|
Viable Count
Viable count is a method used in cell culture to determine the number of living cells in a culture. This is different from other cell counting, cell counting techniques because it makes a distinction between live and dead cells. Method A dilution of the cells to be counted is prepared and mixed with Trypan blue, this is normally the stain of choice because it is taken up by dead cells and actively excluded from live cells. Once the cells have been stained they are counted using a Hemocytometer, then a calculation is carried out to determine the original concentration of live cells. Use in Cell Culture Determining the viable cell count is important for calculating dilutions required for the subculture_(biology), passaging of cells, as well as determining the size and number of flasks needed during growth time. It is also vital when seeding plates for assays, such as the plaque assay, because the plates need a known number of live replicating cells for the virus to attach to and rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Culture
Cell culture or tissue culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. The term "tissue culture" was coined by American pathologist Montrose Thomas Burrows. This technique is also called micropropagation. After the cells of interest have been isolated from living tissue, they can subsequently be maintained under carefully controlled conditions the need to be kept at body temperature (37 °C) in an incubator. These conditions vary for each cell type, but generally consist of a suitable vessel with a substrate or rich medium that supplies the essential nutrients (amino acids, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals), growth factors, hormones, and gases ( CO2, O2), and regulates the physio-chemical environment (pH buffer, osmotic pressure, temperature). Most cells require a surface or an artificial substrate to form an adherent culture as a monolayer (one single-cell thick), whereas others can be grown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Counting
Cell counting is any of various methods for the counting or similar quantification of cells in the life sciences, including medical diagnosis and treatment. It is an important subset of cytometry, with applications in research and clinical practice. For example, the complete blood count can help a physician to determine why a patient feels unwell and what to do to help. Cell counts within liquid media (such as blood, plasma, lymph, or laboratory rinsate) are usually expressed as a number of cells per unit of volume, thus expressing a concentration (for example, 5,000 cells per milliliter). Uses Numerous procedures in biology and medicine require the counting of cells. By the counting of cells in a known small volume, the concentration can be mediated. Examples of the need for cell counting include: * In medicine, the concentration of various blood cells, such as red blood cells and white blood cells, can give crucial information regarding the health situation of a person (see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
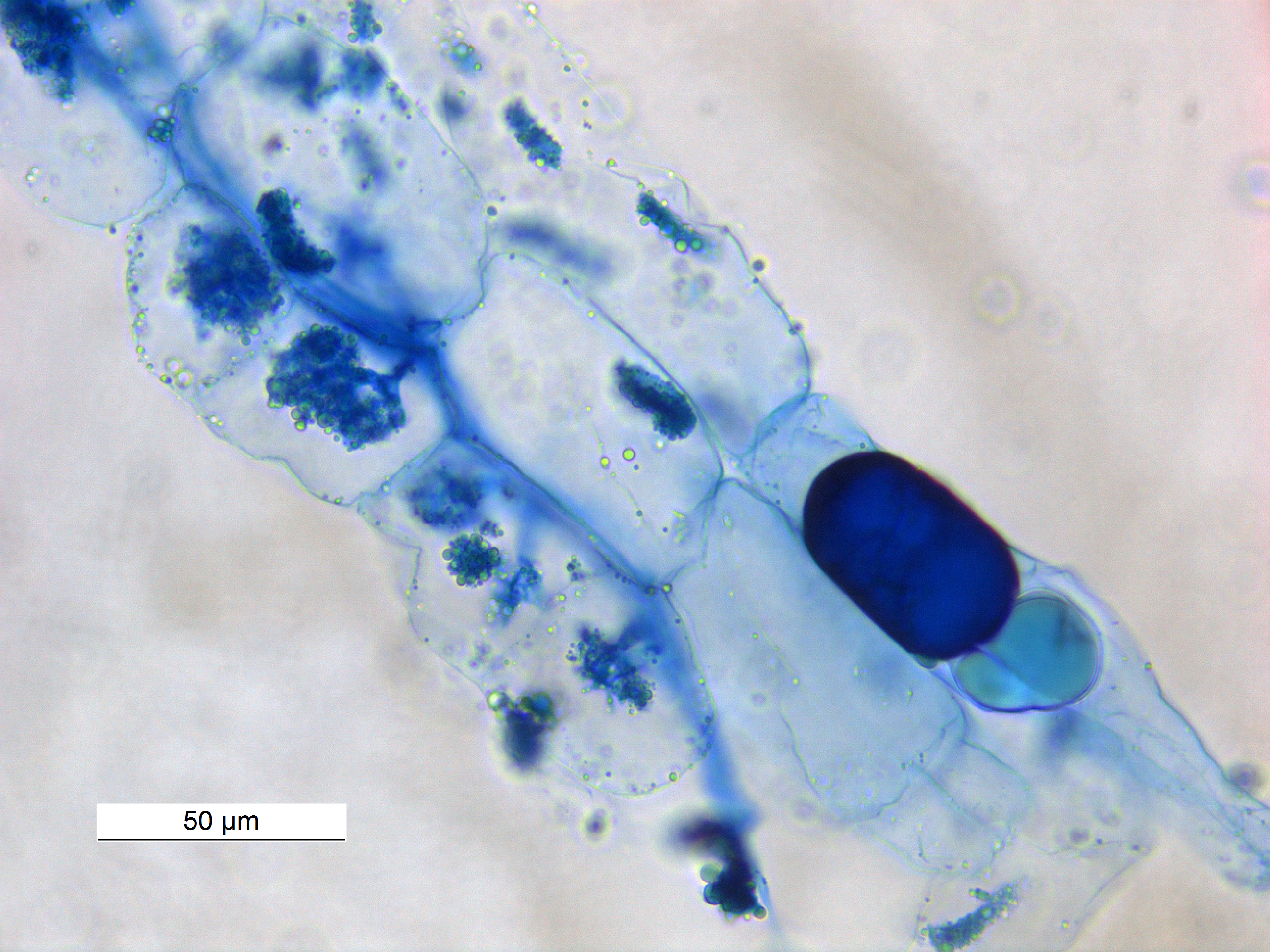
Trypan Blue
Trypan blue is an azo dye. It is a direct dye for cotton textiles. In biosciences, it is used as a vital stain to selectively colour dead tissues or cells blue. Live cells or tissues with intact cell membranes are not coloured. Since cells are very selective in the compounds that pass through the membrane, in a viable cell trypan blue is not absorbed; however, it traverses the membrane in a dead cell. Hence, dead cells appear as a distinctive blue colour under a microscope. Since live cells are excluded from staining, this staining method is also described as a dye exclusion method. Background and chemistry Trypan blue is derived from toluidine, that is, any of several isomeric bases, C14H16N2, derived from toluene. Trypan blue is so-called because it can kill trypanosomes, the parasites that cause sleeping sickness. An analog of trypan blue, suramin, is used pharmacologically against trypanosomiasis. Trypan blue is also known as diamine blue and Niagara blue. The extinctio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemocytometer
The hemocytometer (or haemocytometer) is a counting-chamber device originally designed and usually used for counting blood cells. The hemocytometer was invented by Louis-Charles Malassez and consists of a thick glass microscope slide with a rectangular indentation that creates a precision volume chamber. This chamber is engraved with a laser-etched grid of perpendicular lines. The device is carefully crafted so that the area bounded by the lines is known, and the depth of the chamber is also known. By observing a defined area of the grid, it is therefore possible to count the number of cells or particles in a specific volume of fluid, and thereby calculate the concentration of cells in the fluid overall. A well used type of hemocytometer is the ''Neubauer'' counting chamber. Other types of hemocytometers with different rulings are in use for different applications. Fuchs-Rosenthal rulings, commonly used for spinal fluid counting, Howard Mold rulings used for mold on food and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subculture (biology)
In biology, a subculture is either a new cell culture or a microbiological culture made by transferring some or all cells from a previous culture to fresh growth medium. This action is called subculturing or passaging the cells. Subculturing is used to prolong the lifespan and/or increase the number of cells or microorganisms in the culture. Role Cell lines and microorganisms cannot be held in culture indefinitely due to the gradual rise in toxic metabolites, use of nutrients and increase in cell number due to growth. Once nutrients are depleted and levels of toxic byproducts increase, the bacteria in the overnight culture enter the stationary phase, where proliferation is greatly reduced or ceased (the cell density value plateaus). When microorganisms from this overnight culture are transferred into the fresh media, nutrients trigger the growth of the microorganism and it goes through the lag phase, a period of slow growth and adaptation to the new environment, and then the log p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
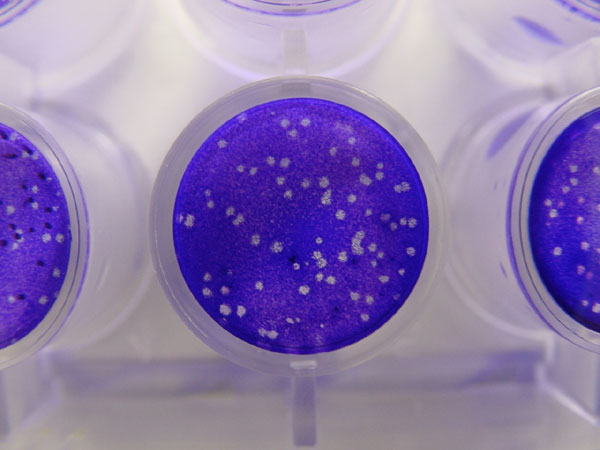
Plaque Assay
Virus quantification involves counting the number of viruses in a specific volume to determine the virus concentration. It is used in both research and development (R&D) in commercial and academic laboratories as well as production situations where the quantity of virus at various steps is an important variable. For example, the production of viral vaccines, recombinant proteins using viral vectors and viral antigens all require virus quantification to continually adapt and monitor the process in order to optimize production yields and respond to ever changing demands and applications. Examples of specific instances where known viruses need to be quantified include clone screening, multiplicity of infection (MOI) optimization and adaptation of methods to cell culture. This page discusses various techniques currently used to quantify viruses in liquid samples. These methods are separated into two categories, traditional vs. modern methods. Traditional methods are industry-stand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |