|
Vesicouterine Fistula
Vesicouterine fistula refers to an abnormal communication between the bladder and uterus. The first case of vesicouterine fistula was reported in 1908. It was however first described in 1957 by Abdel Fattah Youssef, an obstetrician and gynaecologist in Kasr el-Aini hospital, Cairo, Egypt. It is characterized by a vesicouterine fistula above the level of the internal os, absence of menstrual bleeding, cyclical presence of blood in urine and absence of urinary incontinence with a patent cervical canal following a lower segment caesarean section. Six of such cases had been reported by other clinicians before the term Menouria was coined by Youssef. Pathology Vesicouterine fistula is the least common type of urogenital fistula accounting for 1-4% of urogenital fistulas. It occurs following lower segment caesarean section and the incidence is increasing due to the increasing incidence of caesarean deliveries. The occurrence of menoruria in the absence of vaginal bleeding or passage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urogynaecology
Urogynecology or urogynaecology is a surgical sub-specialty of urology and gynecology. History In 1893, Howard Kelly, a gynecologist and pioneering urogynecologist, invented an air cystoscope which was simply a handheld, hollow tube with a glass partition. When the American Surgical Society, later the American College of Surgeons, met in Baltimore in 1900, a contest was held between Howard Kelly and Hugh Hampton Young, who is often considered the father of modern urology. Using his air cystoscope, Kelly inserted ureteral catheters in a female patient in just 3 minutes. Young equaled this time in a male patient. Young HH. A Surgeon's Autobiography. New York: Harcourt, 1940. So began the friendly competitive rivalry between gynecologists and urologists in the area of female urology and urogynecology. This friendly competition continued for decades. In modern times, the mutual interest of obstetricians, gynecologists, and urologists in pelvic floor problems in women has led to a more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachytherapy
Brachytherapy is a form of radiation therapy where a sealed radiation source is placed inside or next to the area requiring treatment. ''Brachy'' is Greek for short. Brachytherapy is commonly used as an effective treatment for cervical, prostate, breast, esophageal and skin cancer and can also be used to treat tumours in many other body sites. Treatment results have demonstrated that the cancer-cure rates of brachytherapy are either comparable to surgery and external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) or are improved when used in combination with these techniques. Brachytherapy can be used alone or in combination with other therapies such as surgery, EBRT and chemotherapy. Brachytherapy contrasts with unsealed source radiotherapy, in which a therapeutic radionuclide (radioisotope) is injected into the body to chemically localize to the tissue requiring destruction. It also contrasts to External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT), in which high-energy x-rays (or occasionally gamma-rays from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
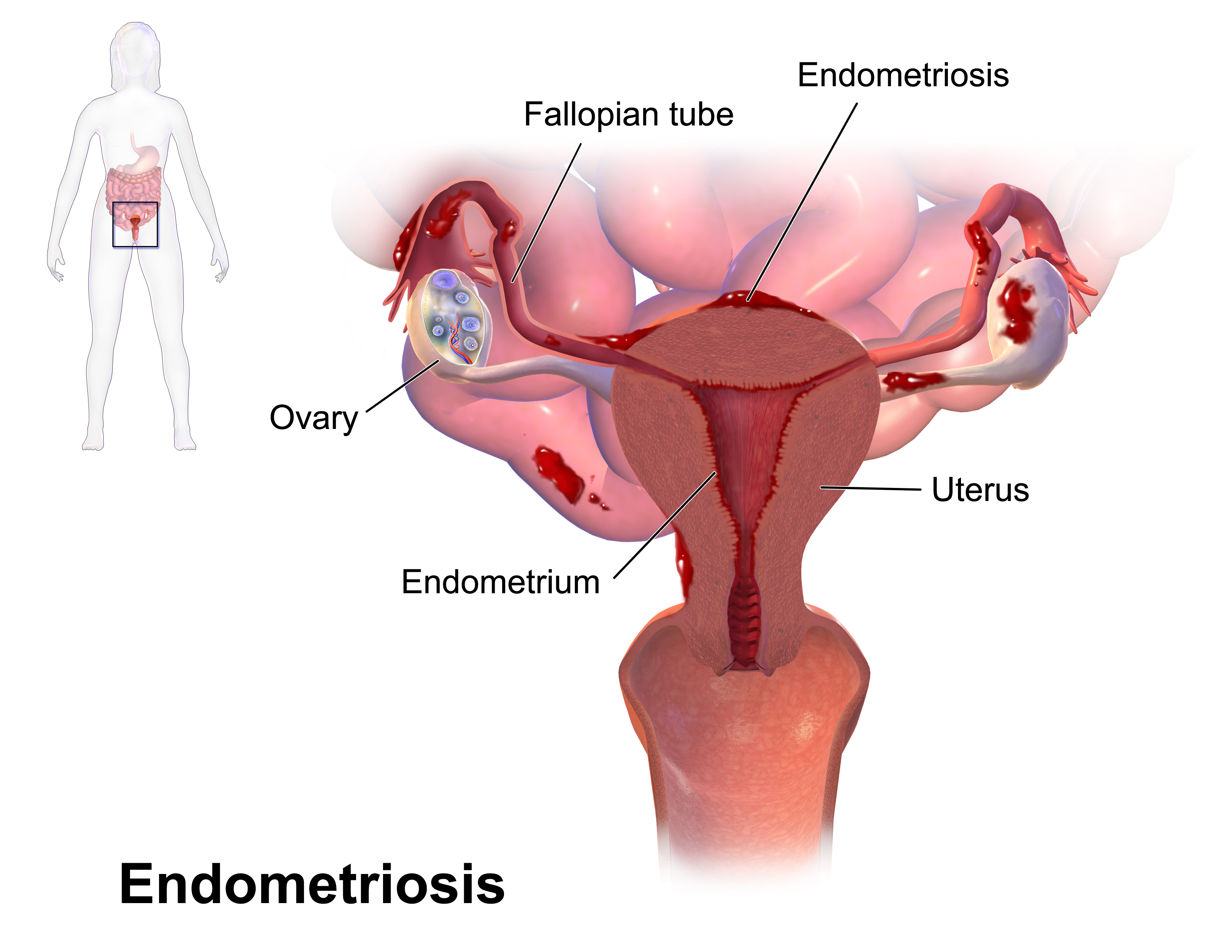
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a disease of the female reproductive system in which cells similar to those in the endometrium, the layer of tissue that normally covers the inside of the uterus, grow outside the uterus. Most often this is on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and tissue around the uterus and ovaries; in rare cases it may also occur in other parts of the body. Some symptoms include pelvic pain, heavy periods, pain with bowel movements, and infertility. Nearly half of those affected have chronic pelvic pain, while in 70% pain occurs during menstruation. Pain during sexual intercourse is also common. Infertility occurs in up to half of affected individuals. About 25% of individuals have no symptoms and 85% of those seen with infertility in a tertiary center have no pain. Endometriosis can have both social and psychological effects. The cause is not entirely clear. Risk factors include having a family history of the condition. The areas of endometriosis bleed each month (menstrua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiofrequency Ablation
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA), also called fulguration, is a medical procedure in which part of the electrical conduction system of the heart, tumor or other dysfunctional tissue is ablated using the heat generated from medium frequency alternating current (in the range of 350–500 kHz). RFA is generally conducted in the outpatient setting, using either local anesthetics or conscious sedation anesthesia. When it is delivered via catheter, it is called radiofrequency catheter ablation. Two important advantages of radio frequency current (over previously used low frequency AC or pulses of DC) are that it does not directly stimulate nerves or heart muscle and therefore can often be used without the need for general anesthesia, and that it is very specific for treating the desired tissue without significant collateral damage; due to this, it is gaining in popularity as an alternative for eligible patients who do not want to undergo surgery. Documented benefits have led to RFA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catheterize
In medicine, a catheter (/ˈkæθətər/) is a thin tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. Catheters are manufactured for specific applications, such as cardiovascular, urological, gastrointestinal, neurovascular and ophthalmic procedures. The process of inserting a catheter is ''catheterization''. In most uses, a catheter is a thin, flexible tube (''soft'' catheter) though catheters are available in varying levels of stiffness depending on the application. A catheter left inside the body, either temporarily or permanently, may be referred to as an "indwelling catheter" (for example, a peripherally inserted central catheter). A permanently inserted catheter may be referred to as a "permcath" (originally a trademark). Catheters can be inserted into a body cavity, duct, or vessel, brain, skin or adipose tissue. Functionally, they all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy () is an operation performed in the abdomen or pelvis using small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) with the aid of a camera. The laparoscope aids diagnosis or therapeutic interventions with a few small cuts in the abdomen.MedlinePlus > Laparoscopy Update Date: 21 August 2009. Updated by: James Lee, MD // No longer valid Laparoscopic surgery, also called minimally invasive procedure, bandaid surgery, or keyhole surgery, is a modern surgical technique. There are a number of advantages to the patient with laparoscopic surgery versus an exploratory laparotomy. These include reduced pain due to smaller incisions, reduced hemorrhaging, and shorter recovery time. The key element is the use of a laparoscope, a long fiber optic cable system that allows viewing of the affected area by snaking the cable from a more distant, but more easily accessible location. Laparoscopic surgery includes operations within the abdominal or pelvic cavities, whereas keyhole surgery perform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progesterone (medication)
Progesterone (P4) is a medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone. It is a progestogen and is used in combination with estrogens mainly in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and low sex hormone levels in women. It is also used in women to support pregnancy and fertility and to treat gynecological disorders. Progesterone can be taken by mouth, in through the vagina, and by injection into muscle or fat, among other routes. A progesterone vaginal ring and progesterone intrauterine device used for birth control also exist in some areas of the world. Progesterone is well tolerated and often produces few or no side effects. However, a number of side effects are possible, for instance mood changes. If progesterone is taken by mouth or at high doses, certain central side effects including sedation, sleepiness, and cognitive impairment can also occur. The medication is a naturally occurring progestogen and hence is an agonist of the progesterone receptor (PR), t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Contraceptive Pill
Oral contraceptives, abbreviated OCPs, also known as birth control pills, are medications taken by mouth for the purpose of birth control. Female Two types of female oral contraceptive pill, taken once per day, are widely available: * The combined oral contraceptive pill contains estrogen and a progestin. Colloquially known as "The Pill". * The progestogen-only pill, colloquially known as "minipill". * Ormeloxifene is a selective estrogen receptor modulator which offers the benefit of only having to be taken once a week. Emergency contraception pills ("morning after pills") are taken at the time of intercourse, or within a few days afterwards: * Levonorgestrel, sold under the brand name Plan B * Ulipristal acetate * Mifepristone and misoprostol, when used in combination, are more than 95% effective during the first 50 days of pregnancy. Male * Male oral contraceptive Male contraceptives, also known as male birth control, are methods of preventing pregnancy that solely invol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watchful Waiting
Watchful waiting (also watch and wait or WAW) is an approach to a medical problem in which time is allowed to pass before medical intervention or therapy is used. During this time, repeated testing may be performed. Related terms include ''expectant management'', ''active surveillance'', and ''masterly inactivity''. The term ''masterly inactivity'' is also used in nonmedical contexts. A distinction can be drawn between ''watchful waiting'' and ''medical observation'', but some sources equate the terms. Usually, watchful waiting is an outpatient process and may have a duration of months or years. In contrast, medical observation is usually an inpatient process, often involving frequent or even continuous monitoring and may have a duration of hours or days. Medical uses Often watchful waiting is recommended in situations with a high likelihood of self-resolution if there is high uncertainty concerning the diagnosis, and the risks of intervention or therapy may outweigh the benefit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold Standard (test)
In medicine and statistics, a gold standard test is usually the diagnostic test or benchmark that is the best available under reasonable conditions. In other words, a gold standard is the most accurate test possible without restrictions. Both meanings are different because for example, in medicine, dealing with conditions that would require an autopsy to have a perfect diagnosis, the gold standard test would be the best one that keeps the patient alive instead of the autopsy. In medicine "Gold standard" can refer to the criteria by which scientific evidence is evaluated. For example, in resuscitation research, the "gold standard" test of a medication or procedure is whether or not it leads to an increase in the number of neurologically intact survivors that walk out of the hospital.''ACLS: Principles and Practice''. p. 62. Dallas: American Heart Association, 2003. . Other types of medical research might regard a significant decrease in 30-day mortality as the gold standard. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computerised Tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry to measure X-ray attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, it can also be used to form images of non-living objects. The 1979 Nob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from CT and PET scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft-tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, though "Open" MRI designs mostly relieve this. Additionally, implants and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |