''P. falciparum'' malaria as well as malaria due to other species of ''Plasmodium''. Artemisinin is extracted from the plant '' Artemisia annua'', sweet wormwood, a herb employed in Chinese traditional medicine. A precursor compound can be produced using a genetically engineered yeast, which is much more efficient than using the plant. Artemisinin and its derivatives are all sesquiterpene lactones containing an unusual peroxide bridge. This endoperoxide 1,2,4-trioxane ring is responsible for their antimalarial properties. Few other natural compounds with such a peroxide bridge are known. Artemisinin and its derivatives have been used for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ringer's Lactate
Ringer's lactate solution (RL), also known as sodium lactate solution, Lactated Ringer’s, and Hartmann's solution, is a mixture of sodium chloride, sodium lactate, potassium chloride, and calcium chloride in water. It is used for replacing fluids and electrolytes in those who have low blood volume or low blood pressure. It may also be used to treat metabolic acidosis and to wash the eye following a chemical burn. It is given by intravenous infusion or applied to the affected area. Side effects may include allergic reactions, high blood potassium, hypervolemia, and high blood calcium. It may not be suitable for mixing with certain medications and some recommend against use in the same infusion as a blood transfusion. Ringer's lactate solution has a lower rate of acidosis as compared with normal saline. Use is generally safe in pregnancy and breastfeeding. Ringer's lactate solution is in the crystalloid family of medications. It is isotonic, i.e. it has the same tonici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Saline
Saline (also known as saline solution) is a mixture of sodium chloride (salt) and water. It has a number of uses in medicine including cleaning wounds, removal and storage of contact lenses, and help with dry eyes. By injection into a vein it is used to treat dehydration such as that from gastroenteritis and diabetic ketoacidosis. Large amounts may result in fluid overload, swelling, acidosis, and high blood sodium. In those with long-standing low blood sodium, excessive use may result in osmotic demyelination syndrome. Saline is in the crystalloid family of medications. It is most commonly used as a sterile 9 g of salt per litre (0.9%) solution, known as normal saline. Higher and lower concentrations may also occasionally be used. Saline is acidic, with a pH of 5.5 (due mainly to dissolved carbon dioxide). The medical use of saline began around 1831. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In 2020, sodium was the 274th most commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opioid
Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid use disorder, reversing opioid overdose, and suppressing cough. Extremely potent opioids such as carfentanil are approved only for veterinary use. Opioids are also frequently used non-medically for their euphoric effects or to prevent withdrawal. Opioids can cause death and have been used for executions in the United States. Side effects of opioids may include itchiness, sedation, nausea, respiratory depression, constipation, and euphoria. Long-term use can cause tolerance, meaning that increased doses are required to achieve the same effect, and physical dependence, meaning that abruptly discontinuing the drug leads to unpleasant withdrawal symptoms. The euphoria attracts recreational use, and frequent, escalating recreational use of op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Urea Nitrogen
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) is a medical test that measures the amount of urea nitrogen found in blood. The liver produces urea in the urea cycle as a waste product of the digestion of protein. Normal human adult blood should contain 6 to 20 mg/dL (2.1 to 7.1 mmol/L) of urea nitrogen. Individual laboratories will have different reference ranges as the assay used can vary between laboratories. The test is used to detect renal problems. It is not considered as reliable as creatinine or BUN/creatinine ratio blood studies. Interpretation BUN is an indication of renal (kidney) health. The normal range is 2.1–7.1 mmol/ L or 6–20 mg/ dL. The main causes of an increase in BUN are: high protein diet, decrease in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) (suggestive of kidney failure), decrease in blood volume (hypovolemia), congestive heart failure, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, fever, rapid cell destruction from infections, athletic activity, excessive muscle breakdown, and incr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocytes) of almost all vertebrates (the exception being the fish family Channichthyidae) as well as the tissues of some invertebrates. Hemoglobin in blood carries oxygen from the respiratory organs (''e.g.'' lungs or gills) to the rest of the body (''i.e.'' tissues). There it releases the oxygen to permit aerobic respiration to provide energy to power functions of an organism in the process called metabolism. A healthy individual human has 12to 20grams of hemoglobin in every 100mL of blood. In mammals, the chromoprotein makes up about 96% of the red blood cells' dry content (by weight), and around 35% of the total content (including water). Hemoglobin has an oxygen-binding capacity of 1.34mL O2 per gram, which increases the total blood oxy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Function
Assessment of kidney function occurs in different ways, using the presence of symptoms and signs, as well as measurements using urine tests, blood tests, and medical imaging. Functions of a healthy kidney include maintaining a person's fluid balance, maintaining an acid-base balance; regulating electrolytes including sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes; clearing toxins; regulating blood pressure; and regulating hormones, such as erythropoietin; and activation of vitamin D. Introduction The functions of the kidney include maintenance of acid-base balance; regulation of fluid balance; regulation of sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes; clearance of toxins; absorption of glucose, amino acids, and other small molecules; regulation of blood pressure; production of various hormones, such as erythropoietin; and activation of vitamin D. Much of renal physiology is studied at the level of the nephron, the smallest functional unit of the kidney. Each neph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver Function Tests
Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), albumin, bilirubin (direct and indirect), and others. The liver transaminases aspartate transaminase (AST or SGOT) and alanine transaminase (ALT or SGPT) are useful biomarkers of liver injury in a patient with some degree of intact liver function. Most liver diseases cause only mild symptoms initially, but these diseases must be detected early. Hepatic (liver) involvement in some diseases can be of crucial importance. This testing is performed on a patient's blood sample. Some tests are associated with functionality (e.g., albumin), some with cellular integrity (e.g., transaminase), and some with conditions linked to the biliary tract (gamma-glutamyl transferase and alkaline phosphatase). Because some of these tests do not m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
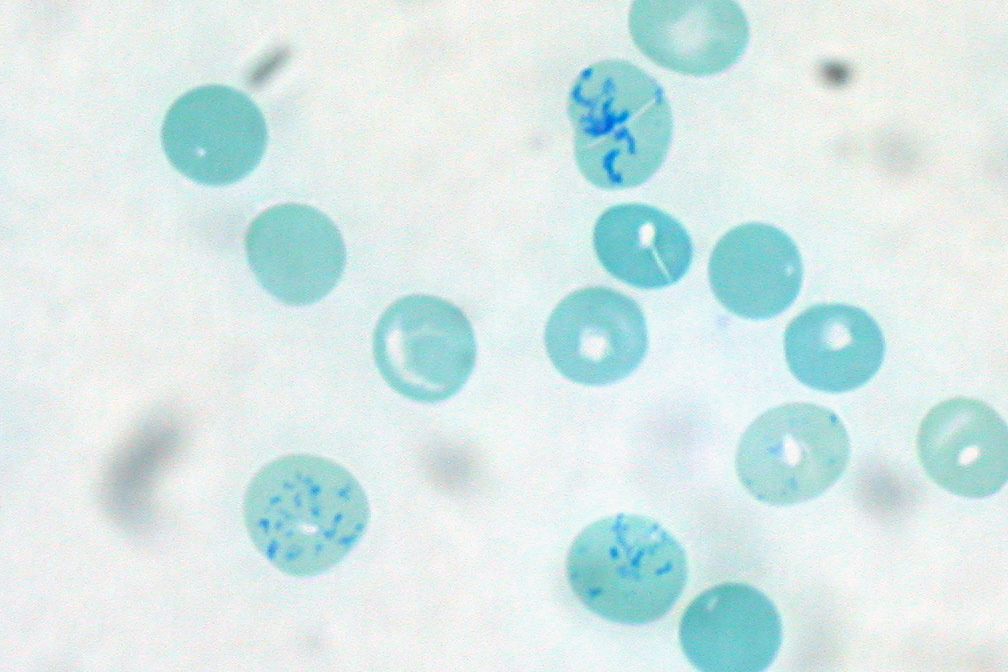
Reticulocyte
Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells (RBCs). In the process of erythropoiesis (red blood cell formation), reticulocytes develop and mature in the bone marrow and then circulate for about a day in the blood stream before developing into mature red blood cells. Like mature red blood cells, in mammals, reticulocytes do not have a cell nucleus. They are called reticulocytes because of a reticular (mesh-like) network of ribosomal RNA that becomes visible under a microscope with certain stains such as new methylene blue and Romanowsky stain. Clinical significance To accurately measure reticulocyte counts, automated counters use a combination of laser excitation, detectors and a fluorescent dye that marks RNA and DNA (such as titan yellow or polymethine). Reticulocytes appear slightly bluer than other red cells when looked at with the normal Romanowsky stain. Reticulocytes are also relatively large, a characteristic that is described by the mean corpuscular volume. The n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |