|
Vena Comitans
Vena comitans is Latin for accompanying vein. It refers to a vein that is usually paired, with both veins lying on the sides of an artery. They are found in close proximity to arteries so that the pulsations of the artery aid venous return. Because they are generally found in pairs, they are often referred to by their plural form: venae comitantes. Venae comitantes are usually found with certain smaller arteries, especially those in the extremities. Larger arteries, on the other hand, generally do not have venae comitantes. They usually have a single, similarly sized vein which is not as intimately associated with the artery. Examples of arteries and their venae comitantes: * Radial artery and radial veins * Ulnar artery and ulnar veins * Brachial artery and brachial veins * Anterior tibial artery and anterior tibial veins * Posterior tibial artery and Posterior tibial veins * Fibular artery and Fibular veins Examples of arteries that do not have venae comitantes (i.e. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venous Return
Venous return is the rate of blood flow back to the heart. It normally limits cardiac output. Superposition of the cardiac function curve and venous return curve is used in one hemodynamic model. __TOC__ Physiology Venous return (VR) is the flow of blood back to the heart. Under steady-state conditions, venous return must equal cardiac output (Q), when averaged over time because the cardiovascular system is essentially a closed loop. Otherwise, blood would accumulate in either the systemic or pulmonary circulations. Although cardiac output and venous return are interdependent, each can be independently regulated. The circulatory system is made up of two circulations (pulmonary and systemic) situated in series between the right ventricle (RV) and left ventricle (LV). Balance is achieved, in large part, by the Frank–Starling mechanism. For example, if systemic venous return is suddenly increased (e.g., changing from upright to supine position), right ventricular preload increases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
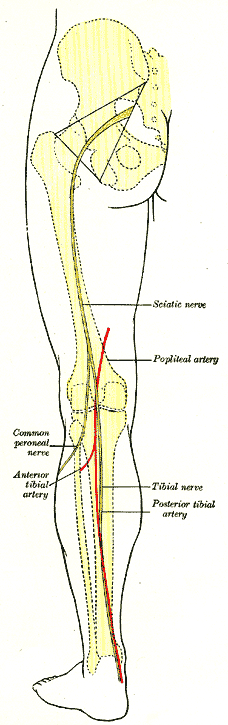
Posterior Tibial Artery
The posterior tibial artery of the lower limb is an artery that carries blood to the posterior compartment of the leg and plantar surface of the foot. It branches from the popliteal artery via the tibial-fibular trunk. Structure The posterior tibial artery arises from the popliteal artery in the popliteal fossa. It is accompanied by a deep vein, the posterior tibial vein, along its course. It passes just posterior to the medial malleolus of the tibia, but anterior to the Achilles tendon. It passes into the foot deep to the flexor retinaculum of the foot. It runs through the tarsal tunnel. Branches The posterior tibial artery gives rise to: * medial plantar artery. * lateral plantar artery. * fibular artery, which is said to rise from the bifurcation of the tibial-fibular trunk and the posterior tibial artery. * calcaneal branch to the medial aspect of the calcaneus. Function The posterior tibial artery supplies oxygenated blood to the posterior compartment of the le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subclavian Artery
In human anatomy, the subclavian arteries are paired major arteries of the upper thorax, below the clavicle. They receive blood from the aortic arch. The left subclavian artery supplies blood to the left arm and the right subclavian artery supplies blood to the right arm, with some branches supplying the head and thorax. On the left side of the body, the subclavian comes directly off the aortic arch, while on the right side it arises from the relatively short brachiocephalic artery when it bifurcates into the subclavian and the right common carotid artery. The usual branches of the subclavian on both sides of the body are the vertebral artery, the internal thoracic artery, the thyrocervical trunk, the costocervical trunk and the dorsal scapular artery, which may branch off the transverse cervical artery, which is a branch of the thyrocervical trunk. The subclavian becomes the axillary artery at the lateral border of the first rib. Structure From its origin, the subclavian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axillary Vein
In human anatomy, the axillary vein is a large blood vessel that conveys blood from the lateral aspect of the thorax, axilla (armpit) and upper limb toward the heart. There is one axillary vein on each side of the body. Structure Its origin is at the lower margin of the teres major muscle and a continuation of the brachial vein. This large vein is formed by the brachial vein and the basilic vein. At its terminal part, it is also joined by the cephalic vein. Other tributaries include the subscapular vein, circumflex humeral vein, lateral thoracic vein and thoraco-acromial vein. It terminates at the lateral margin of the first rib, at which it becomes the subclavian vein. It is accompanied along its course by a similarly named artery An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axillary Artery
In human anatomy, the axillary artery is a large blood vessel that conveys oxygenated blood to the lateral aspect of the thorax, the axilla (armpit) and the upper limb. Its origin is at the lateral margin of the first rib, before which it is called the subclavian artery. After passing the lower margin of teres major it becomes the brachial artery. Structure The axillary artery is often referred to as having three parts, with these divisions based on its location relative to the Pectoralis minor muscle, which is superficial to the artery. * First part – the part of the artery superior to the pectoralis minor * Second part – the part of the artery posterior to the pectoralis minor * Third part – the part of the artery inferior to the pectoralis minor. Relations The axillary artery is accompanied by the axillary vein, which lies medial to the artery, along its length. In the axilla, the axillary artery is surrounded by the brachial plexus. The second part of the axill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibular Veins
In anatomy, the fibular veins (also known as peroneal veins) are accompanying veins (venae comitantes) of the fibular artery. Structure The fibular veins are deep veins that help carry blood from the lateral compartment of the leg. They drain into the posterior tibial veins, which in turn drain into the popliteal vein. The fibular veins accompany the fibular artery. See also * Fibular artery * Common fibular nerve * Venae comitantes Additional images File:Gray440_color.png, Cross-section through middle of leg. File:Ultrasonography of thrombosis of the fibular veins, coronal plane, annotated.jpg, Coronal plane The coronal plane (also known as the frontal plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into dorsal and ventral sections. It is perpendicular to the sagittal and transverse planes. Details The coronal plane is an example of a longitud ... (seen from medial side of lower leg) ultrasonography of deep vein thrombosis of the fibular veins, seen as hyperechoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibular Artery
In anatomy, the fibular artery, also known as the peroneal artery, supplies blood to the lateral compartment of the leg. It arises from the tibial-fibular trunk. Structure The fibular artery arises from the bifurcation of tibial-fibular trunk into the fibular and posterior tibial arteries in the upper part of the leg proper, just below the knee. It runs towards the foot in the deep posterior compartment of the leg, just medial to the fibula. It supplies a perforating branch to both the lateral and anterior compartments of the leg; it also provides a nutrient artery to the fibula. Some sources claim that the fibular artery arises directly from the posterior tibial artery, but vascular and plastic surgeons note the clinical significance of the tibial-fibular trunk. The fibular artery is accompanied by small veins (venae comitantes) known as fibular veins. Branches Communication branch to posterior tibial artery. Perforating branch to anterior lateral malleolar artery. A ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Tibial Veins
The posterior tibial veins are veins of the leg in humans. They drain the posterior compartment of the leg and the plantar surface of the foot to the popliteal vein. Structure The posterior tibial veins receive blood from the medial and lateral plantar veins. They drain the posterior compartment of the leg and the plantar surface of the foot to the popliteal vein, which it forms when it joins with the anterior tibial vein. The posterior tibial vein is accompanied by an homonym artery, the posterior tibial artery, along its course. It lies posterior to the medial malleolus in the ankle. They receive the most important perforator vein Perforator veins are so called because they perforate the deep fascia of muscles, to connect the superficial veins to the deep veins where they drain. Perforator veins play an essential role in maintaining normal blood draining. They have valves ...s: the Cockett perforators, superior, medial and inferior. Additional images File:Gray440_c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Tibial Veins
The anterior tibial vein is a vein in the lower leg. In human anatomy, there are two anterior tibial veins. They originate and receive blood from the dorsal venous arch, on the back of the foot and empties into the popliteal vein. The anterior tibial veins drain the ankle joint, knee joint, tibiofibular joint, and the anterior portion of the lower leg. The two anterior tibial veins ascend in the interosseous membrane between the tibia and fibula and unite with the posterior tibial veins to form the popliteal vein. Like most deep veins in legs, anterior tibial veins are accompanied by the homonym artery, the anterior tibial artery The anterior tibial artery is an artery of the leg. It carries blood to the anterior compartment of the leg and dorsal surface of the foot, from the popliteal artery. Structure Course The anterior tibial artery is a branch of the poplitea ..., along its course. References Veins of the lower limb {{Circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Artery
In human anatomy, the radial artery is the main artery of the lateral aspect of the forearm. Structure The radial artery arises from the bifurcation of the brachial artery in the antecubital fossa. It runs distally on the anterior part of the forearm. There, it serves as a landmark for the division between the anterior and posterior compartments of the forearm, with the posterior compartment beginning just lateral to the artery. The artery winds laterally around the wrist, passing through the anatomical snuff box and between the heads of the first dorsal interosseous muscle. It passes anteriorly between the heads of the adductor pollicis, and becomes the deep palmar arch, which joins with the deep branch of the ulnar artery. Along its course, it is accompanied by a similarly named vein, the radial vein. Branches The named branches of the radial artery may be divided into three groups, corresponding with the three regions in which the vessel is situated. In the fore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Tibial Artery
The anterior tibial artery is an artery of the leg. It carries blood to the anterior compartment of the leg and dorsal surface of the foot, from the popliteal artery. Structure Course The anterior tibial artery is a branch of the popliteal artery. It originates at the distal end of the popliteus muscle posterior to the tibia. The artery typically passes anterior to the popliteus muscle prior to passing between the tibia and fibula through an oval opening at the superior aspect of the interosseus membrane. The artery then descends between the tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus muscles. It is accompanied by the anterior tibial vein, and the deep peroneal nerve, along its course. It crosses the anterior aspect of the ankle joint, at which point it becomes the dorsalis pedis artery. Branches The branches of the anterior tibial artery are: *posterior tibial recurrent artery * anterior tibial recurrent artery * muscular branches * anterior medial malleolar ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachial Veins
In human anatomy, the brachial veins are venae comitantes of the brachial artery in the arm proper. Because they are deep to muscle, they are considered deep veins. Their course is that of the brachial artery (in reverse): they begin where radial veins and ulnar veins join (corresponding to the bifurcation of the brachial artery). They end at the inferior border of the teres major muscle. At this point, the brachial veins join the basilic vein to form the axillary vein. The brachial veins also have small tributaries that drain the muscles of the upper arm, such as biceps brachii muscle and triceps brachii muscle. Additional Images File:Slide8UUU.JPG, Brachial vein File:Gray576.png, The veins of the right axilla The axilla (also, armpit, underarm or oxter) is the area on the human body directly under the shoulder joint. It includes the axillary space, an anatomical space within the shoulder girdle between the arm and the thoracic cage, bounded superior ..., viewed f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |