|
Vaginal Intraepithelial Neoplasia
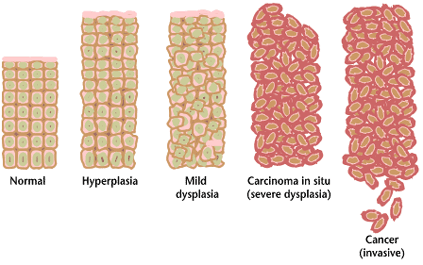
Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia (VAIN) is a condition that describes premalignant histological findings in the vagina characterized by dysplastic changes. The disorder is rare and generally has no symptoms. VAIN can be detected by the presence of abnormal cells in a Papanicolaou test (Pap smear). Like cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, VAIN comes in three stages, VAIN 1, 2, and 3. In VAIN 1, a third of the thickness of the cells in the vaginal skin are abnormal, while in VAIN 3, the full thickness is affected. VAIN 3 is also known as carcinoma in-situ, or stage 0 vaginal cancer.Cancer Research UK (2002)The stages of cancer of the vagina. CancerHelp UK. Retrieved January 3, 2008. Infection with certain types of the human papillomavirus Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premalignant Condition
A precancerous condition is a condition, tumor or lesion involving abnormal cells which are associated with an increased risk of developing into cancer. Clinically, precancerous conditions encompass a variety of abnormal tissues with an increased risk of developing into cancer. Some of the most common precancerous conditions include certain colon polyps, which can progress into colon cancer, monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance, which can progress into multiple myeloma or myelodysplastic syndrome. and cervical dysplasia, which can progress into cervical cancer. Bronchial premalignant lesions can progress to squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Pathologically, precancerous tissue can range from benign neoplasias, which are tumors which don't invade neighboring normal tissues or spread to distant organs, to dysplasia, a collection of highly abnormal cells which, in some cases, has an increased risk of progressing to anaplasia and invasive cancer which is life-threate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histological
Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. Although one may divide microscopic anatomy into ''organology'', the study of organs, ''histology'', the study of tissues, and ''cytology'', the study of cells, modern usage places all of these topics under the field of histology. In medicine, histopathology is the branch of histology that includes the microscopic identification and study of diseased tissue. In the field of paleontology, the term paleohistology refers to the histology of fossil organisms. Biological tissues Animal tissue classification There are four basic types of animal tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. All animal tissues are considered to be subtypes of these four principal tissue types (fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagina
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen. At the deep end, the cervix (neck of the uterus) bulges into the vagina. The vagina allows for sexual intercourse and birth. It also channels menstrual flow, which occurs in humans and closely related primates as part of the menstrual cycle. Although research on the vagina is especially lacking for different animals, its location, structure and size are documented as varying among species. Female mammals usually have two external openings in the vulva; these are the urethral opening for the urinary tract and the vaginal opening for the genital tract. This is different from male mammals, who usually have a single urethral opening for both urination and reproduction. The vaginal opening is much larger than the nearby urethral opening, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysplasia
Dysplasia is any of various types of abnormal growth or development of cells (microscopic scale) or organs (macroscopic scale), and the abnormal histology or anatomical structure(s) resulting from such growth. Dysplasias on a mainly microscopic scale include epithelial dysplasia and fibrous dysplasia of bone. Dysplasias on a mainly macroscopic scale include hip dysplasia (human), hip dysplasia, myelodysplastic syndrome, and multicystic dysplastic kidney. In one of the modern histopathology, histopathological senses of the term, dysplasia is sometimes differentiated from other categories of tissue change including hyperplasia, metaplasia, and neoplasia, and dysplasias are thus generally not cancerous. An exception is that the myelodysplasias include a range of benign tumor, benign, precancerous condition, precancerous, and cancerous forms. Various other dysplasias tend to be precancerous. The word's meanings thus cover a spectrum of histopathological variations. Microscopic sca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymptomatic
In medicine, any disease is classified asymptomatic if a patient tests as carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. Whenever a medical condition fails to show noticeable symptoms after a diagnosis it might be considered asymptomatic. Infections of this kind are usually called subclinical infections. Diseases such as mental illnesses or psychosomatic conditions are considered subclinical if they present some individual symptoms but not all those normally required for a clinical diagnosis. The term clinically silent is also found. Producing only a few, mild symptoms, disease is paucisymptomatic. Symptoms appearing later, after an asymptomatic incubation period, mean a pre-symptomatic period has existed. Importance Knowing that a condition is asymptomatic is important because: * It may develop symptoms later and only then require treatment. * It may resolve itself or become benign. * It may be contagious, and the contribution of asymptomatic and pre-symptomat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pap Test
The Papanicolaou test (abbreviated as Pap test, also known as Pap smear (AE), cervical smear (BE), cervical screening (BE), or smear test (BE)) is a method of cervical screening used to detect potentially precancerous and cancerous processes in the cervix (opening of the uterus or womb) or colon (in both men and women). Abnormal findings are often followed up by more sensitive diagnostic procedures and, if warranted, interventions that aim to prevent progression to cervical cancer. The test was independently invented in the 1920s by Georgios Papanikolaou and Aurel Babeș and named after Papanikolaou. A simplified version of the test was introduced by Anna Marion Hilliard in 1957. A Pap smear is performed by opening the vagina with a speculum and collecting cells at the outer opening of the cervix at the transformation zone (where the outer squamous cervical cells meet the inner glandular endocervical cells), using an Ayre spatula or a cytobrush. A similar method is used to co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), also known as cervical dysplasia, is the abnormal growth of cells on the surface of the cervix that could potentially lead to cervical cancer. More specifically, CIN refers to the potentially precancerous transformation of cells of the cervix. CIN most commonly occurs at the squamocolumnar junction of the cervix, a transitional area between the squamous epithelium of the vagina and the columnar epithelium of the endocervix. It can also occur in vaginal walls and vulvar epithelium. CIN is graded on a 1–3 scale, with 3 being the most abnormal (see classification section below). Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is necessary for the development of CIN, but not all with this infection develop cervical cancer. Many women with HPV infection never develop CIN or cervical cancer. Typically, HPV resolves on its own. However, those with an HPV infection that lasts more than one or two years have a higher risk of developing a higher grade of CIN. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinoma In-situ
Carcinoma ''in situ'' (CIS) is a group of abnormal cells. While they are a form of neoplasm, there is disagreement over whether CIS should be classified as cancer. This controversy also depends on the exact CIS in question (i.e. cervical, skin, breast). Some authors do not classify them as cancer, however, recognizing that they can potentially become cancer. Others classify certain types as a non-invasive form of cancer. The term "pre-cancer" has also been used. These abnormal cells grow in their normal place, thus "''in situ''" (from Latin for "in its place"). For example, carcinoma ''in situ'' of the skin, also called Bowen's disease, is the accumulation of dysplastic epidermal cells within the epidermis only, that has failed to penetrate into the deeper dermis. For this reason, CIS will usually not form a tumor. Rather, the lesion is flat (in the skin, cervix, etc.) or follows the existing architecture of the organ (in the breast, lung, etc.). Exceptions include CIS of the colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaginal Cancer
Vaginal cancer is an extraordinarily rare form of cancer that develops in the tissue of the vagina. Primary vaginal cancer originates from the vaginal tissue – most frequently squamous cell carcinoma, but primary vaginal adenocarcinoma, sarcoma, and melanoma have also been reported – while secondary vaginal cancer involves the metastasis of a cancer that originated in a different part of the body. Secondary vaginal cancer is more common. Signs of vaginal cancer may include abnormal vaginal bleeding, dysuria, tenesmus, or pelvic pain, though as many as 20% of women diagnosed with vaginal cancer are asymptomatic at the time of diagnosis. Vaginal cancer occurs more frequently in women over age 50, and the mean age of diagnosis of vaginal cancer is 60 years. It often can be cured if found and treated in early stages. Surgery alone or surgery combined with pelvic radiation is typically used to treat vaginal cancer. Description Carcinoma of the vagina occurs in less than 2% of wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
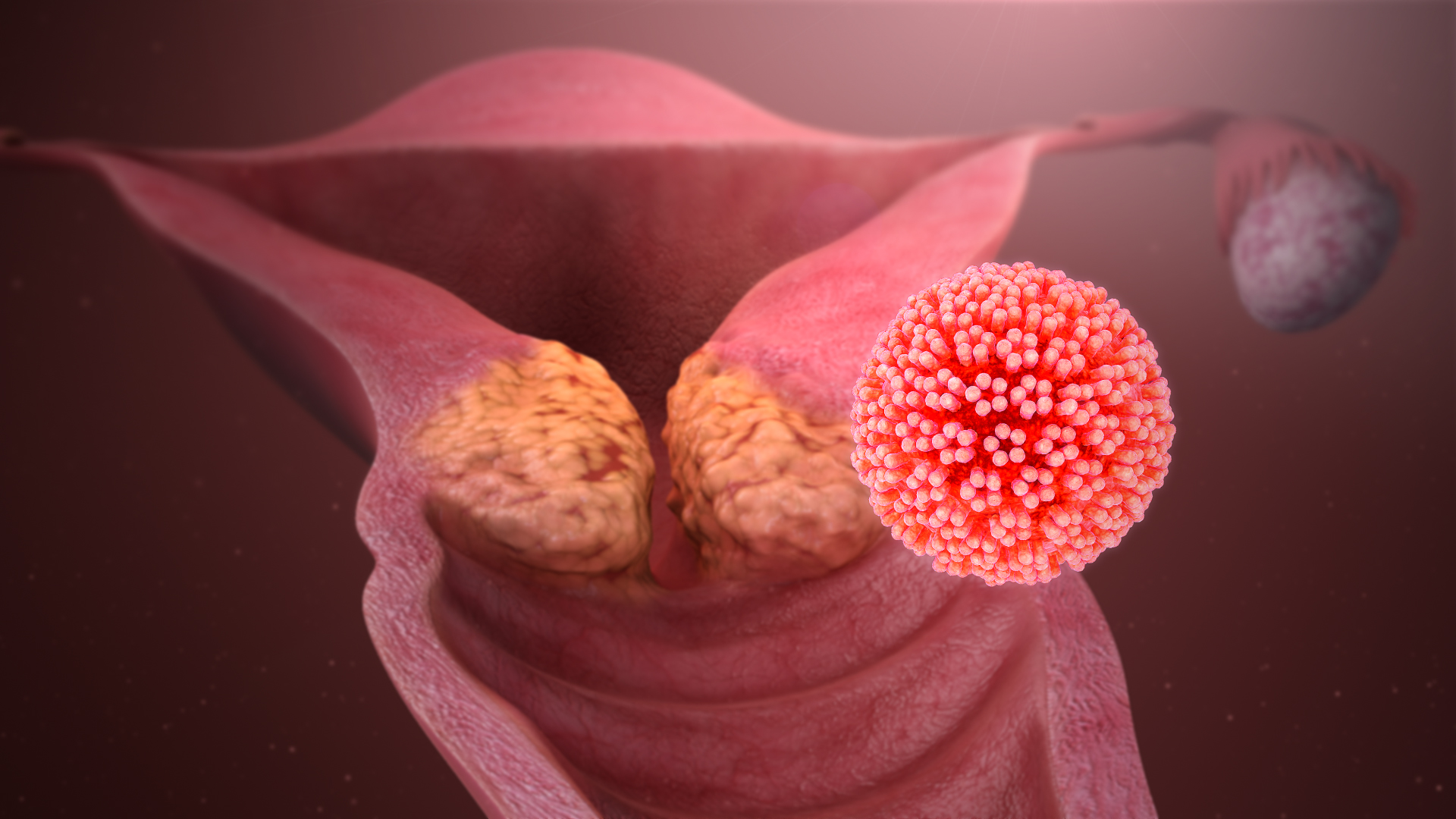
Human Papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and results in either warts or precancerous lesions. These lesions, depending on the site affected, increase the risk of cancer of the cervix, vulva, vagina, penis, anus, mouth, tonsils, or throat. Nearly all cervical cancer is due to HPV and two strains – HPV16 and HPV18 – account for 70% of cases. HPV16 is responsible for almost 90% of HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers. Between 60% and 90% of the other cancers listed above are also linked to HPV. HPV6 and HPV11 are common causes of genital warts and laryngeal papillomatosis. An HPV infection is caused by ''human papillomavirus'', a DNA virus from the papillomavirus family. Over 170 types have been described. An individual can become infected with more than one type of HPV, and the dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HPV Vaccine
Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccines are vaccines that prevent infection by certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV). Available HPV vaccines protect against either two, four, or nine types of HPV. All HPV vaccines protect against at least HPV types 16 and 18, which cause the greatest risk of cervical cancer. It is estimated that HPV vaccines may prevent 70% of cervical cancer, 80% of anal cancer, 60% of vaginal cancer, 40% of vulvar cancer, and show more than 90% efficacy in preventing HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers. They additionally prevent some genital warts, with the quadrivalent and nonavalent vaccines that protect against HPV types HPV-6 and HPV-11 providing greater protection. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends HPV vaccines as part of routine vaccinations in all countries, along with other prevention measures. The vaccines require two or three doses depending on a person's age and immune status. Vaccinating girls around the ages of nine to thirteen i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, Prescription drug, prescription and Over-the-counter drug, over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, Animal feed, animal foods & feed and Veterinary medicine, veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C), but the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act, as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is not d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)