|
Vagotomy
A vagotomy is a surgical procedure that involves removing part of the vagus nerve. Types A plain vagotomy eliminates the parasympathetic supply from the stomach to the left side of the transverse colon. Other techniques focus on branches leading from the retroperitoneum to the stomach. Highly selective vagotomy refers to denervation of only those branches supplying the lower esophagus and stomach (leaving the nerve of Latarjet in place to ensure the emptying function of the stomach remains intact). It is one of the treatments of peptic ulcer. Vagotomy is an essential component of surgical management of peptic (duodenal and gastric) ulcer disease (PUD). Vagotomy was once commonly performed to treat and prevent PUD; however, with the availability of excellent acid secretion control with H2 receptor antagonists, such as cimetidine, ranitidine, and famotidine, and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), such as pantoprazole, rabeprazole, omeprazole, and lansoprazole, the need for surgical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagus Nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, cranial nerve X, or simply CN X, is a cranial nerve that interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. It comprises two nerves—the left and right vagus nerves—but they are typically referred to collectively as a single subsystem. The vagus is the longest nerve of the autonomic nervous system in the human body and comprises both sensory and motor fibers. The sensory fibers originate from neurons of the nodose ganglion, whereas the motor fibers come from neurons of the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus and the nucleus ambiguus. The vagus was also historically called the pneumogastric nerve. Structure Upon leaving the medulla oblongata between the olive and the inferior cerebellar peduncle, the vagus nerve extends through the jugular foramen, then passes into the carotid sheath between the internal carotid artery and the internal jugular vein down to the neck, chest, and abdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastroesophageal Reflux
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the upper gastrointestinal chronic diseases where stomach content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/or complications. Symptoms include dental corrosion, dysphagia, heartburn, odynophagia, regurgitation, non-cardiac chest pain, extraesophageal symptoms such as chronic cough, hoarseness, reflux-induced laryngitis, or asthma. On the long term, and when not treated, complications such as esophagitis, esophageal stricture, and Barrett's esophagus may arise. Risk factors include obesity, pregnancy, smoking, hiatal hernia, and taking certain medications. Medications that may cause or worsen the disease include benzodiazepines, calcium channel blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, NSAIDs, and certain asthma medicines. Acid reflux is due to poor closure of the lower esophageal sphincter, which is at the junction between the stomach and the esoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pathological condition such as a disease or injury, to help improve bodily function, appearance, or to repair unwanted ruptured areas. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure, operation, or simply "surgery". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments or surgical nurse. The person or subject on which the surgery is performed can be a person or an animal. A surgeon is a person who practices surgery and a surgeon's assistant is a person who practices surgical assistance. A surgical team is made up of the surgeon, the surgeon's assistant, an anaesthetist, a circulating nurse and a surgical technologist. Surgery usually spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Hypothalamus
The lateral hypothalamus (LH), also called the lateral hypothalamic area (LHA), contains the primary orexinergic nucleus within the hypothalamus that widely projects throughout the nervous system; this system of neurons mediates an array of cognitive and physical processes, such as promoting feeding behavior and arousal, reducing pain perception, and regulating body temperature, digestive functions, and blood pressure, among many others. Clinically significant disorders that involve dysfunctions of the orexinergic projection system include narcolepsy, motility disorders or functional gastrointestinal disorders involving visceral hypersensitivity (e.g., irritable bowel syndrome), and eating disorders. The neurotransmitter glutamate and the endocannabinoids (e.g., anandamide) and the orexin neuropeptides orexin-A and orexin-B are the primary signaling neurochemicals in orexin neurons; pathway-specific neurochemicals include GABA, melanin-concentrating hormone, nociceptin, glucos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
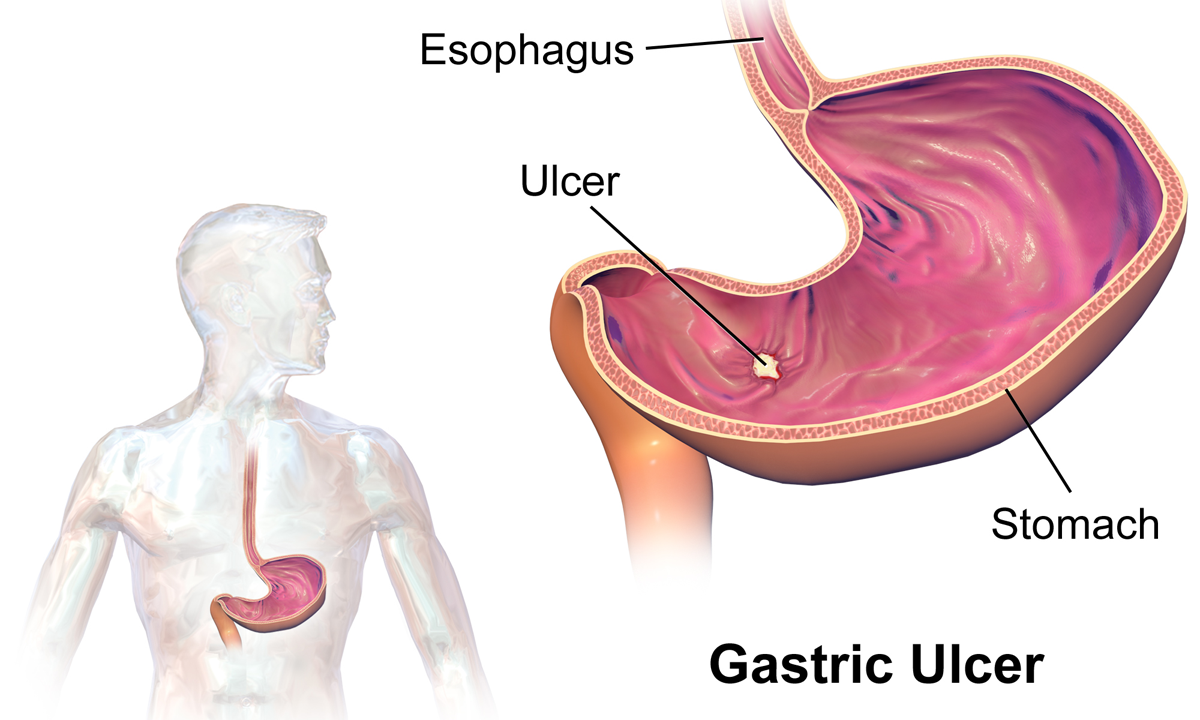
Stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is involved in the gastric phase of digestion, following chewing. It performs a chemical breakdown by means of enzymes and hydrochloric acid. In humans and many other animals, the stomach is located between the oesophagus and the small intestine. The stomach secretes digestive enzymes and gastric acid to aid in food digestion. The pyloric sphincter controls the passage of partially digested food ( chyme) from the stomach into the duodenum, where peristalsis takes over to move this through the rest of intestines. Structure In the human digestive system, the stomach lies between the oesophagus and the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine). It is in the left upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity. The top of the stomach lies ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptic Ulcer Disease
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is a break in the inner lining of the stomach, the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines is a duodenal ulcer. The most common symptoms of a duodenal ulcer are waking at night with upper abdominal pain and upper abdominal pain that improves with eating. With a gastric ulcer, the pain may worsen with eating. The pain is often described as a burning or dull ache. Other symptoms include belching, vomiting, weight loss, or poor appetite. About a third of older people have no symptoms. Complications may include bleeding, perforation, and blockage of the stomach. Bleeding occurs in as many as 15% of cases. Common causes include the bacteria ''Helicobacter pylori'' and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Other, less common causes include tobacco smoking, stress as a result of other serious health conditions, Behçet's di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals Of Surgery
The ''Annals of Surgery'' is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal of surgical science and practice. It was started in 1885 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (United States, United Kingdom). See also * List of medical journals References External linksAnnals of Surgery @ PubMed Central
PubMed Central (PMC) is a free digital repository that archives open access full-text scholarly articles that have been published in biomedical and life sciences journals. As one of the major research databases developed by the National Center f ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perforated Ulcer
A perforated ulcer is a condition in which an untreated ulcer has burned through the mucosal wall in a segment of the gastrointestinal tract (e.g., the stomach or colon) allowing gastric contents to leak into the abdominal cavity. Signs and symptoms A perforated ulcer can be grouped into a stercoral perforation which involves a number of different things that causes perforation of the intestine wall. The first symptom of a perforated peptic ulcer is usually sudden, severe, sharp pain in the abdomen. The pain is typically at its maximum immediately and persists. It is characteristically made worse by any movement, and greatly intensifies with coughing or sneezing. Causes Causes include alcohol, smoking, consuming highly acidic foods and beverages (such as coffee), and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Diagnosis The ulcer is known initially as a peptic ulcer before the ulcer burns through the full thickness of the stomach or duodenal wall. A diagnosis is made by taki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastric Dumping Syndrome
Dumping syndrome occurs when food, especially sugar, moves too quickly from the stomach to the duodenum—the first part of the small intestine—in the upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract. This condition is also called rapid gastric emptying. It is mostly associated with conditions following gastric or esophageal surgery, though it can also arise secondary to diabetes or to the use of certain medications; it is caused by an absent or insufficiently functioning pyloric sphincter, the valve between the stomach and the duodenum. Dumping syndrome has two forms, based on when symptoms occur. Early dumping syndrome occurs 10 to 30 minutes after a meal. It results from rapid movement of fluid into the intestine following a sudden addition of a large amount of food from the stomach. The small intestine expands rapidly due to the presence of hypertonic/ hyperosmolar contents from the stomach, especially sweet foods. This causes symptoms due to the shift of fluid into the intestinal lumen, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adverse Events
An adverse event (AE) is any untoward medical occurrence in a patient or clinical investigation subject administered a pharmaceutical product and which does not necessarily have a causal relationship with this treatment. An adverse event can therefore be any unfavourable and unintended sign (including an abnormal laboratory finding), symptom, or disease temporally associated with the use of a medicinal (investigational) product, whether or not related to the medicinal (investigational) product. AEs in patients participating in clinical trials must be reported to the study sponsor and if required could be reported to the local ethics committee. Adverse events categorized as "serious" (results in death, illness requiring hospitalization, events deemed life-threatening, results in persistent or significant incapacity, a congenital anomaly, birth defect or medically important condition) must be reported to the regulatory authorities immediately, whereas non-serious adverse events are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghrelin
Ghrelin (; or lenomorelin, INN) is a hormone produced by enteroendocrine cells of the gastrointestinal tract, especially the stomach, and is often called a "hunger hormone" because it increases the drive to eat. Blood levels of ghrelin are highest before meals when hungry, returning to lower levels after mealtimes. Ghrelin may help prepare for food intake by increasing gastric motility and stimulating the secretion of gastric acid. Ghrelin activates cells in the anterior pituitary gland and hypothalamic arcuate nucleus, including neuropeptide Y neurons that initiate appetite. Ghrelin stimulates brain structures having a specific receptor – the growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1A (GHSR-1A). Ghrelin also participates in regulation of reward cognition, learning and memory, the sleep-wake cycle, taste sensation, reward behavior, and glucose metabolism. History and name Ghrelin was discovered after the ghrelin receptor (called growth hormone secretagogue type 1A receptor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adipogenesis
Adipogenesis is the formation of adipocytes (fat cells) from stem cells. It involves 2 phases, determination, and terminal differentiation. Determination is mesenchymal stem cells committing to the adipocyte precursor cells, also known as preadipocytes which lose the potential to differentiate to other types of cells such as chondrocytes, myocytes, and osteoblasts. Terminal differentiation is that preadipocytes differentiate into mature adipocytes. Adipocytes can arise either from preadipocytes resident in adipose tissue, or from bone-marrow derived progenitor cells that migrate to adipose tissue. Introduction Adipocytes play a vital role in energy homeostasis and process the largest energy reserve as triglycerol in the body of animals. Adipocytes stay in a dynamic state, they start expanding when the energy intake is higher than the expenditure and undergo mobilization when the energy expenditure exceeds the intake. This process is highly regulated by counter regulatory hormones t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)