|
Vertex Figures
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a general -polytope is sliced off. Definitions Take some corner or vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connected edge. Draw lines across the connected faces, joining adjacent points around the face. When done, these lines form a complete circuit, i.e. a polygon, around the vertex. This polygon is the vertex figure. More precise formal definitions can vary quite widely, according to circumstance. For example Coxeter (e.g. 1948, 1954) varies his definition as convenient for the current area of discussion. Most of the following definitions of a vertex figure apply equally well to infinite tilings or, by extension, to space-filling tessellation with polytope cells and other higher-dimensional polytopes. As a flat slice Make a slice through the corner of the polyhedron, cutting through all the edges connected to the vertex. The cut surface is the vertex figure (a plane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-polytope
In geometry, a 4-polytope (sometimes also called a polychoron, polycell, or polyhedroid) is a four-dimensional polytope. It is a connected and closed figure, composed of lower-dimensional polytopal elements: Vertex (geometry), vertices, Edge (geometry), edges, Face (geometry), faces (polygons), and Cell (mathematics), cells (Polyhedron, polyhedra). Each face is shared by exactly two cells. The 4-polytopes were discovered by the Swiss mathematician Ludwig Schläfli before 1853. The two-dimensional analogue of a 4-polytope is a polygon, and the three-dimensional analogue is a polyhedron. Topologically 4-polytopes are closely related to the Convex uniform honeycomb, uniform honeycombs, such as the cubic honeycomb, which tessellate 3-space; similarly the 3D cube is related to the infinite 2D square tiling. Convex 4-polytopes can be ''cut and unfolded'' as polyhedral net, nets in 3-space. Definition A 4-polytope is a closed Four-dimensional space, four-dimensional figure. It compr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schläfli Symbol
In geometry, the Schläfli symbol is a notation of the form \ that defines List of regular polytopes and compounds, regular polytopes and tessellations. The Schläfli symbol is named after the 19th-century Swiss mathematician Ludwig Schläfli, who generalized Euclidean space, Euclidean geometry to more than three dimensions and discovered all their convex regular polytopes, including the six that occur in four dimensions. Definition The Schläfli symbol is a Recursive definition, recursive description, starting with \ for a p-sided regular polygon that is Convex set, convex. For example, is an equilateral triangle, is a Square (geometry), square, a convex regular pentagon, etc. Regular star polygons are not convex, and their Schläfli symbols \ contain irreducible fractions p/q, where p is the number of vertices, and q is their turning number. Equivalently, \ is created from the vertices of \, connected every q. For example, \ is a pentagram; \ is a pentagon. A regular pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Icosahedron Vertfig
Great may refer to: Descriptions or measurements * Great, a relative measurement in physical space, see Size * Greatness, being divine, majestic, superior, majestic, or transcendent People * List of people known as "the Great" * Artel Great (born 1981), American actor * Great Osobor (born 2002), Spanish-born British basketball player Other uses * ''Great'' (1975 film), a British animated short about Isambard Kingdom Brunel * ''Great'' (2013 film), a German short film * Great (supermarket), a supermarket in Hong Kong * GReAT, Graph Rewriting and Transformation, a Model Transformation Language * Gang Resistance Education and Training Gang Resistance Education And Training, abbreviated G.R.E.A.T., provides a school-based, police officer-instructed program in America that includes classroom instruction and a variety of learning activities. The program was originally adminis ..., or GREAT, a school-based and police officer-instructed program * Global Research and Analysis Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual Polyhedron
In geometry, every polyhedron is associated with a second dual structure, where the vertices of one correspond to the faces of the other, and the edges between pairs of vertices of one correspond to the edges between pairs of faces of the other. Such dual figures remain combinatorial or abstract polyhedra, but not all can also be constructed as geometric polyhedra. Starting with any given polyhedron, the dual of its dual is the original polyhedron. Duality preserves the symmetries of a polyhedron. Therefore, for many classes of polyhedra defined by their symmetries, the duals belong to a corresponding symmetry class. For example, the regular polyhedrathe (convex) Platonic solids and (star) Kepler–Poinsot polyhedraform dual pairs, where the regular tetrahedron is self-dual. The dual of an isogonal polyhedron (one in which any two vertices are equivalent under symmetries of the polyhedron) is an isohedral polyhedron (one in which any two faces are equivalent .., and vice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Face (geometry)
In solid geometry, a face is a flat surface (a Plane (geometry), planar region (mathematics), region) that forms part of the boundary of a solid object. For example, a cube has six faces in this sense. In more modern treatments of the geometry of polyhedra and higher-dimensional polytopes, a "face" is defined in such a way that it may have any dimension. The vertices, edges, and (2-dimensional) faces of a polyhedron are all faces in this more general sense. Polygonal face In elementary geometry, a face is a polygon on the boundary of a polyhedron. (Here a "polygon" should be viewed as including the 2-dimensional region inside it.) Other names for a polygonal face include polyhedron side and Euclidean plane ''tessellation, tile''. For example, any of the six square (geometry), squares that bound a cube is a face of the cube. Sometimes "face" is also used to refer to the 2-dimensional features of a 4-polytope. With this meaning, the 4-dimensional tesseract has 24 square faces, each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph Theory
In mathematics and computer science, graph theory is the study of ''graph (discrete mathematics), graphs'', which are mathematical structures used to model pairwise relations between objects. A graph in this context is made up of ''Vertex (graph theory), vertices'' (also called ''nodes'' or ''points'') which are connected by ''Glossary of graph theory terms#edge, edges'' (also called ''arcs'', ''links'' or ''lines''). A distinction is made between undirected graphs, where edges link two vertices symmetrically, and directed graphs, where edges link two vertices asymmetrically. Graphs are one of the principal objects of study in discrete mathematics. Definitions Definitions in graph theory vary. The following are some of the more basic ways of defining graphs and related mathematical structures. Graph In one restricted but very common sense of the term, a graph is an ordered pair G=(V,E) comprising: * V, a Set (mathematics), set of vertices (also called nodes or points); * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertex (geometry)
In geometry, a vertex (: vertices or vertexes), also called a corner, is a point (geometry), point where two or more curves, line (geometry), lines, or line segments Tangency, meet or Intersection (geometry), intersect. For example, the point where two lines meet to form an angle and the point where edge (geometry), edges of polygons and polyhedron, polyhedra meet are vertices. Definition Of an angle The ''vertex'' of an angle is the point where two Line (mathematics)#Ray, rays begin or meet, where two line segments join or meet, where two lines intersect (cross), or any appropriate combination of rays, segments, and lines that result in two straight "sides" meeting at one place. :(3 vols.): (vol. 1), (vol. 2), (vol. 3). Of a polytope A vertex is a corner point of a polygon, polyhedron, or other higher-dimensional polytope, formed by the intersection (Euclidean geometry), intersection of Edge (geometry), edges, face (geometry), faces or facets of the object. In a polygon, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperplane
In geometry, a hyperplane is a generalization of a two-dimensional plane in three-dimensional space to mathematical spaces of arbitrary dimension. Like a plane in space, a hyperplane is a flat hypersurface, a subspace whose dimension is one less than that of the ambient space. Two lower-dimensional examples of hyperplanes are one-dimensional lines in a plane and zero-dimensional points on a line. Most commonly, the ambient space is -dimensional Euclidean space, in which case the hyperplanes are the -dimensional "flats", each of which separates the space into two half spaces. A reflection across a hyperplane is a kind of motion ( geometric transformation preserving distance between points), and the group of all motions is generated by the reflections. A convex polytope is the intersection of half-spaces. In non-Euclidean geometry, the ambient space might be the -dimensional sphere or hyperbolic space, or more generally a pseudo-Riemannian space form, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
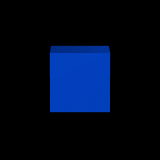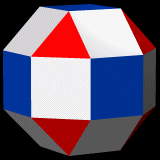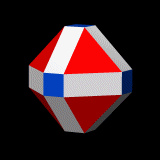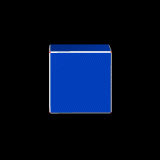
Rhombicuboctahedron
In geometry, the rhombicuboctahedron is an Archimedean solid with 26 faces, consisting of 8 equilateral triangles and 18 squares. It was named by Johannes Kepler in his 1618 Harmonices Mundi, being short for ''truncated cuboctahedral rhombus'', with cuboctahedral rhombus being his name for a rhombic dodecahedron. The rhombicuboctahedron is an Archimedean solid, and its dual is a Catalan solid, the deltoidal icositetrahedron. The elongated square gyrobicupola is a polyhedron that is similar to a rhombicuboctahedron, but it is not an Archimedean solid because it is not vertex-transitive. The rhombicuboctahedron is found in diverse cultures in architecture, toys, the arts, and elsewhere. Construction The rhombicuboctahedron may be constructed from a cube by drawing a smaller one in the middle of each face, parallel to the cube's edges. After removing the edges of a cube, the squares may be joined by adding more squares adjacent between them, and the corners may be filled by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertex Configuration
In geometry, a vertex configuration is a shorthand notation for representing a polyhedron or Tessellation, tiling as the sequence of Face (geometry), faces around a Vertex (geometry), vertex. It has variously been called a vertex description, vertex type, vertex symbol, vertex arrangement, vertex pattern, face-vector, vertex sequence. It is also called a Cundy and Rollett symbol for its usage for the Archimedean solids in their 1952 book ''Mathematical Models (Cundy and Rollett), Mathematical Models''.Laughlin (2014), p. 16 For uniform polyhedron, uniform polyhedra, there is only one vertex type and therefore the vertex configuration fully defines the polyhedron. (Chirality (mathematics), Chiral polyhedra exist in mirror-image pairs with the same vertex configuration.) For example, "" indicates a vertex belonging to 4 faces, alternating triangles and pentagons. This vertex configuration defines the vertex-transitive icosidodecahedron. The notation is cyclic and therefore is equival ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |