|
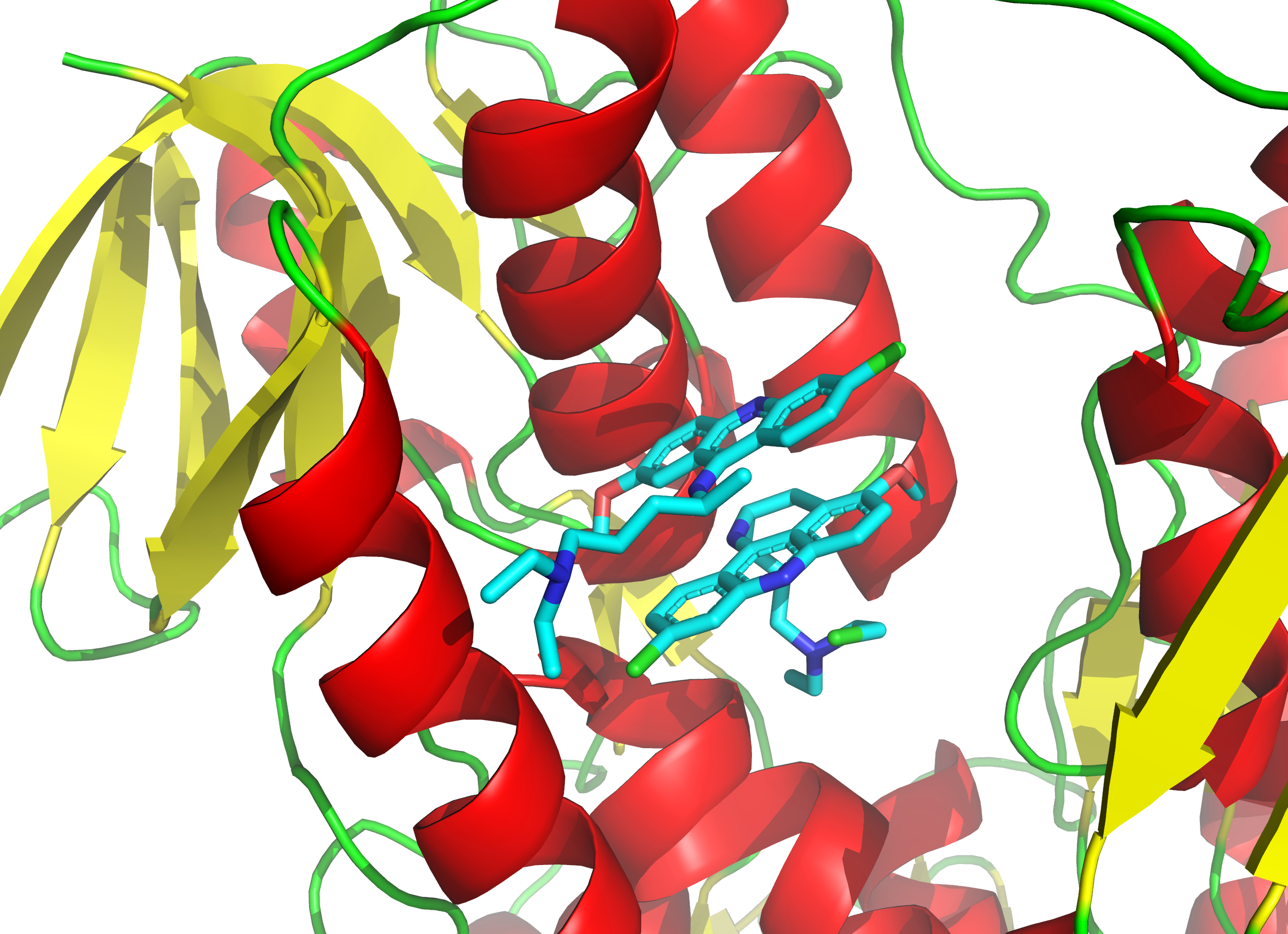
Verubecestat
Verubecestat (MK-8931) was an experimental drug for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. It is an inhibitor of beta-secretase 1 (BACE1), which, after initial promise proved disappointing. In April 2012 phase I clinical results were announced. Phase 1b results have also been reported. it was in two phase 2/3 clinical trials that have progressed to phase 3. EPOCH, was to complete data collection for the primary outcome measure by June 2017. However, in February 2017 Merck halted its late-stage trial of verubecestat for mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease after it was reported as having "virtually no chance of finding a positive clinical effect" according to an independent panel of experts. The results of Merck's trial of verubecestat on patients with prodromal In medicine, a prodrome is an early sign or symptom (or set of signs and symptoms) that often indicates the onset of a disease before more diagnostically specific signs and symptoms develop. It is derived from the Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-secretase 1
Beta-secretase 1, also known as beta-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1, beta-site APP cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1), membrane-associated aspartic protease 2, memapsin-2, aspartyl protease 2, and ASP2, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''BACE1'' gene. Expression of BACE1 is observed mainly in neurons. BACE1 is an aspartic acid protease important in the formation of myelin sheaths in peripheral nerve cells: in mice the expression of BACE1 is high in the postnatal stages, when myelination occurs. * The transmembrane protein contains two active site aspartate residues in its extracellular protein domain and may function as a dimer, its cytoplasmic tail is required for the correct maturation and an efficient intracellular trafficking, but doesn't affect the activity. It is produced as a pro-enzyme, the endoproteolitc removal occurs after BACE leaves Endoplasmic reticulum, in the Golgi apparatus. In addition the pro-peptide receives additional sugars to increase t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term memory, remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include primary progressive aphasia, problems with language, Orientation (mental), disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and challenging behaviour, behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the typical life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years. The cause of Alzheimer's disease is poorly understood. There are many environmental and genetic risk factors associated with its development. The strongest genetic risk factor is from an alle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many famous scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it. In print since 1845, it is the oldest continuously published magazine in the United States. ''Scientific American'' is owned by Springer Nature, which in turn is a subsidiary of Holtzbrinck Publishing Group. History ''Scientific American'' was founded by inventor and publisher Rufus Porter (painter), Rufus Porter in 1845 as a four-page weekly newspaper. The first issue of the large format newspaper was released August 28, 1845. Throughout its early years, much emphasis was placed on reports of what was going on at the United States Patent and Trademark Office, U.S. Patent Office. It also reported on a broad range of inventions including perpetual motion machines, an 1860 device for buoying vessels by Abraham Lincoln, and the universal joint which now can be found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme Inhibitor
An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and blocks its activity. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions necessary for life, in which substrate molecules are converted into products. An enzyme facilitates a specific chemical reaction by binding the substrate to its active site, a specialized area on the enzyme that accelerates the most difficult step of the reaction. An enzyme inhibitor stops ("inhibits") this process, either by binding to the enzyme's active site (thus preventing the substrate itself from binding) or by binding to another site on the enzyme such that the enzyme's catalysis of the reaction is blocked. Enzyme inhibitors may bind reversibly or irreversibly. Irreversible inhibitors form a chemical bond with the enzyme such that the enzyme is inhibited until the chemical bond is broken. By contrast, reversible inhibitors bind non-covalently and may spontaneously leave the enzyme, allowing the enzyme to resume its function. Reve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Endpoint
Clinical endpoints or clinical outcomes are outcome measures referring to occurrence of disease, symptom, sign or laboratory abnormality constituting a target outcome in clinical research trials. The term may also refer to any disease or sign that strongly motivates withdrawal of an individual or entity from the trial, then often termed a ''humane (clinical) endpoint''. The primary endpoint of a clinical trial is the endpoint for which the trial is powered. Secondary endpoints are additional endpoints, preferably also pre-specified, for which the trial may not be powered. Surrogate endpoints are trial endpoints that have outcomes that substitute for a clinical endpoint, often because studying the clinical endpoint is difficult, for example using an increase in blood pressure as a surrogate for death by cardiovascular disease, where strong evidence of a causal link exists. Scope In a general sense, a clinical endpoint is included in the entities of interest in a trial. The resu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prodromal
In medicine, a prodrome is an early sign or symptom (or set of signs and symptoms) that often indicates the onset of a disease before more diagnostically specific signs and symptoms develop. It is derived from the Greek word ''prodromos'', meaning "running before". Prodromes may be non-specific symptoms or, in a few instances, may clearly indicate a particular disease, such as the prodromal migraine aura. For example, fever, malaise, headache and lack of appetite frequently occur in the prodrome of many infective disorders. A prodrome can be the early precursor to an episode of a chronic neurological disorder such as a migraine headache or an epileptic seizure, where prodrome symptoms may include euphoria or other changes in mood, insomnia, abdominal sensations, disorientation, aphasia, or photosensitivity. Such a prodrome occurs on a scale of days to an hour before the episode, where an aura occurs more immediate to it. Prodromal labour, mistakenly called "false labour," refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme Inhibitors
An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and blocks its activity. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions necessary for life, in which substrate molecules are converted into products. An enzyme facilitates a specific chemical reaction by binding the substrate to its active site, a specialized area on the enzyme that accelerates the most difficult step of the reaction. An enzyme inhibitor stops ("inhibits") this process, either by binding to the enzyme's active site (thus preventing the substrate itself from binding) or by binding to another site on the enzyme such that the enzyme's catalysis of the reaction is blocked. Enzyme inhibitors may bind reversibly or irreversibly. Irreversible inhibitors form a chemical bond with the enzyme such that the enzyme is inhibited until the chemical bond is broken. By contrast, reversible inhibitors bind non-covalently and may spontaneously leave the enzyme, allowing the enzyme to resume its function. Reve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |