|
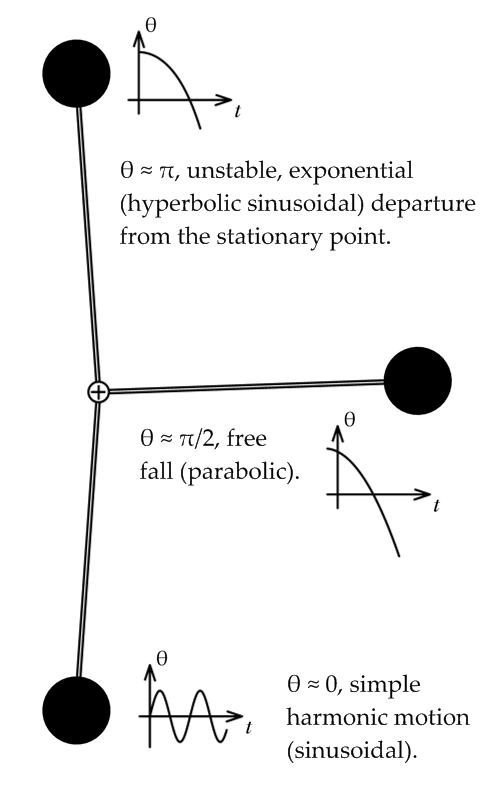
Variable Structure Systems
A variable structure system, or VSS, is a discontinuous nonlinear system of the form :\dot = \varphi( \mathbf, t ) where \mathbf \triangleq _1, x_2, \ldots, x_n \in \mathbb^n is the state vector, t \in \mathbb is the time variable, and \varphi(\mathbf,t) \triangleq \varphi_1(\mathbf,t), \varphi_2(\mathbf,t), \ldots, \varphi_n(\mathbf,t) : \mathbb^ \mapsto \mathbb^n is a ''piecewise continuous'' function. Due to the ''piecewise'' continuity of these systems, they behave like different continuous nonlinear systems in different regions of their state space. At the boundaries of these regions, their dynamics switch abruptly. Hence, their ''structure'' ''varies'' over different parts of their state space. The development of variable structure control depends upon methods of analyzing variable structure systems, which are special cases of hybrid dynamical systems. See also *Variable structure control *Sliding mode control *Hybrid system *Nonlinear control *Robust control * Optima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classification Of Discontinuities
Continuous functions are of utmost importance in mathematics, functions and applications. However, not all functions are continuous. If a function is not continuous at a point in its domain, one says that it has a discontinuity there. The set of all points of discontinuity of a function may be a discrete set, a dense set, or even the entire domain of the function. This article describes the classification of discontinuities in the simplest case of functions of a single real variable taking real values. The oscillation of a function at a point quantifies these discontinuities as follows: * in a removable discontinuity, the distance that the value of the function is off by is the oscillation; * in a jump discontinuity, the size of the jump is the oscillation (assuming that the value ''at'' the point lies between these limits of the two sides); * in an essential discontinuity, oscillation measures the failure of a limit to exist; the limit is constant. A special case is if the fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optimal Control
Optimal control theory is a branch of mathematical optimization that deals with finding a control for a dynamical system over a period of time such that an objective function is optimized. It has numerous applications in science, engineering and operations research. For example, the dynamical system might be a spacecraft with controls corresponding to rocket thrusters, and the objective might be to reach the moon with minimum fuel expenditure. Or the dynamical system could be a nation's economy, with the objective to minimize unemployment; the controls in this case could be fiscal and monetary policy. A dynamical system may also be introduced to embed operations research problems within the framework of optimal control theory. Optimal control is an extension of the calculus of variations, and is a mathematical optimization method for deriving control policies. The method is largely due to the work of Lev Pontryagin and Richard Bellman in the 1950s, after contributions to calcu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamical Systems
In mathematics, a dynamical system is a system in which a function describes the time dependence of a point in an ambient space. Examples include the mathematical models that describe the swinging of a clock pendulum, the flow of water in a pipe, the random motion of particles in the air, and the number of fish each springtime in a lake. The most general definition unifies several concepts in mathematics such as ordinary differential equations and ergodic theory by allowing different choices of the space and how time is measured. Time can be measured by integers, by real or complex numbers or can be a more general algebraic object, losing the memory of its physical origin, and the space may be a manifold or simply a set, without the need of a smooth space-time structure defined on it. At any given time, a dynamical system has a state representing a point in an appropriate state space. This state is often given by a tuple of real numbers or by a vector in a geometri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear Systems
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathematicians, and many other scientists because most systems are inherently nonlinear in nature. Nonlinear dynamical systems, describing changes in variables over time, may appear chaotic, unpredictable, or counterintuitive, contrasting with much simpler linear systems. Typically, the behavior of a nonlinear system is described in mathematics by a nonlinear system of equations, which is a set of simultaneous equations in which the unknowns (or the unknown functions in the case of differential equations) appear as variables of a polynomial of degree higher than one or in the argument of a function which is not a polynomial of degree one. In other words, in a nonlinear system of equations, the equation(s) to be solved cannot be written as a linear combination of the u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prentice Hall
Prentice Hall was an American major educational publisher owned by Savvas Learning Company. Prentice Hall publishes print and digital content for the 6–12 and higher-education market, and distributes its technical titles through the Safari Books Online e-reference service. History On October 13, 1913, law professor Charles Gerstenberg and his student Richard Ettinger founded Prentice Hall. Gerstenberg and Ettinger took their mothers' maiden names, Prentice and Hall, to name their new company. Prentice Hall became known as a publisher of trade books by authors such as Norman Vincent Peale; elementary, secondary, and college textbooks; loose-leaf information services; and professional books. Prentice Hall acquired the training provider Deltak in 1979. Prentice Hall was acquired by Gulf+Western in 1984, and became part of that company's publishing division Simon & Schuster. S&S sold several Prentice Hall subsidiaries: Deltak and Resource Systems were sold to National Educatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
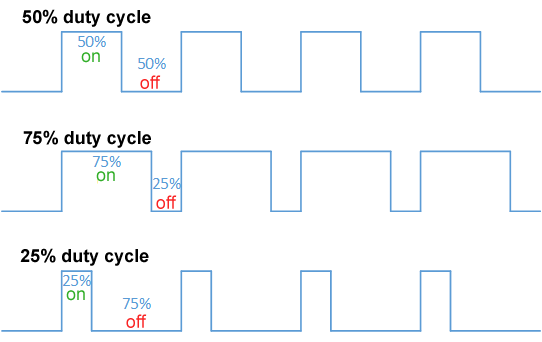
Pulse-width Modulation
Pulse-width modulation (PWM), or pulse-duration modulation (PDM), is a method of reducing the average power delivered by an electrical signal, by effectively chopping it up into discrete parts. The average value of voltage (and current) fed to the load is controlled by turning the switch between supply and load on and off at a fast rate. The longer the switch is on compared to the off periods, the higher the total power supplied to the load. Along with maximum power point tracking (MPPT), it is one of the primary methods of reducing the output of solar panels to that which can be utilized by a battery. PWM is particularly suited for running inertial loads such as motors, which are not as easily affected by this discrete switching, because their inertia causes them to react slowly. The PWM switching frequency has to be high enough not to affect the load, which is to say that the resultant waveform perceived by the load must be as smooth as possible. The rate (or frequency) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse-density Modulation
Pulse-density modulation, or PDM, is a form of modulation used to represent an analog signal with a binary signal. In a PDM signal, specific amplitude values are not encoded into codewords of pulses of different weight as they would be in pulse-code modulation (PCM); rather, the relative density of the pulses corresponds to the analog signal's amplitude. The output of a 1-bit DAC is the same as the PDM encoding of the signal. Pulse-width modulation (PWM) is a special case of PDM where the switching frequency is fixed and all the pulses corresponding to one sample are contiguous in the digital signal. For a 50% voltage with a resolution of 8-bits, a PWM waveform will turn on for 128 clock cycles and then off for the remaining 128 cycles. With PDM and the same clock rate the signal would alternate between on and off every other cycle. The average is 50% for both waveforms, but the PDM signal switches more often. For 100% or 0% level, they are the same. Description In a pulse-den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta-sigma Modulation
Delta-sigma (ΔΣ; or sigma-delta, ΣΔ) modulation is a method for encoding analog signals into digital signals as found in an analog-to-digital converter (ADC). It is also used to convert high bit-count, low-frequency digital signals into lower bit-count, higher-frequency digital signals as part of the process to convert digital signals into analog as part of a digital-to-analog converter (DAC). In a conventional ADC, an analog signal is sampled with a sampling frequency and subsequently quantized in a multi-level quantizer into a digital signal. This process introduces quantization error noise. The first step in a delta-sigma modulation is delta modulation. In delta modulation the change in the signal (its delta) is encoded, rather than the absolute value. The result is a stream of pulses, as opposed to a stream of numbers as is the case with pulse-code modulation (PCM). In delta-sigma modulation, accuracy of the modulation is improved by passing the digital output thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switching Amplifier
A class-D amplifier or switching amplifier is an electronic amplifier in which the amplifying devices (transistors, usually MOSFETs) operate as electronic switches, and not as linear gain devices as in other amplifiers. They operate by rapidly switching back and forth between the supply rails, being fed by a modulator using pulse width, pulse density, or related techniques to encode the audio input into a pulse train. The audio passes through a simple low-pass filter into the loudspeaker. The high-frequency pulses are blocked. Since the pairs of output transistors are never conducting at the same time, there is no other path for current flow apart from the low-pass filter/loudspeaker. For this reason, efficiency can exceed 90%. History The first Class-D amplifier was invented by British scientist Alec Reeves in the 1950s and was first called by that name in 1955. The first commercial product was a kit module called the X-10 released by Sinclair Radionics in 1964. Howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H-bridge
A H-bridge is an electronic circuit that switches the polarity of a voltage applied to a load. These circuits are often used in robotics and other applications to allow DC motors to run forwards or backwards. The name is derived from its common schematic diagram representation, with four switching elements configured as the branches of a letter "H" and the load connected as the cross-bar. Most DC-to-AC converters (power inverters), most AC/AC converters, the DC-to-DC push–pull converter, isolated DC-to-DC converter most motor controllers, and many other kinds of power electronics use H bridges. In particular, a bipolar stepper motor is almost always driven by a motor controller containing two H bridges. General H-bridges are available as integrated circuits, or can be built from discrete components. The term ''H-bridge'' is derived from the typical graphical representation of such a circuit. An H-bridge is built with four switches (solid-state or mechanical). When the swit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robust Control
In control theory, robust control is an approach to controller design that explicitly deals with uncertainty. Robust control methods are designed to function properly provided that uncertain parameters or disturbances are found within some (typically compact) set. Robust methods aim to achieve robust performance and/or stability in the presence of bounded modelling errors. The early methods of Bode and others were fairly robust; the state-space methods invented in the 1960s and 1970s were sometimes found to lack robustness, prompting research to improve them. This was the start of the theory of robust control, which took shape in the 1980s and 1990s and is still active today. In contrast with an adaptive control policy, a robust control policy is static, rather than adapting to measurements of variations, the controller is designed to work assuming that certain variables will be unknown but bounded. (Section 1.5) In German; an English version is also available Criteria for robustn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear System
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathematicians, and many other scientists because most systems are inherently nonlinear in nature. Nonlinear dynamical systems, describing changes in variables over time, may appear chaotic, unpredictable, or counterintuitive, contrasting with much simpler linear systems. Typically, the behavior of a nonlinear system is described in mathematics by a nonlinear system of equations, which is a set of simultaneous equations in which the unknowns (or the unknown functions in the case of differential equations) appear as variables of a polynomial of degree higher than one or in the argument of a function which is not a polynomial of degree one. In other words, in a nonlinear system of equations, the equation(s) to be solved cannot be written as a linear combination of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |