|
Vascular Layer
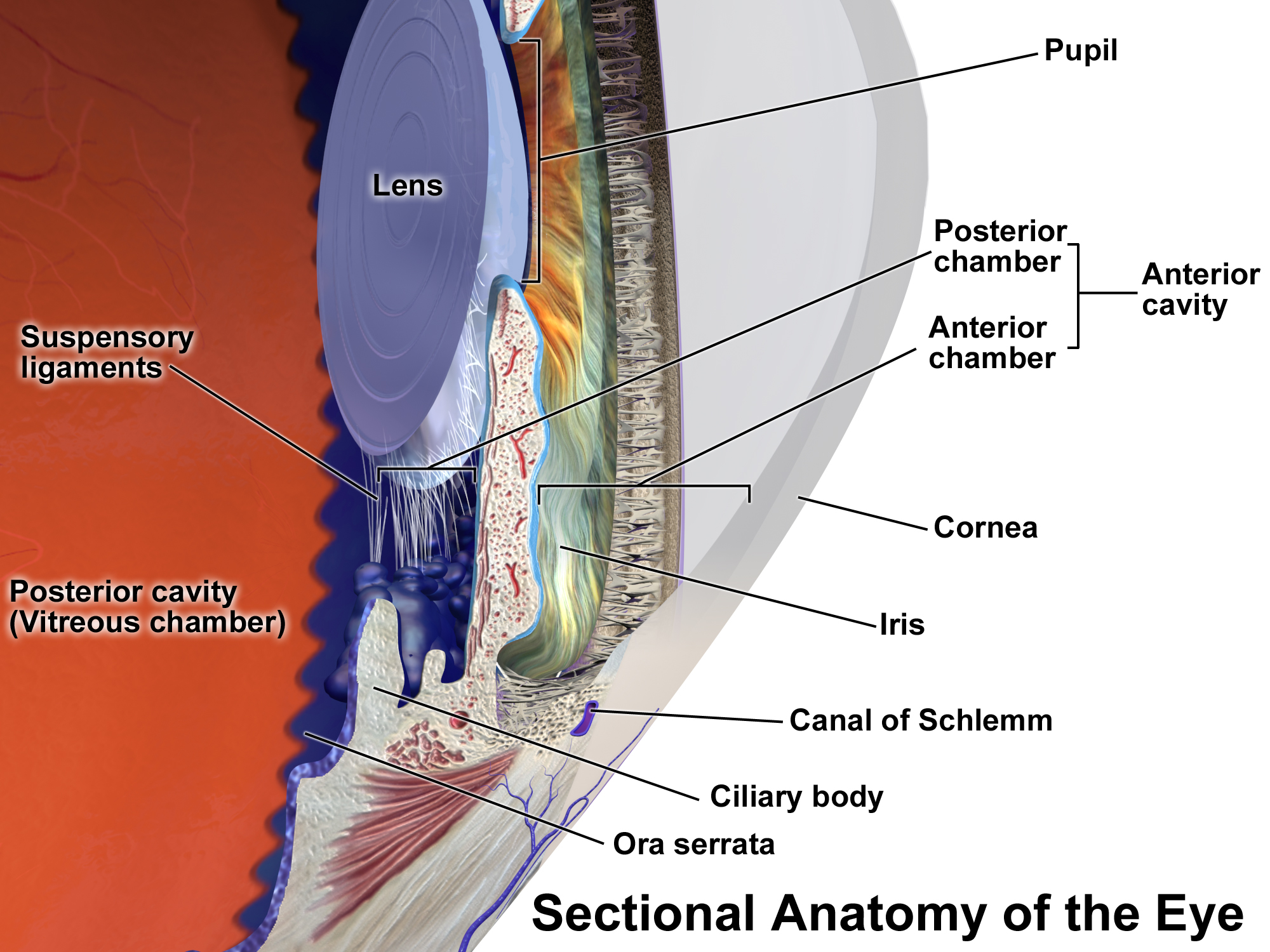
The uvea (; Latin, Lat. ''uva'', "grape"), also called the ''uveal layer'', ''uveal coat'', ''uveal tract'', ''vascular tunic'' or ''vascular layer'' is the pigmented middle of the three concentric layers that make up an human eye, eye. History and etymology The originally medieval Latin term comes from the Latin word ''uva'' ("grape") and is a reference to its grape-like appearance (reddish-blue or almost black colour, wrinkled appearance and grape-like size and shape when stripped intact from a cadaveric eye). In fact, it is a partial loan translation of the Ancient Greek term for the choroid, which literally means “covering resembling a grape”. Its use as a technical term for part of the eye is ancient, but it only referred to the choroid in Middle English and before. Structure Regions The uvea is the vascular middle layer of the eye. It is traditionally divided into three areas, from front to back, the: * Iris (anatomy), Iris * Ciliary body * Choroid Function The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iris (anatomy)
In humans and most mammals and birds, the iris (plural: ''irides'' or ''irises'') is a thin, annular structure in the eye, responsible for controlling the diameter and size of the pupil, and thus the amount of light reaching the retina. Eye color is defined by the iris. In optical terms, the pupil is the eye's aperture, while the iris is the diaphragm. Structure The iris consists of two layers: the front pigmented fibrovascular layer known as a stroma and, beneath the stroma, pigmented epithelial cells. The stroma is connected to a sphincter muscle (sphincter pupillae), which contracts the pupil in a circular motion, and a set of dilator muscles ( dilator pupillae), which pull the iris radially to enlarge the pupil, pulling it in folds. The sphincter pupillae is the opposing muscle of the dilator pupillae. The pupil's diameter, and thus the inner border of the iris, changes size when constricting or dilating. The outer border of the iris does not change size. The constricti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for regulating the body's unconscious actions. The parasympathetic system is responsible for stimulation of "rest-and-digest" or "feed and breed" activities that occur when the body is at rest, especially after eating, including sexual arousal, salivation, lacrimation (tears), urination, digestion, and defecation. Its action is described as being complementary to that of the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for stimulating activities associated with the fight-or-flight response. Nerve fibres of the parasympathetic nervous system arise from the central nervous system. Specific nerves include several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Uveitis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Uveitis is described anatomically, by the part of the eye affected, as anterior, intermediate or posterior, or panuveitic if all parts are involved. Anterior uveitis ( iridocyclytis) is the most common, with the incidence of uveitis overall affecting approximately 1:4500, most commonly those between the ages of 20-60. Symptoms include eye pain, eye redness, floaters and blurred vision, and ophthalmic examination may show dilated ciliary blood vessels and the presence of cells in the anterior chamber. Uveitis may arise spontaneously, have a genetic component, or be associated with an autoimmune disease or infection. While the eye is a relatively protected environment, its immune mechanisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iridocyclitis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Uveitis is described anatomically, by the part of the eye affected, as anterior, intermediate or posterior, or panuveitic if all parts are involved. Anterior uveitis ( iridocyclytis) is the most common, with the incidence of uveitis overall affecting approximately 1:4500, most commonly those between the ages of 20-60. Symptoms include eye pain, eye redness, floaters and blurred vision, and ophthalmic examination may show dilated ciliary blood vessels and the presence of cells in the anterior chamber. Uveitis may arise spontaneously, have a genetic component, or be associated with an autoimmune disease or infection. While the eye is a relatively protected environment, its immune mechanisms may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iritis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Uveitis is described anatomically, by the part of the eye affected, as anterior, intermediate or posterior, or panuveitic if all parts are involved. Anterior uveitis ( iridocyclytis) is the most common, with the incidence of uveitis overall affecting approximately 1:4500, most commonly those between the ages of 20-60. Symptoms include eye pain, eye redness, floaters and blurred vision, and ophthalmic examination may show dilated ciliary blood vessels and the presence of cells in the anterior chamber. Uveitis may arise spontaneously, have a genetic component, or be associated with an autoimmune disease or infection. While the eye is a relatively protected environment, its immune mechanisms may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choroiditis
Chorioretinitis is an inflammation of the choroid (thin pigmented vascular coat of the eye) and retina of the eye. It is a form of posterior uveitis. If only the choroid is inflamed, not the retina, the condition is termed choroiditis. The ophthalmologist's goal in treating these potentially blinding conditions is to eliminate the inflammation and minimize the potential risk of therapy to the patient. Symptoms Symptoms may include the presence of floating black spots, blurred vision, pain or redness in the eye, sensitivity to light, or excessive tearing. Causes Chorioretinitis is often caused by toxoplasmosis and cytomegalovirus infections (mostly seen in immunodeficient subjects such as people with HIV/AIDS or on immunosuppressant drugs). Congenital toxoplasmosis via transplacental transmission can also lead to sequelae such as chorioretinitis along with hydrocephalus and cerebral calcifications. Other possible causes of chorioretinitis are syphilis, sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uveitis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Uveitis is described anatomically, by the part of the eye affected, as anterior, intermediate or posterior, or panuveitic if all parts are involved. Anterior uveitis ( iridocyclytis) is the most common, with the incidence of uveitis overall affecting approximately 1:4500, most commonly those between the ages of 20-60. Symptoms include eye pain, eye redness, floaters and blurred vision, and ophthalmic examination may show dilated ciliary blood vessels and the presence of cells in the anterior chamber. Uveitis may arise spontaneously, have a genetic component, or be associated with an autoimmune disease or infection. While the eye is a relatively protected environment, its immune mechanisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigens
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. The term ''antigen'' originally referred to a substance that is an antibody generator. Antigens can be proteins, peptides (amino acid chains), polysaccharides (chains of monosaccharides/simple sugars), lipids, or nucleic acids. Antigens are recognized by antigen receptors, including antibodies and T-cell receptors. Diverse antigen receptors are made by cells of the immune system so that each cell has a specificity for a single antigen. Upon exposure to an antigen, only the lymphocytes that recognize that antigen are activated and expanded, a process known as clonal selection. In most cases, an antibody can only react to and bind one specific antigen; in some instances, however, antibodies may cross-react and bind more than one antigen. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sympathetic Ophthalmia
Sympathetic ophthalmia (SO), also called spared eye injury, is a diffuse granulomatous inflammation of the uveal layer of both eyes following trauma to one eye. It can leave the affected person completely blind. Symptoms may develop from days to several years after a penetrating eye injury. It typically results from a delayed hypersensitivity reaction. Signs and symptoms Eye floaters and loss of accommodation are among the earliest symptoms. The disease may progress to severe inflammation of the uveal layer of the eye (uveitis) with pain and sensitivity of the eyes to light. The affected eye often remains relatively painless while the inflammatory disease spreads through the uvea, where characteristic focal infiltrates in the choroid named Dalén–Fuchs nodules can be seen. The retina, however, usually remains uninvolved, although perivascular cuffing of the retinal vessels with inflammatory cells may occur. Swelling of the optic disc (papilledema), secondary glaucoma, vitil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that result in damage to the optic nerve (or retina) and cause vision loss. The most common type is open-angle (wide angle, chronic simple) glaucoma, in which the drainage angle for fluid within the eye remains open, with less common types including closed-angle (narrow angle, acute congestive) glaucoma and normal-tension glaucoma. Open-angle glaucoma develops slowly over time and there is no pain. Peripheral vision may begin to decrease, followed by central vision, resulting in blindness if not treated. Closed-angle glaucoma can present gradually or suddenly. The sudden presentation may involve severe eye pain, blurred vision, mid-dilated pupil, redness of the eye, and nausea. Vision loss from glaucoma, once it has occurred, is permanent. Eyes affected by glaucoma are referred to as being glaucomatous. Risk factors for glaucoma include increasing age, high pressure in the eye, a family history of glaucoma, and use of steroid medication. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system. The autonomic nervous system functions to regulate the body's unconscious actions. The sympathetic nervous system's primary process is to stimulate the body's fight or flight response. It is, however, constantly active at a basic level to maintain homeostasis. The sympathetic nervous system is described as being antagonistic to the parasympathetic nervous system which stimulates the body to "feed and breed" and to (then) "rest-and-digest". Structure There are two kinds of neurons involved in the transmission of any signal through the sympathetic system: pre-ganglionic and post-ganglionic. The shorter preganglionic neurons originate in the thoracolumbar division o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciliary Body
The ciliary body is a part of the eye that includes the ciliary muscle, which controls the shape of the lens, and the ciliary epithelium, which produces the aqueous humor. The aqueous humor is produced in the non-pigmented portion of the ciliary body. The ciliary body is part of the uvea, the layer of tissue that delivers oxygen and nutrients to the eye tissues. The ciliary body joins the ora serrata of the choroid to the root of the iris.Cassin, B. and Solomon, S. ''Dictionary of Eye Terminology''. Gainesville, Florida: Triad Publishing Company, 1990. Structure The ciliary body is a ring-shaped thickening of tissue inside the eye that divides the posterior chamber from the vitreous body. It contains the ciliary muscle, vessels, and fibrous connective tissue. Folds on the inner ciliary epithelium are called ciliary processes, and these secrete aqueous humor into the posterior chamber. The aqueous humor then flows through the pupil into the anterior chamber. The ciliary bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |