|
Vernix
Vernix caseosa, also known as vernix or birthing custard, is the waxy white substance found coating the skin of newborn human babies. It is produced by dedicated cells and is thought to have some protective roles during fetal development and for a few hours after birth. Etymology In Latin, ''vernix'' means ''varnish'' and ''caseosa'' means ''cheesy''. The term was first published in 1846 in the ''Dunglison Dictionary of Medical Sciences''. In-utero development Vernix is produced during a distinct phase of the epidermal development. Around the 21st week of gestation, periderm cells are being shed and replaced with stratum corneum; these shedding mix with secretions of sebum by the sebaceous glands to form vernix, which gradually covers the body in an anteroposterior and dorsoventral pattern. Vernix, in itself, is also believed to aid in the formation of stratum corneum. By early third trimester, the process is complete. Soon enough, part of the vernix is emulsified by increasin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanugo
Lanugo is very thin, soft, usually unpigmented, downy hair that is sometimes found on the body of a fetus or newborn. It is the first hair to be produced by the fetal hair follicles, and it usually appears around sixteen weeks of gestation and is abundant by week twenty. It is normally shed before birth, around seven or eight months of gestation, but is sometimes present at birth. It disappears on its own within a few weeks. It is replaced by hair covering the same surfaces, which is called vellus hair. This hair is thinner and more difficult to see. The more visible hair that persists into adulthood is called terminal hair. It forms in specific areas and is hormone-dependent. The term is from the Latin ''lana'', meaning "wool." Humans Fetal development During human development, the lanugo grows on fetuses as a normal part of gestation, but it is usually shed and replaced by vellus hair at about thirty-three to thirty-six weeks of gestational age. As the lanugo is shed from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
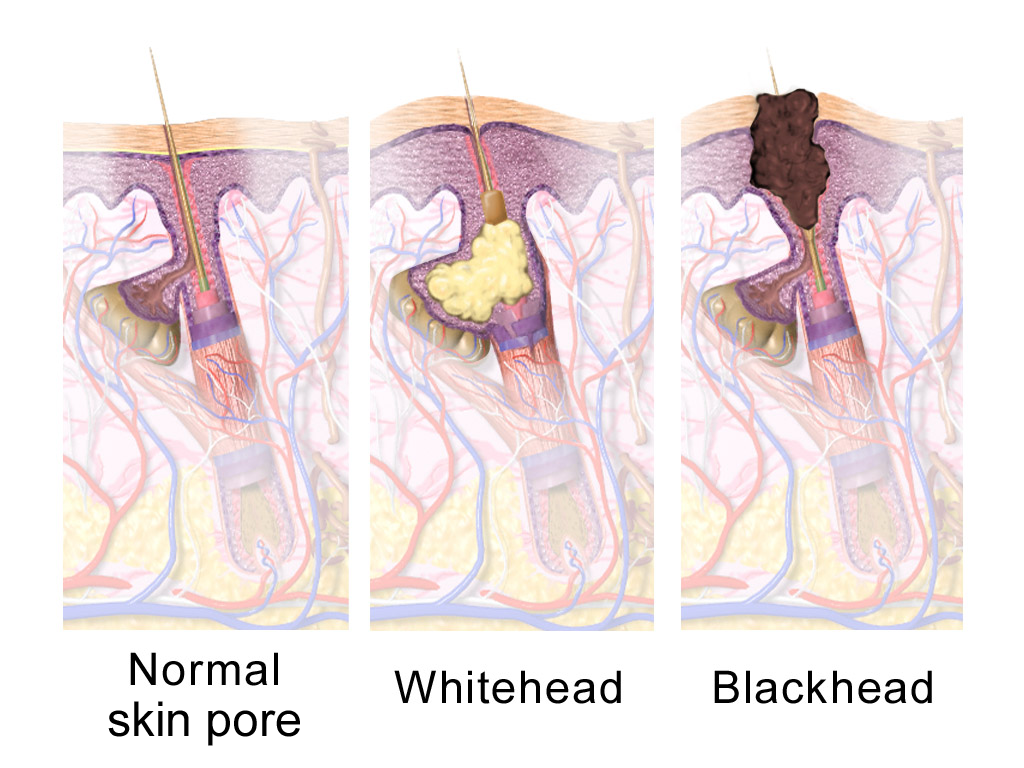
Sebum
A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest number on the face and scalp, but also on all parts of the skin except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. In the eyelids, meibomian glands, also called tarsal glands, are a type of sebaceous gland that secrete a special type of sebum into tears. Surrounding the female nipple, areolar glands are specialized sebaceous glands for lubricating the nipple. Fordyce spots are benign, visible, sebaceous glands found usually on the lips, gums and inner cheeks, and genitals. Structure Location Sebaceous glands are found throughout all areas of the skin, except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There are two types of sebaceous glands, those connected to hair follicles and those that exist independently. Sebaceous glands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebaceous Gland
A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest number on the face and scalp, but also on all parts of the skin except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. In the eyelids, meibomian glands, also called tarsal glands, are a type of sebaceous gland that secrete a special type of sebum into tears. Surrounding the female nipple, areolar glands are specialized sebaceous glands for lubricating the nipple. Fordyce spots are benign, visible, sebaceous glands found usually on the lips, gums and inner cheeks, and genitals. Structure Location Sebaceous glands are found throughout all areas of the skin, except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There are two types of sebaceous glands, those connected to hair follicles and those that exist independently. Sebaceous glands are found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceramide
Ceramides are a family of waxy lipid molecules. A ceramide is composed of N-acetylsphingosine and a fatty acid. Ceramides are found in high concentrations within the cell membrane of eukaryotic cells, since they are component lipids that make up sphingomyelin, one of the major lipids in the lipid bilayer. Contrary to previous assumptions that ceramides and other sphingolipids found in cell membrane were purely supporting structural elements, ceramide can participate in a variety of cellular signaling: examples include regulating differentiation, proliferation, and programmed cell death (PCD) of cells. The word ''ceramide'' comes from the Latin ''cera'' (wax) and ''amide''. Ceramide is a component of vernix caseosa, the waxy or cheese-like white substance found coating the skin of newborn human infants. Pathways for ceramide synthesis There are three major pathways of ceramide generation. First, the sphingomyelinase pathway uses an enzyme to break down sphingomyelin in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infant
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used to refer to juveniles of other organisms. A newborn is, in colloquial use, an infant who is only hours, days, or up to one month old. In medical contexts, a newborn or neonate (from Latin, ''neonatus'', newborn) is an infant in the first 28 days after birth; the term applies to premature, full term, and postmature infants. Before birth, the offspring is called a fetus. The term ''infant'' is typically applied to very young children under one year of age; however, definitions may vary and may include children up to two years of age. When a human child learns to walk, they are called a toddler instead. Other uses In British English, an ''infant school'' is for children aged between four and seven. As a legal term, ''infancy'' is more lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squalene
Squalene is an organic compound. It is a triterpenoid with the formula C30H50. It is a colourless oil, although impure samples appear yellow. It was originally obtained from shark liver oil (hence its name, as ''Squalus'' is a genus of sharks). All plants and animals produce squalene as a biochemical intermediate to sterol biosynthesis. An estimated 12% of bodily squalene in humans is found in Sebaceous gland, sebum. Squalene has a role in topical skin lubrication and protection. Squalene is a precursor (chemistry), precursor for synthesis of all plant and animal sterols, including cholesterol and steroid hormones in the human body. Squalene is an important ingredient in some vaccine adjuvants: The Novartis and GlaxoSmithKline adjuvants are called MF59 and AS03, respectively. Role in steroid synthesis Squalene is the biochemical precursor to steroids. The squalene conversion begins with oxidation (via squalene monooxygenase) of one of its terminal double bonds, resulting in 2,3- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triglyceride
A triglyceride (TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids (from ''tri-'' and ''glyceride''). Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates, as well as vegetable fat. They are also present in the blood to enable the bidirectional transference of adipose fat and blood glucose from the liver, and are a major component of human skin oils. Many types of triglycerides exist. One specific classification focuses on saturated and unsaturated types. Saturated fats have ''no'' C=C groups; unsaturated fats feature one or more C=C groups. Unsaturated fats tend to have a lower melting point than saturated analogues; as a result, they are often liquid at room temperature. Chemical structure Triglycerides are tri-esters consisting of a glycerol bound to three fatty acid molecules. Alcohols have a hydroxyl (HO–) group. Organic acids have a carboxyl (–COOH) group. Alcohols and organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wax Ester
A wax ester (WE) is an ester of a fatty acid and a fatty alcohol. Wax esters comprise the main components of three commercially important waxes: carnauba wax, candelilla wax, and beeswax.. Wax esters are formed by combining one fatty acid with one fatty alcohol: :RCOOH + R'OH RCOOR' + H2O Various types of wax esters exist. Some are saturated, and others contain unsaturated centers. Saturated wax esters have higher melting points and are more likely to be solid at room temperature. Unsaturated wax esters have a lower melting point and are more likely to be liquid at room temperature. Both fatty acids and fatty alcohols may be made of different carbon chain length. In the end, there are many different possible combinations of fatty acids and fatty alcohols and each combination will have a unique set of properties in terms of steric orientation and phase transition. The chain lengths of fatty acids and fatty alcohols in naturally occurring wax esters vary. The fatty acids in wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sterol Ester
Sterol esters are a heterogeneous group of chemical compounds. They are created when the hydroxyl group of a sterol and a fatty acid undergo an esterification reaction. They can be found in trace amounts in every cell type but are highly enriched in foam cells and are common components of human skin oil. Plant sterol esters have been shown to reduce the level of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol in blood when ingested. Plant sterol esters used for dietary supplements are made from phytosterols and fatty acids also derived from plants. They are added to certain oil-containing products like margarine, milk, or yogurt to make functional foods for controlling cholesterol levels. Studies have indicated that consumption of about 2 grams per day of phytosterol esters provides a reduction in LDL cholesterol of around 10%. Sterol esters are added to certain Unilever products under the brand name Becel/Flora. See also * Phytosterols * Stanol ester * Sitosterolemia Sitosterolemia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phospholipid
Phospholipids, are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids typically have omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA integrated as part of the phospholipid molecule. The phosphate group can be modified with simple organic molecules such as choline, ethanolamine or serine. Phospholipids are a key component of all cell membranes. They can form lipid bilayers because of their amphiphilic characteristic. In eukaryotes, cell membranes also contain another class of lipid, sterol, interspersed among the phospholipids. The combination provides fluidity in two dimensions combined with mechanical strength against rupture. Purified phospholipids are produced commercially and have found applications in nanotechnology and materials science. The first phospholipid identified in 1847 as such in biological tissues was lecith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids (up to 70% by weight) in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important dietary sources of fuel for animals and important structural components for cells. History The concept of fatty acid (''acide gras'') was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: ''graisse acide'' and ''acide huileux'' ("acid fat" and "oily acid"). Types of fatty acids Fatty acids are classified in many ways: by length, by saturation vs unsaturati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |