|
Vicious Cycle
A vicious circle (or cycle) is a complex chain of events that reinforces itself through a feedback loop, with detrimental results. It is a system with no tendency toward equilibrium (social, economic, ecological, etc.), at least in the short run. Each iteration of the cycle reinforces the previous one, in an example of positive feedback. A vicious circle will continue in the direction of its momentum until an external factor intervenes to break the cycle. A well-known example of a vicious circle in economics is hyperinflation. A virtuous circle is an equivalent system with a favorable outcome. Examples Vicious circles in the subprime mortgage crisis The contemporary subprime mortgage crisis is a complex group of vicious circles, both in its genesis and in its manifold outcomes, most notably the late 2000s recession. A specific example is the circle related to housing. As housing prices decline, more homeowners go " underwater", when the market value of a home drops below ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
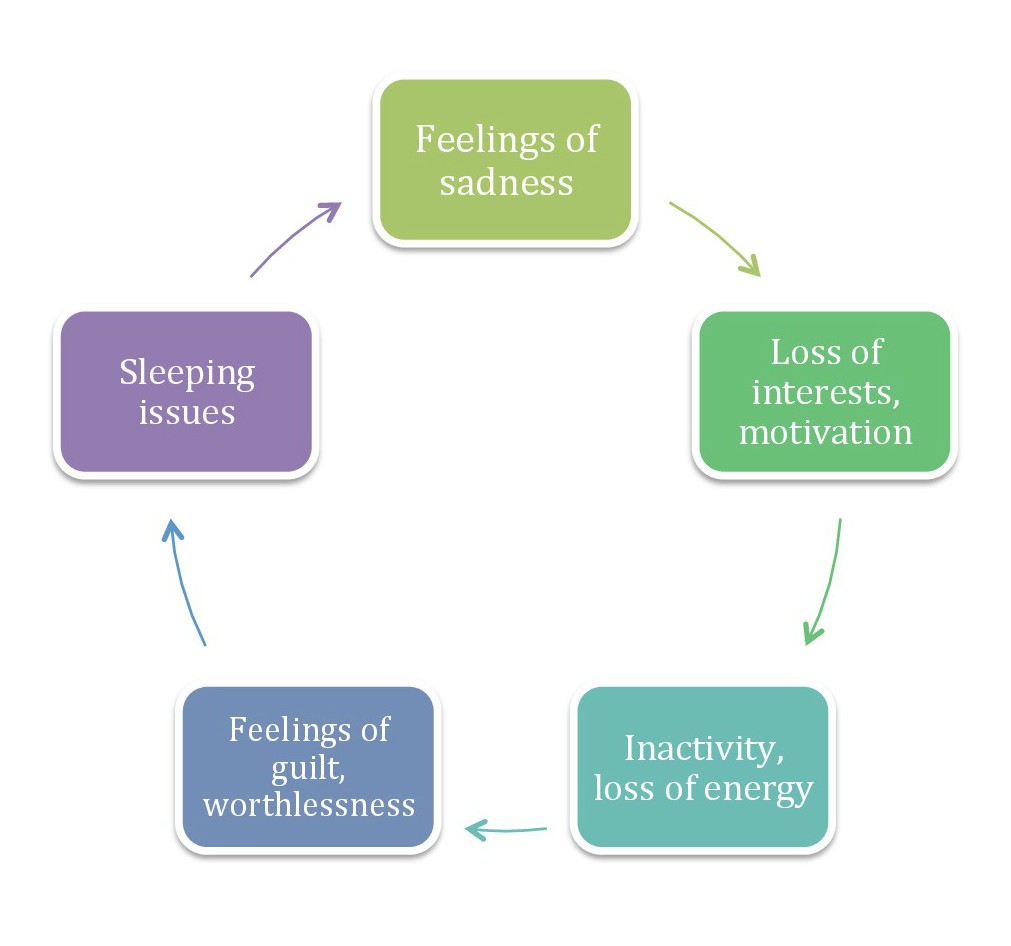
Cycle Of Depression
Cycle, cycles, or cyclic may refer to: Anthropology and social sciences * Cyclic history, a theory of history * Cyclical theory, a theory of American political history associated with Arthur Schlesinger, Sr. * Social cycle, various cycles in social sciences ** Business cycle, the downward and upward movement of gross domestic product (GDP) around its ostensible, long-term growth trend Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Cycle'' (2008 film), a Malayalam film * ''Cycle'' (2017 film), a Marathi film Literature * ''Cycle'' (magazine), an American motorcycling enthusiast magazine * Literary cycle, a group of stories focused on common figures Music Musical terminology * Cycle (music), a set of musical pieces that belong together **Cyclic form, a technique of construction involving multiple sections or movements **Interval cycle, a collection of pitch classes generated from a sequence of the same interval class **Song cycle, individually complete songs designed to be perfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poverty Cycle
In economics, a cycle of poverty or poverty trap is caused by self-reinforcing mechanisms that cause poverty, once it exists, to persist unless there is outside intervention. It can persist across generations, and when applied to developing countries, is also known as a development trap. Families trapped in the cycle of poverty have few to no resources. There are many self-reinforcing disadvantages that make it virtually impossible for individuals to break the cycle. This occurs when poor people do not have the resources necessary to escape poverty, such as financial capital, education, or connections. Impoverished individuals do not have access to economic and social resources as a result of their poverty. This lack may increase their poverty. This could mean that the poor remain poor throughout their lives.Hutchinson Encycloped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflexivity (sociology)
In epistemology, and more specifically, the sociology of knowledge, reflexivity refers to circular relationships between cause and effect, especially as embedded in human belief structures. A reflexive relationship is bidirectional with both the cause and the effect affecting one another in a relationship in which neither can be assigned as causes or effects. Within sociology more broadly—the field of origin—reflexivity means an act of self-reference where examination or action "bends back on", refers to, and affects the entity instigating the action or examination. It commonly refers to the capacity of an agent to recognise forces of socialisation and alter their place in the social structure. A low level of reflexivity would result in individuals shaped largely by their environment (or "society"). A high level of social reflexivity would be defined by individuals shaping ''their own'' norms, tastes, politics, desires, and so on. This is similar to the notion of autonomy. (S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rational Addiction
In behavioral economics, rational addiction is the hypothesis that addictions can be usefully modeled as specific kinds of rational, forward-looking, optimal consumption plans. The canonical theory comes from work done by Kevin M. Murphy and Gary Becker.Becker, Gary S., and Kevin M. Murphy (1988) "A Theory of Rational Addiction." ''Journal of Political Economy'' 96 (4): 675–700. https://doi.org/10.1086/261558. Economic theory Though controversial, this theoretical approach has become "one of the standard models in the literature on addictive behavior" in economics,Ferguson, Brian S. (2000) "Interpreting the rational addiction model". ''Health Economics'', Vol. 9: Iss. 7, pp. 587-598 and a variety of extensions and modifications have been developed and published by other authors over the years. A survey of researchers who had authored or co-authored peer-reviewed articles on rational addiction theory indicates that the researchers see the theories as successful in a number of wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop which exacerbates the effects of a small disturbance. That is, the effects of a perturbation on a system include an increase in the magnitude of the perturbation. That is, ''A produces more of B which in turn produces more of A''.Keesing, R.M. (1981). Cultural anthropology: A contemporary perspective (2nd ed.) p.149. Sydney: Holt, Rinehard & Winston, Inc. In contrast, a system in which the results of a change act to reduce or counteract it has negative feedback. Both concepts play an important role in science and engineering, including biology, chemistry, and cybernetics. Mathematically, positive feedback is defined as a positive loop gain around a closed loop of cause and effect. That is, positive feedback is in phase with the input, in the sense that it adds to make the input larger. Positive feedback tends to cause system instability. When the loop gain is p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endogeneity (econometrics)
In econometrics, endogeneity broadly refers to situations in which an explanatory variable is correlated with the error term. The distinction between endogenous and exogenous variables originated in simultaneous equations models, where one separates variables whose values are determined by the model from variables which are predetermined; ignoring simultaneity in the estimation leads to biased estimates as it violates the exogeneity assumption of the Gauss–Markov theorem. The problem of endogeneity is often ignored by researchers conducting non-experimental research and doing so precludes making policy recommendations. Instrumental variable techniques are commonly used to address this problem. Besides simultaneity, correlation between explanatory variables and the error term can arise when an unobserved or omitted variable is confounding both independent and dependent variables, or when independent variables are measured with error. Exogeneity versus endogeneity In a st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closed Timelike Curve
In mathematical physics, a closed timelike curve (CTC) is a world line in a Lorentzian manifold, of a material particle in spacetime, that is "closed", returning to its starting point. This possibility was first discovered by Willem Jacob van Stockum in 1937 and later confirmed by Kurt Gödel in 1949,Stephen Hawking, ''My Brief History'', chapter 11 who discovered a solution to the equations of general relativity (GR) allowing CTCs known as the Gödel metric; and since then other GR solutions containing CTCs have been found, such as the Tipler cylinder and traversable wormholes. If CTCs exist, their existence would seem to imply at least the theoretical possibility of time travel backwards in time, raising the spectre of the grandfather paradox, although the Novikov self-consistency principle seems to show that such paradoxes could be avoided. Some physicists speculate that the CTCs which appear in certain GR solutions might be ruled out by a future theory of quantum gravity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycle Of Violence
The term cycle of violence refers to repeated and dangerous acts of violence as a cyclical pattern,''The cycle of violence.'' Domestic Violence and Abuse, Signs of Abuse and Abusive Relationships. HELPGUIDE.org. Retrieved November 21, 2011. associated with high emotions and doctrines of or . The pattern, or cycle, repeats and can happen many times during a relationship. Each phase may last a different length of time, and over time the level of violence may increase. The phrase has been increasingly wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycle Of Poverty
In economics, a cycle of poverty or poverty trap is caused by self-reinforcing cycle, self-reinforcing mechanisms that cause poverty, once it exists, to persist unless there is outside intervention. It can persist across generations, and when applied to developing countries, is also known as a development trap. Families trapped in the cycle of poverty have few to no resources. There are many feedback loop, self-reinforcing disadvantaged, disadvantages that make it virtually impossible for individuals to break the cycle. This occurs when poverty, poor people do not have the resources necessary to escape poverty, such as financial capital, education, or connections. Impoverished individuals do not have access to economic and social resources as a result of their poverty. This lack may increase their poverty. This could mean that the poor remain poor throughout their lives. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chain Reaction
A chain reaction is a sequence of reactions where a reactive product or by-product causes additional reactions to take place. In a chain reaction, positive feedback leads to a self-amplifying chain of events. Chain reactions are one way that systems which are not in thermodynamic equilibrium can release energy or increase entropy in order to reach a state of higher entropy. For example, a system may not be able to reach a lower energy state by releasing energy into the environment, because it is hindered or prevented in some way from taking the path that will result in the energy release. If a reaction results in a small energy release making way for more energy releases in an expanding chain, then the system will typically collapse explosively until much or all of the stored energy has been released. A macroscopic metaphor for chain reactions is thus a snowball causing a larger snowball until finally an avalanche results (" snowball effect"). This is a result of stored gravit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
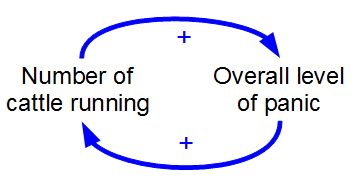
Causal Loop Diagram
A causal loop diagram (CLD) is a causal diagram that aids in visualizing how different variables in a system are causally interrelated. The diagram consists of a set of words and arrows. Causal loop diagrams are accompanied by a narrative which describes the causally closed situation the CLD describes. Closed loops, or causal feedback loops, in the diagram are very important features of CLDs. The words with arrows coming in and out represent variables, or quantities whose value changes over time and the links represent a causal relationship between the two variables (i.e., they do not represent a material flow). A link marked + indicates a positive relation where an increase in the causal variable leads, all else equal, to an increase in the effect variable, or a decrease in the causal variable leads, all else equal, to a decrease in the effect variable. A link marked - indicates a negative relation where an increase in the causal variable leads, all else equal, to a decrease in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catch-22 (logic)
A catch-22 is a paradoxical situation from which an individual cannot escape because of contradictory rules or limitations. The term was coined by Joseph Heller, who used it in his 1961 novel ''Catch-22''. An example is Brantley Foster in '' The Secret of My Success'': "How can I get any experience until I get a job that me experience?" Catch-22s often result from rules, regulations, or procedures that an individual is subject to, but has no control over, because to fight the rule is to accept it. Another example is a situation in which someone is in need of something that can only be had by not being in need of it (e.g. the only way to qualify for a loan is to prove to the bank that you do not need a loan). One connotation of the term is that the creators of the "catch-22" situation have created arbitrary rules in order to justify and conceal their own abuse of power. Origin and meaning Joseph Heller coined the term in his 1961 novel ''Catch-22'', which describes absurd bureau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |