|
Verteporfin
Verteporfin (trade name Visudyne), a benzoporphyrin derivative, is a medication used as a photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy to eliminate the abnormal blood vessels in the eye associated with conditions such as the wet form of macular degeneration. Verteporfin accumulates in these abnormal blood vessels and, when stimulated by nonthermal red light with a wavelength of 689 nm in the presence of oxygen, produces highly reactive short-lived singlet oxygen and other reactive oxygen radicals, resulting in local damage to the endothelium and blockage of the vessels.Verteporfin Verteporfin is also used off-label for the treatment of central serous retinopathy. Administration Verteporfin is usually injected intravenously into the largest arm vein. It is injected at a dose of 6 mg/m2 and light-activated. It is usually is given 15 minutes before laser treatment. This dose can be repeated 4 times per year. Contraindications Porphyria. Side effects Most common side effec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photodynamic Therapy
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a form of phototherapy involving light and a photosensitizing chemical substance, used in conjunction with molecular oxygen to elicit cell death (phototoxicity). PDT is popularly used in treating acne. It is used clinically to treat a wide range of medical conditions, including wet age-related macular degeneration, psoriasis, atherosclerosis and has shown some efficacy in anti-viral treatments, including herpes. It also treats malignant cancers including head and neck, lung, bladder and particular skin. The technology has also been tested for treatment of prostate cancer, both in a dog model and in human prostate cancer patients. It is recognised as a treatment strategy that is both minimally invasive and minimally toxic. Other light-based and laser therapies such as laser wound healing and rejuvenation, or intense pulsed light hair removal do not require a photosensitizer. Photosensitisers have been employed to sterilise blood plasma and wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzoporphyrin
Porphyrins ( ) are a group of heterocyclic macrocycle organic compounds, composed of four modified pyrrole subunits interconnected at their α carbon atoms via methine bridges (=CH−). The parent of porphyrin is porphine, a rare chemical compound of exclusively theoretical interest. Substituted porphines are called porphyrins. With a total of 26 π-electrons, of which 18 π-electrons form a planar, continuous cycle, the porphyrin ring structure is often described as aromatic. One result of the large conjugated system is that porphyrins typically absorb strongly in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum, i.e. they are deeply colored. The name "porphyrin" derives from the Greek word πορφύρα (''porphyra''), meaning ''purple''. Complexes of porphyrins Concomitant with the displacement of two N-''H'' protons, porphyrins bind metal ions in the N4 "pocket". The metal ion usually has a charge of 2+ or 3+. A schematic equation for these syntheses is shown: :H2porphyr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous Therapy
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water by mouth. It may also be used to administer medications or other medical therapy such as blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route of administration is also used for the consump ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Serous Retinopathy
Central serous chorioretinopathy (CSC or CSCR), also known as central serous retinopathy (CSR), is an eye disease that causes visual impairment, often temporary, usually in one eye. When the disorder is active it is characterized by leakage of fluid under the retina that has a propensity to accumulate under the central macula. This results in blurred or distorted vision (metamorphopsia). A blurred or gray spot in the central visual field is common when the retina is detached. Reduced visual acuity may persist after the fluid has disappeared. The disease is considered of unknown cause. It mostly affects white males in the age group 20 to 50 (male:female ratio 6:1) and occasionally other groups. The condition is believed to be exacerbated by stress or corticosteroid use. Pathophysiology Recently, central serous chorioretinopathy has been understood to be part of the pachychoroid spectrum. In pachychoroid spectrum disorders, of which CSR represents stage II, the choroid, the hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosensitizing Agents
Photosensitizers produce a physicochemical change in a neighboring molecule by either donating an electron to the substrate or by abstracting a hydrogen atom from the substrate. At the end of this process, the photosensitizer eventually returns to its ground state, where it remains chemically intact until the photosensitizer absorbs more light. This means that the photosensitizer remains unchanged before and after the energetic exchange, much like heterogeneous photocatalysis. One branch of chemistry which frequently utilizes photosensitizers is polymer chemistry, using photosensitizers in reactions such as photopolymerization, photocrosslinking, and photodegradation. Photosensitizers are also used to generate prolonged excited electronic states in organic molecules with uses in photocatalysis, photon upconversion and photodynamic therapy. Generally, photosensitizers absorb electromagnetic radiation consisting of infrared radiation, visible light radiation, and ultraviolet radiat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dupuytren's Contracture
Dupuytren's contracture (also called Dupuytren's disease, Morbus Dupuytren, Viking disease, palmar fibromatosis and Celtic hand) is a condition in which one or more fingers become progressively bent in a flexed position. It is named after Guillaume Dupuytren, who first described the underlying mechanism of action, followed by the first successful operation in 1831 and publication of the results in ''The Lancet'' in 1834. It usually begins as small, hard nodules just under the skin of the palm, then worsens over time until the fingers can no longer be fully straightened. While typically not painful, some aching or itching may be present. The ring finger followed by the little and middle fingers are most commonly affected. It can affect one or both hands. The condition can interfere with activities such as preparing food, writing, putting the hand in a tight pocket, putting on gloves, or shaking hands. The cause is unknown but might have a genetic component. Risk factors include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholestasis
Cholestasis is a condition where bile cannot flow from the liver to the duodenum. The two basic distinctions are an obstructive type of cholestasis where there is a mechanical blockage in the duct system that can occur from a gallstone or malignancy, and metabolic types of cholestasis which are disturbances in bile formation that can occur because of genetic defects or acquired as a side effect of many medications. Classification is further divided into acute or chronic and extrahepatic or intrahepatic. Signs and symptoms The signs and symptoms of cholestasis vary according to the cause. In case of sudden onset, the disease is likely to be acute, while the gradual appearance of symptoms suggests chronic pathology. In many cases, patients may experience pain in the abdominal area. Localization of pain to the upper right quadrant can be indicative of cholecystitis or choledocholithiasis, which can progress to cholestasis. Pruritus or itching is often present in many patients with c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) are a Protein superfamily, superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor that functions as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are important for the clearance (pharmacology), clearance of various compounds, as well as for hormone synthesis and breakdown. In 1963, Ronald W. Estabrook, Estabrook, David Y. Cooper, Cooper, and Otto Rosenthal, Rosenthal described the role of CYP as a catalyst in steroid hormone synthesis and drug metabolism. In plants, these proteins are important for the biosynthesis of secondary metabolite, defensive compounds, fatty acids, and hormones. CYP enzymes have been identified in all kingdom (biology), kingdoms of life: animals, plants, fungus, fungi, protists, bacteria, and archaea, as well as in viruses. However, they are not omnipresent; for example, they have not been found in ''Escherichia coli''. , more than 300,000 distinct CYP proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanacetum Parthenium
''Tanacetum parthenium'', known as feverfew, is a flowering plant in the daisy family, Asteraceae. It may be grown as an ornament, and may be identified by its synonyms, ''Chrysanthemum parthenium'' and ''Pyrethrum parthenium''. Description The plant is a herbaceous perennial that grows into a small bush, up to high, with pungently-scented leaves. The leaves are light yellowish green, variously pinnatifid. The conspicuous daisy-like flowers are up to across, borne in lax corymbs. The outer, ray florets have white ligules and the inner, disc florets are yellow and tubular. It spreads rapidly by seed, and will cover a wide area after a few years. Distribution and cultivation Feverfew is native to Eurasia, specifically the Balkan Peninsula, Anatolia, and the Caucasus, but cultivation has spread it around the world and the rest of Europe, North America, and Chile. A perennial herb, it should be planted in full sun, apart, and cut back to the ground in the autumn. It grows u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
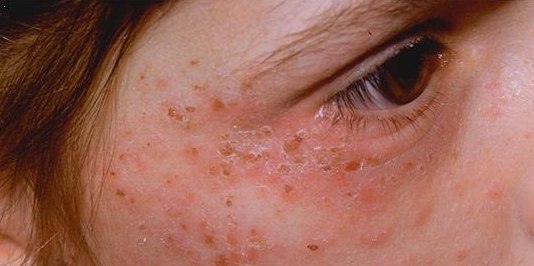
Photosensitivity
Photosensitivity is the amount to which an object reacts upon receiving photons, especially visible light. In medicine, the term is principally used for abnormal reactions of the skin, and two types are distinguished, photoallergy and phototoxicity. The photosensitive ganglion cells in the mammalian eye are a separate class of light-detecting cells from the photoreceptor cells that function in vision. Skin reactions Human medicine Sensitivity of the skin to a light source can take various forms. People with particular skin types are more sensitive to sunburn. Particular medications make the skin more sensitive to sunlight; these include most of the tetracycline antibiotics, heart drugs amiodarone, and sulfonamides. Some dietary supplements, such as St. John's Wort, include photosensitivity as a possible side effect. Particular conditions lead to increased light sensitivity. Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus experience skin symptoms after sunlight exposure; some types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyria
Porphyria is a group of liver disorders in which substances called porphyrins build up in the body, negatively affecting the skin or nervous system. The types that affect the nervous system are also known as acute porphyria, as symptoms are rapid in onset and short in duration. Symptoms of an attack include abdominal pain, chest pain, vomiting, confusion, constipation, fever, high blood pressure, and high heart rate. The attacks usually last for days to weeks. Complications may include paralysis, low blood sodium levels, and seizures. Attacks may be triggered by alcohol, smoking, hormonal changes, fasting, stress, or certain medications. If the skin is affected, blisters or itching may occur with sunlight exposure. Most types of porphyria are inherited from one or both of a person's parents and are due to a mutation in one of the genes that make heme. They may be inherited in an autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, or X-linked dominant manner. One type, ''porphyria c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous Therapy
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water by mouth. It may also be used to administer medications or other medical therapy such as blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route of administration is also used for the consump ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)