|
Vacuum Level
In physics, the vacuum level refers to the energy of a free stationary electron that is outside of any material (it is in a perfect vacuum). It may be taken as infinitely far away from a solid, or, defined to be near a surface. Its definition and measurement are often discussed in UPS literature, for example As the vacuum level is a property of the electron and free space, it is often used as the level of alignment for the energy levels of two different materials. The vacuum level alignment approach may or may not hold due to details of the interface. It is particularly important in the design of vacuum device components such as cathodes. If defined as being close to a surface, then the vacuum level is typically not a constant due to the equilibrium electric fields in vacuum. The value of the vacuum level depends on the surface chosen due to variations in work function. The phrase "vacuum level" also occurs often in texts on squeezed light where it refers to an unsqueezed measureme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family, and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no known components or substructure. The electron's mass is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton. Quantum mechanical properties of the electron include an intrinsic angular momentum ( spin) of a half-integer value, expressed in units of the reduced Planck constant, . Being fermions, no two electrons can occupy the same quantum state, in accordance with the Pauli exclusion principle. Like all elementary particles, electrons exhibit properties of both particles and waves: They can collide with other particles and can be diffracted like light. The wave properties of electrons are easier to observe with experiments than those of other particles like neutrons and protons because electrons have a lower mass and hence a longer de Broglie wavele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or "void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often discuss ideal test results that would occur in a ''perfect'' vacuum, which they sometimes simply call "vacuum" or free space, and use the term partial vacuum to refer to an actual imperfect vacuum as one might have in a laboratory or in space. In engineering and applied physics on the other hand, vacuum refers to any space in which the pressure is considerably lower than atmospheric pressure. The Latin term ''in vacuo'' is used to describe an object that is surrounded by a vacuum. The ''quality'' of a partial vacuum refers to how closely it approaches a perfect vacuum. Other things equal, lower gas pressure means higher-quality vacuum. For example, a typical vacuum cleaner produces enough suction to reduce air pressure by around 20%. But hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet Photoelectron Spectroscopy
Ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy (UPS) refers to the measurement of kinetic energy spectra of photoelectrons emitted by molecules which have absorbed ultraviolet photons, in order to determine molecular orbital energies in the valence region. Basic theory If Albert Einstein's photoelectric law is applied to a free molecule, the kinetic energy ( E_K) of an emitted photoelectron is given by : E_K = h\nu - I\,, where ''h'' is Planck's constant, ν is the frequency of the ionizing light, and I is an ionization energy for the formation of a singly charged ion in either the ground state or an excited state. According to Koopmans' theorem, each such ionization energy may be identified with the energy of an occupied molecular orbital. The ground-state ion is formed by removal of an electron from the highest occupied molecular orbital, while excited ions are formed by removal of an electron from a lower occupied orbital. History Prior to 1960, virtually all measurements of photoel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Space
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or "void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often discuss ideal test results that would occur in a ''perfect'' vacuum, which they sometimes simply call "vacuum" or free space, and use the term partial vacuum to refer to an actual imperfect vacuum as one might have in a laboratory or in space. In engineering and applied physics on the other hand, vacuum refers to any space in which the pressure is considerably lower than atmospheric pressure. The Latin term ''in vacuo'' is used to describe an object that is surrounded by a vacuum. The ''quality'' of a partial vacuum refers to how closely it approaches a perfect vacuum. Other things equal, lower gas pressure means higher-quality vacuum. For example, a typical vacuum cleaner produces enough suction to reduce air pressure by around 20%. But high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Level
A quantum mechanical system or particle that is bound—that is, confined spatially—can only take on certain discrete values of energy, called energy levels. This contrasts with classical particles, which can have any amount of energy. The term is commonly used for the energy levels of the electrons in atoms, ions, or molecules, which are bound by the electric field of the nucleus, but can also refer to energy levels of nuclei or vibrational or rotational energy levels in molecules. The energy spectrum of a system with such discrete energy levels is said to be quantized. In chemistry and atomic physics, an electron shell, or principal energy level, may be thought of as the orbit of one or more electrons around an atom's nucleus. The closest shell to the nucleus is called the " shell" (also called "K shell"), followed by the " shell" (or "L shell"), then the " shell" (or "M shell"), and so on farther and farther from the nucleus. The shells correspond with the principal quan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Work Function
In solid-state physics, the work function (sometimes spelt workfunction) is the minimum thermodynamic work (i.e., energy) needed to remove an electron from a solid to a point in the vacuum immediately outside the solid surface. Here "immediately" means that the final electron position is far from the surface on the atomic scale, but still too close to the solid to be influenced by ambient electric fields in the vacuum. The work function is not a characteristic of a bulk material, but rather a property of the surface of the material (depending on crystal face and contamination). Definition The work function for a given surface is defined by the difference :W = -e\phi - E_, where is the charge of an electron, is the electrostatic potential in the vacuum nearby the surface, and is the Fermi level (electrochemical potential of electrons) inside the material. The term is the energy of an electron at rest in the vacuum nearby the surface. In practice, one directly controls by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
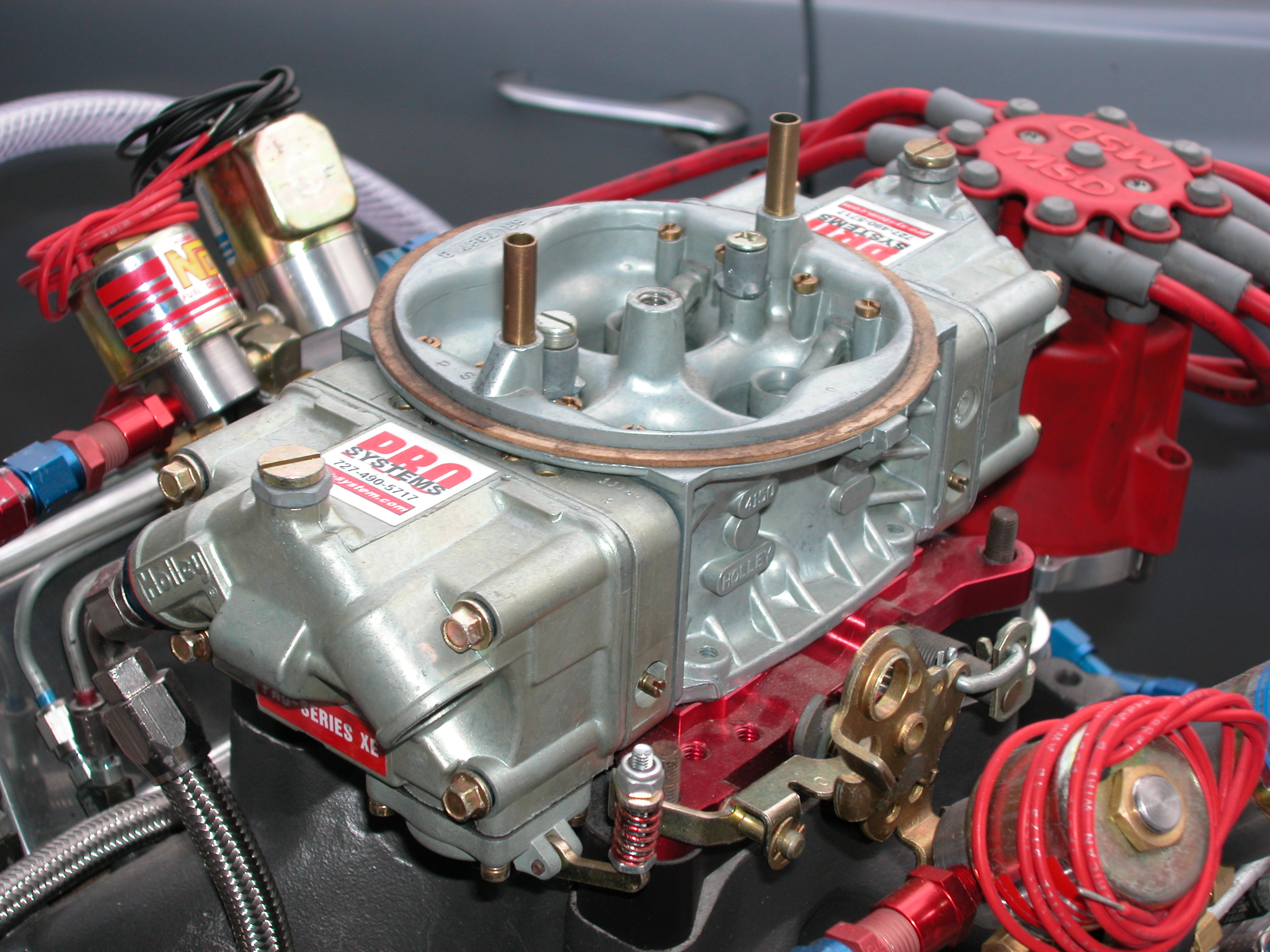
Carburetor
A carburetor (also spelled carburettor) is a device used by an internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. The primary method of adding fuel to the intake air is through the venturi tube in the main metering circuit, however various other components are also used to provide extra fuel or air in specific circumstances. Since the 1990s, carburetors have been largely replaced by fuel injection for cars and trucks, however carburetors are still used by some small engines (e.g. lawnmowers, generators and concrete mixers) and motorcycles. Diesel engines have always used fuel injection instead of carburetors. Etymology The name "carburetor" is derived from the verb ''carburet'', which means "to combine with carbon," or in particular, "to enrich a gas by combining it with carbon or hydrocarbons." Thus a carburetor mixes intake air with hydrocarbon-based fuel, such as petrol or autogas (LPG). The name is spelled "carburetor" in American English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |