|
Variable Reluctance Sensor
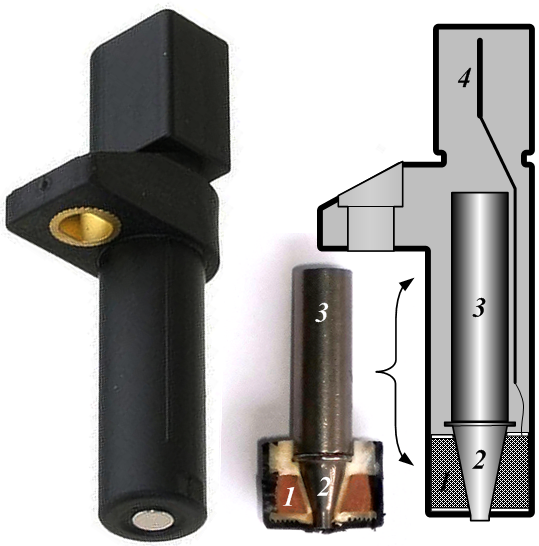
A variable reluctance sensor (commonly called a VR sensor) is a transducer that measures changes in magnetic reluctance. When combined with basic electronic circuitry, the sensor detects the change in presence or proximity of ferrous objects. With more complex circuitry and the addition of software and specific mechanical hardware, a VR sensor can also provide measurements of linear velocity, angular velocity, position, and torque. Uses and applications A VR sensor used as a simple proximity sensor can determine the position of a mechanical link in a piece of industrial equipment. A crankshaft position sensor (in an automobile engine) is used to provide the angular position of the crankshaft to the engine control unit. The engine control unit can then calculate engine speed (angular velocity). Speed sensors used in automobile transmissions are used to measure the rotational speed (angular velocity) of shafts within the transmission. The engine control unit or transmission co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transducer
A transducer is a device that converts energy from one form to another. Usually a transducer converts a signal in one form of energy to a signal in another. Transducers are often employed at the boundaries of automation, measurement, and control systems, where electrical signals are converted to and from other physical quantities (energy, force, torque, light, motion, position, etc.). The process of converting one form of energy to another is known as transduction. Types * Mechanical transducers, so-called as they convert physical quantities into mechanical outputs or vice versa; * Electrical transducers however convert physical quantities into electrical outputs or signals. Examples of these are: ** a thermocouple that changes temperature differences into a small voltage; ** a linear variable differential transformer (LVDT), used to measure displacement (position) changes by means of electrical signals. Sensors, actuators and transceivers Transducers can be categorized b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Reluctance
Magnetic reluctance, or magnetic resistance, is a concept used in the analysis of magnetic circuits. It is defined as the ratio of magnetomotive force (mmf) to magnetic flux. It represents the opposition to magnetic flux, and depends on the geometry and composition of an object. Magnetic reluctance in a magnetic circuit is analogous to electrical resistance in an electrical circuit in that resistance is a measure of the opposition to the electric current. The definition of magnetic reluctance is analogous to Ohm's law in this respect. However, magnetic flux passing through a reluctance does not give rise to dissipation of heat as it does for current through a resistance. Thus, the analogy cannot be used for modelling energy flow in systems where energy crosses between the magnetic and electrical domains. An alternative analogy to the reluctance model which does correctly represent energy flows is the gyrator–capacitor model. Magnetic reluctance is a scalar extensive qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Velocity
In physics, angular velocity or rotational velocity ( or ), also known as angular frequency vector,(UP1) is a pseudovector representation of how fast the angular position or orientation of an object changes with time (i.e. how quickly an object rotates or revolves relative to a point or axis). The magnitude of the pseudovector represents the ''angular speed'', the rate at which the object rotates or revolves, and its direction is normal to the instantaneous plane of rotation or angular displacement. The orientation of angular velocity is conventionally specified by the right-hand rule.(EM1) There are two types of angular velocity. * Orbital angular velocity refers to how fast a point object revolves about a fixed origin, i.e. the time rate of change of its angular position relative to the origin. * Spin angular velocity refers to how fast a rigid body rotates with respect to its center of rotation and is independent of the choice of origin, in contrast to orbital angular v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proximity Sensor
A proximity sensor is a sensor able to detect the presence of nearby objects without any physical contact. A proximity sensor often emits an electromagnetic field or a beam of electromagnetic radiation (infrared, for instance), and looks for changes in the field or return signal. The object being sensed is often referred to as the proximity sensor's target. Different proximity sensor targets demand different sensors. For example, a capacitive proximity sensor or photoelectric sensor might be suitable for a plastic target; an inductive proximity sensor always requires a metal target. Proximity sensors can have a high reliability and long functional life because of the absence of mechanical parts and lack of physical contact between the sensor and the sensed object. Proximity sensors are also used in machine vibration monitoring to measure the variation in distance between a shaft and its support bearing. This is common in large steam turbines, compressors, and motors that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crankshaft Position Sensor
A crank sensor (CKP) is an electronic device used in an internal combustion engine, both petrol and diesel, to monitor the position or rotational speed of the crankshaft. This information is used by engine management systems to control the fuel injection or the ignition system timing and other engine parameters. Before electronic crank sensors were available, the distributor would have to be manually adjusted to a timing mark on petrol engines. The crank sensor can be used in combination with a similar camshaft position sensor (CMP) to monitor the relationship between the pistons and valves in the engine, which is particularly important in engines with variable valve timing. This method is also used to "synchronise" a four stroke engine upon starting, allowing the management system to know when to inject the fuel. It is also commonly used as the primary source for the measurement of engine speed in revolutions per minute. Common mounting locations include the main crank p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine Control Unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by reading values from a multitude of sensors within the engine bay, interpreting the data using multidimensional performance maps (called lookup tables), and adjusting the engine actuators. Before ECUs, air–fuel mixture, ignition timing, and idle speed were mechanically set and dynamically controlled by mechanical and pneumatic means. If the ECU has control over the fuel lines, then it is referred to as an electronic engine management system (EEMS). The fuel injection system has the major role of controlling the engine's fuel supply. The whole mechanism of the EEMS is controlled by a stack of sensors and actuators. Workings Control of air–fuel ratio Most modern engines use some type of fuel injection to deliver fuel to the cylind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guitar Pickup
A pickup is a transducer that captures or senses mechanical vibrations produced by musical instruments, particularly stringed instruments such as the electric guitar, and converts these to an electrical signal that is amplified using an instrument amplifier to produce musical sounds through a loudspeaker in a speaker enclosure. The signal from a pickup can also be recorded directly. Most electric guitars and electric basses use magnetic pickups. Acoustic guitars, upright basses and fiddles often use a piezoelectric pickup. Magnetic pickups A typical magnetic pickup is a transducer (specifically a variable reluctance sensor) that consists of one or more permanent magnets (usually alnico or ferrite) wrapped with a coil of several thousand turns of fine enameled copper wire. The magnet creates a magnetic field which is focused by the pickup's pole piece or pieces. The permanent magnet in the pickup magnetizes the guitar string above it. This causes the string to generate a magn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permanent Magnet
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nickel, cobalt, etc. and attracts or repels other magnets. A permanent magnet is an object made from a material that is magnetized and creates its own persistent magnetic field. An everyday example is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. Materials that can be magnetized, which are also the ones that are strongly attracted to a magnet, are called ferromagnetic (or ferrimagnetic). These include the elements iron, nickel and cobalt and their alloys, some alloys of rare-earth metals, and some naturally occurring minerals such as lodestone. Although ferromagnetic (and ferrimagnetic) materials are the only ones attracted to a magnet strongly enough to be commonly considered magnetic, all other substances respond weak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferromagnetic
Ferromagnetism is a property of certain materials (such as iron) which results in a large observed magnetic permeability, and in many cases a large magnetic coercivity allowing the material to form a permanent magnet. Ferromagnetic materials are the familiar metals noticeably attracted to a magnet, a consequence of their large magnetic permeability. Magnetic permeability describes the induced magnetization of a material due to the presence of an ''external'' magnetic field, and it is this temporarily induced magnetization inside a steel plate, for instance, which accounts for its attraction to the permanent magnet. Whether or not that steel plate acquires a permanent magnetization itself, depends not only on the strength of the applied field, but on the so-called coercivity of that material, which varies greatly among ferromagnetic materials. In physics, several different types of material magnetism are distinguished. Ferromagnetism (along with the similar effect ferrimagneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-lock Braking System
An anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety anti-skid braking system used on aircraft and on land vehicles, such as cars, motorcycles, trucks, and buses. ABS operates by preventing the wheels from locking up during braking, thereby maintaining tractive contact with the road surface and allowing the driver to maintain more control over the vehicle. ABS is an automated system that uses the principles of threshold braking and cadence braking, techniques which were once practiced by skillful drivers before ABS was widespread. ABS operates at a much faster rate and more effectively than most drivers could manage. Although ABS generally offers improved vehicle control and decreases stopping distances on dry and some slippery surfaces, on loose gravel or snow-covered surfaces ABS may significantly increase braking distance, while still improving steering control. Since ABS was introduced in production vehicles, such systems have become increasingly sophisticated and effectiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |