|
Varanopids
Varanopidae is an extinct family of amniotes that resembled monitor lizards and may have filled a similar niche, hence the name. Typically, they are considered synapsids that evolved from an '' Archaeothyris''-like synapsid in the Late Carboniferous. However, some recent studies have recovered them being taxonomically closer to diapsid reptiles. A varanopid from the latest Middle Permian ''Pristerognathus'' Assemblage Zone is the youngest known varanopid and the last member of the "pelycosaur" group of synapsids. Description No known varanopids developed a sail like ''Dimetrodon''. The length of known varanopids, including the tail, varies from . Varanopids already showed some advanced characteristics of true pelycosaurs such as their deep, narrow, elongated skulls. Their jaws were long and their teeth were sharp. However, they were still primitive by mammalian standards. They had long tails, lizard-like bodies, and thin legs. The varanopids were mostly carnivorous, but as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heleosaurus
''Heleosaurus scholtzi'' is an extinct species of basal synapsids, known as pelycosaurs, in the family of Varanopidae during the middle Permian.Reisz, R. R. & Modesto, S. P. 2007. ''Heleosaurus scholtzi'' from the Permian of South Africa: a varanopid synapsid, not a diapsid reptile. ''Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology'' 27 (3): 734-739. At first ''H. scholtzi'' was mistakenly classified as a diapsid. Members of this family were carnivorous and had dermal armor, and somewhat resembled monitor lizards. This family was the most geologically long lived, widespread, and diverse group of early amniotes. To date only two fossils have been found in the rocks of South Africa.Broom, R. "On Some New Fossil Reptiles from the Karroo Beds of Victoria West, South Africa." ''Transactions of the South African Philosophical Society'' 18 (1907): 31-42. Taylor and Francis Online. Web. Botha-Brink, Jennifer. "A Mixed-Age Classed 'Pelycosaur' Aggregation from South Africa: Earliest Evidence of Parental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varanopidae
Varanopidae is an extinct family of amniotes that resembled monitor lizards and may have filled a similar niche, hence the name. Typically, they are considered synapsids that evolved from an '' Archaeothyris''-like synapsid in the Late Carboniferous. However, some recent studies have recovered them being taxonomically closer to diapsid reptiles. A varanopid from the latest Middle Permian ''Pristerognathus'' Assemblage Zone is the youngest known varanopid and the last member of the "pelycosaur" group of synapsids. Description No known varanopids developed a sail like ''Dimetrodon''. The length of known varanopids, including the tail, varies from . Varanopids already showed some advanced characteristics of true pelycosaurs such as their deep, narrow, elongated skulls. Their jaws were long and their teeth were sharp. However, they were still primitive by mammalian standards. They had long tails, lizard-like bodies, and thin legs. The varanopids were mostly carnivorous, but as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
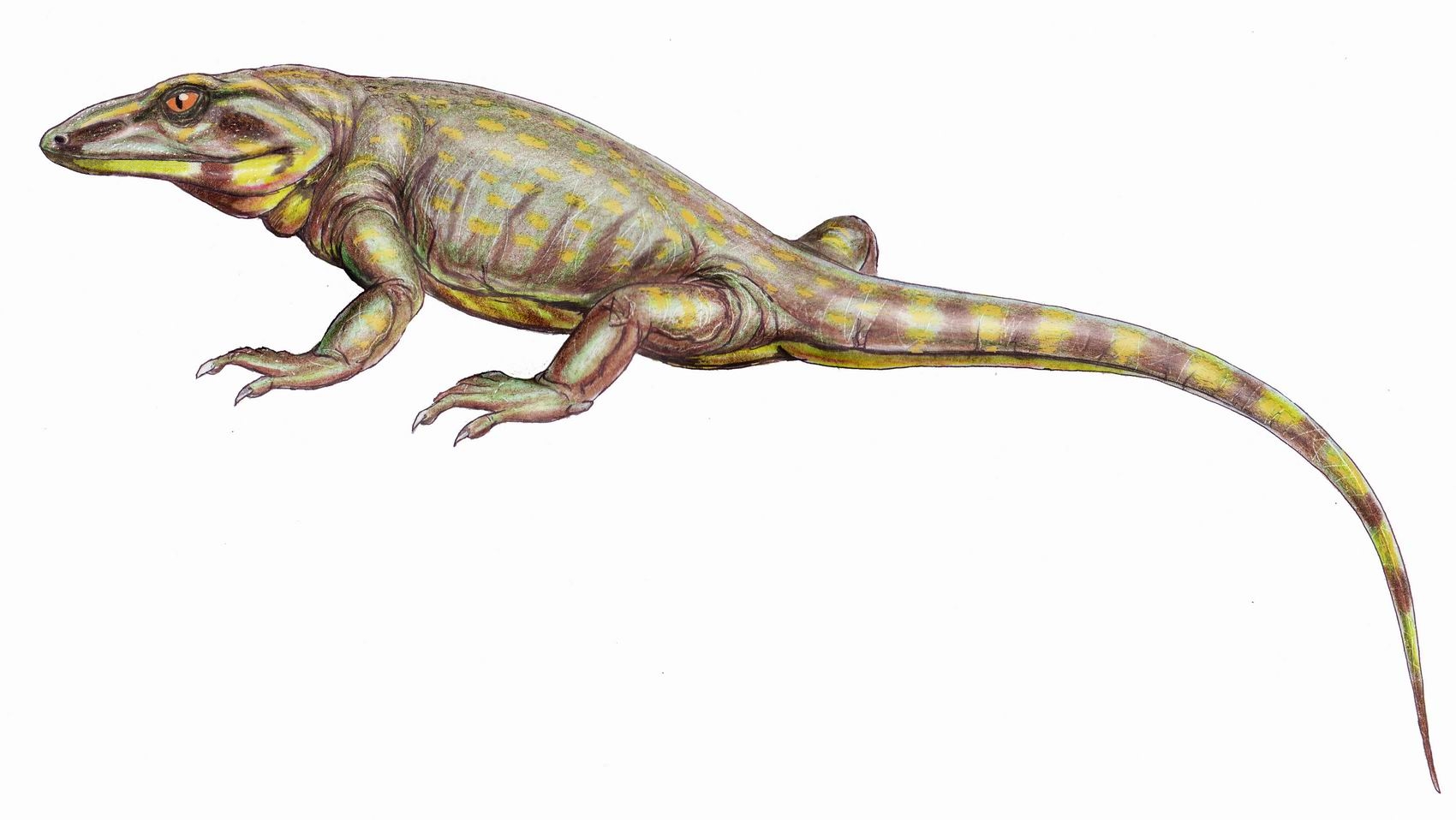
Aerosaurus Wellesi 4
''Aerosaurus'' (meaning "copper lizard") is an extinct genus within Varanopidae, a family of non-mammalian synapsids. It lived between 252-299 million years ago during the Early Permian in North America. The name comes from Latin ''aes'' (''aeris'') (combining stem: ''aer''-) “copper” and Greek ''sauros'' “lizard,” for El Cobre Canyon (from Spanish ''cobre'' “copper”) in northern New Mexico, where the type fossil was found and the site of former copper mines. ''Aerosaurus'' was a small to medium-bodied carnivorous synapsid characterized by its recurved teeth, triangular lateral temporal fenestra, and extended teeth row. Two species are recognized: ''A. greenleeorum'' (1937) and ''A. wellesi'' (1981). History and discovery ''Aerosaurus'' was a taxon named by American paleontologist and biologist Alfred Romer in 1937. There have only been two species named: ''A. greenleeorum'' (1937) and ''A. wellesi'' (1981), both discovered in New Mexico. ''A. greenleeorum'' Romer, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varanops Brevirostris
''Varanops'' is an extinct genus of Early Permian varanopid synapsids known from Texas and Oklahoma of the United States. It was first named by Samuel Wendell Williston in 1911 as a second species of '' Varanosaurus'', ''Varanosaurus brevirostris''. In 1914, Samuel W. Williston reassigned it to its own genus and the type species is ''Varanops brevirostris''. Discovery ''V. brevirostris'' is known from the holotype FMNH UC 644, a three-dimensionally preserved nearly complete and articulated skeleton including a nearly complete skull and mandibles. It was collected in the Indian Creek, 35 site (=''Cacops'' Bonebed), from the Arroyo Formation of the Clear Fork Group, Baylor County of Texas, dating to the early Kungurian stage of the Cisuralian Epoch, about 279.5-272.5 million years ago. Many well preserved specimens from the same locality and horizon of the type specimen, including FMNH UR 2423, nearly complete skull and mandibles, MCZ 1926, compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
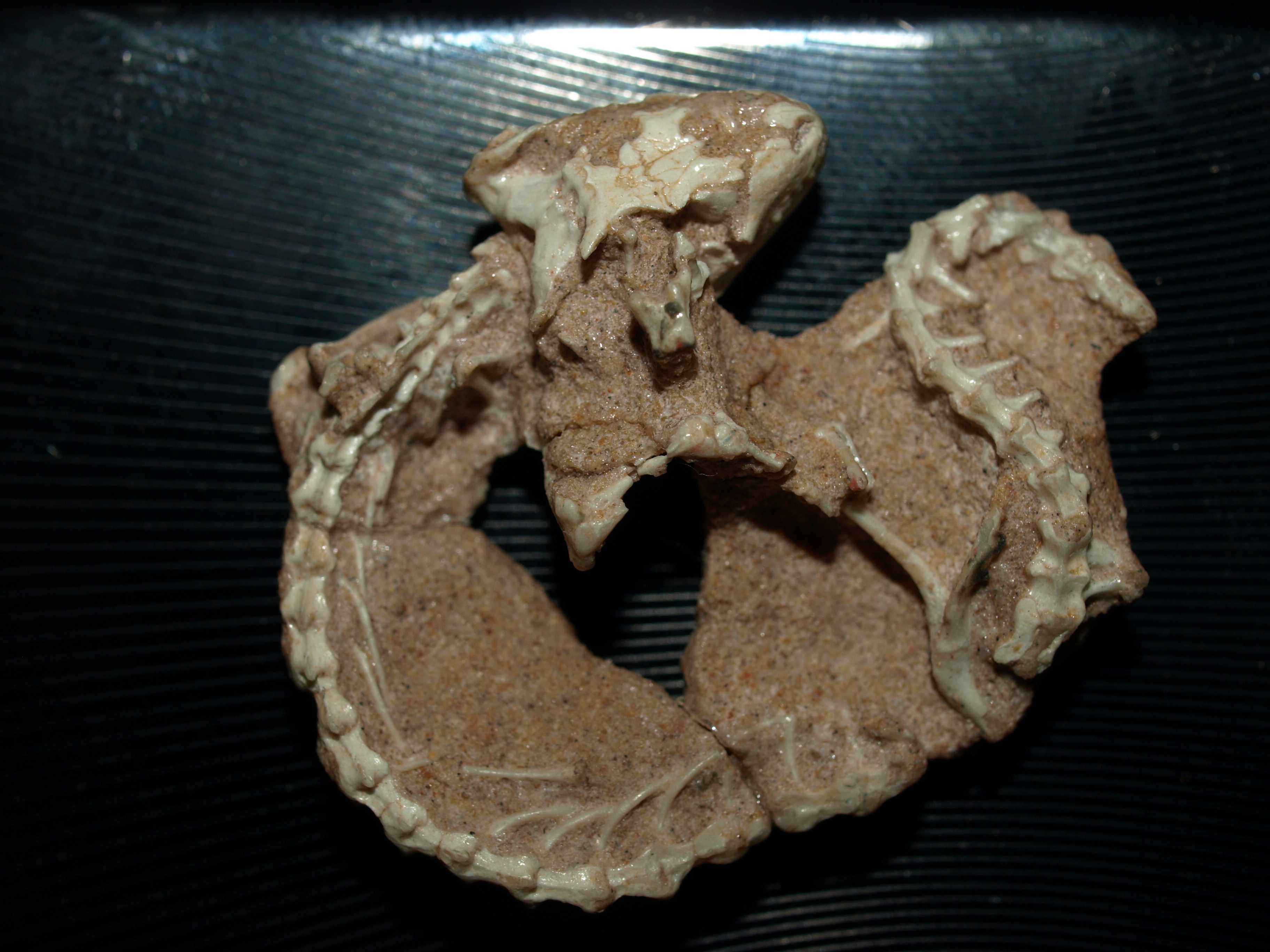
Eoscansor
''Eoscansor'' (EE-oh-SKAN-sor; meaning "dawn climber") is a species of small Varanopidae, varanopid amniote that lives from the upper Pennsylvanian (geology), Pennsylvanian subperiod in northern New Mexico, New Mexico, United States 305 million years ago. The species ''Eoscansor cobrensis'' was 24.5 centimeters (9.6 inches) long and weighed 58.3 grams. The tetrapods teeth indicated that it was insectivorous. The small size and grasping limbs means that was ''E. cobrensis'' highly agile and likely Arboreal locomotion, arboreal (tree climbing). The name ''Eoscansor'' means "dawn climber", derived from Greek language, Greek with "Eo" meaning dawn and "scansor" meaning climber. ''E. cobrensis'' is currently the oldest specialised climbing tetrapod animal pushing back the original record by 15 million years. The species was discovered in the El Cobre Canyon Formation in northern New Mexico near the village of Chama, New Mexico, Chama in 2005 but was not prepared until 2015. The COVID-19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascendonanus
''Ascendonanus'' (meaning "climbing dwarf") is an extinct genus of varanopid amniote from the Early Permian of Germany. It is one of the earliest specialized arboreal (tree-living) tetrapods currently known and outwardly resembled a small lizard. The animal was about 40 cm long, with strongly curved claws, short limbs, a slender, elongated trunk, and a long tail. It would have preyed on insects and other small arthropods. The taxonomic position of varanopids is currently debated between synapsids (related to mammals, the most widely accepted idea) and diapsids (related to reptiles). The fossils of ''Ascendonanus'' are of special scientific importance because they include remains of skin, scales, scutes, bony ossicles, and soft-tissue body outlines, which could indicate that some of the oldest relatives of mammals had a scaly "reptilian-type" appearance. The related small varanopid ''Eoscansor'', recently described from New Mexico, was also adapted to climbing, very likel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesenosaurus And Varanodon
''Mesenosaurus'' is an extinct genus of amniote. It belongs to the family Varanopidae. This genus includes two species: the type species ''Mesenosaurus romeri'' from the middle Permian (upper Kazanian) Mezen River Basin of northern Russia, and ''Mesenosaurus efremovi'' from the early Permian (Artinskian) Richards Spur locality ( Oklahoma, United States). ''M. romeri''’s stratigraphic range is the middle to late Guadalupian while ''M. efremovi''’s stratigraphic range is the Cisuralian. Etymology Famous Russian paleontologist, Ivan Efremov, established ''Mesenosaurus'' as a genus, and named it after its roots with the (literal translation is “lizard from Mezen”). ''Mesenosaurus efremovi'' was named in honor of Ivan Efremov, who erected the genus. Description ''Mesenosaurus'' are small sized varanopid synapsids. They are characterized by mainly cranial features. Many of the postcranial features of this genus have not been analyzed fully due to a lack of fossil evide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert R
Robert Lee Rayford (February 3, 1953 – May 15 1969), sometimes identified as Robert R. due to his age, was an American teenager from Missouri who has been suggested to represent the earliest confirmed case of HIV/AIDS in North America based on evidence which was published in 1988 in which the authors claimed that medical evidence indicated that he was "infected with a virus closely related or identical to human immunodeficiency virus type 1." Rayford died of pneumonia, but his other symptoms baffled the doctors who treated him. A study published in 1988 reported the detection of antibodies against HIV. Results of testing for HIV genetic material were reported once at a scientific conference in Australia in 1999; however, the data has never been published in a peer-reviewed medical or scientific journal. Background Robert Rayford was born on February 3, 1953, in St. Louis, Missouri to Constance Rayford (September 12, 1931 – April 3, 2011) and Joseph Benny Bell (March 24, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arboreal Locomotion
Arboreal locomotion is the locomotion of animals in trees. In habitats in which trees are present, animals have evolved to move in them. Some animals may scale trees only occasionally, but others are exclusively arboreal. The habitats pose numerous mechanical challenges to animals moving through them and lead to a variety of anatomical, behavioral and ecological consequences as well as variations throughout different species.Cartmill, M. (1985). Climbing. In ''Functional Vertebrate Morphology'', eds. M. Hildebrand D. M. Bramble K. F. Liem and D. B. Wake, pp. 73–88. Cambridge: Belknap Press. Furthermore, many of these same principles may be applied to climbing without trees, such as on rock piles or mountains. Some animals are exclusively arboreal in habitat, such as the tree snail. Biomechanics Arboreal habitats pose numerous mechanical challenges to animals moving in them, which have been solved in diverse ways. These challenges include moving on narrow branches, mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pangea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million years ago, and began to break apart about 200 million years ago, at the end of the Triassic and beginning of the Jurassic. In contrast to the present Earth and its distribution of continental mass, Pangaea was centred on the equator and surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa and the Paleo-Tethys and subsequent Tethys Oceans. Pangaea is the most recent supercontinent to have existed and the first to be reconstructed by geologists. Origin of the concept The name "Pangaea" is derived from Ancient Greek ''pan'' (, "all, entire, whole") and ''Gaia'' or Gaea (, "Mother Earth, land"). The concept that the continents once formed a contiguous land mass was hypothesised, with corroborating evidence, by Alfred Wegener, the originator of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamates
Squamata (, Latin ''squamatus'', 'scaly, having scales') is the largest order of reptiles, comprising lizards, snakes, and amphisbaenians (worm lizards), which are collectively known as squamates or scaled reptiles. With over 10,900 species, it is also the second-largest order of extant (living) vertebrates, after the perciform fish. Members of the order are distinguished by their skins, which bear horny scales or shields, and must periodically engage in molting. They also possess movable quadrate bones, making possible movement of the upper jaw relative to the neurocranium. This is particularly visible in snakes, which are able to open their mouths very wide to accommodate comparatively large prey. Squamata is the most variably sized order of reptiles, ranging from the dwarf gecko (''Sphaerodactylus ariasae'') to the Reticulated python (''Malayopython reticulatus'') and the now-extinct mosasaurs, which reached lengths over . Among other reptiles, squamates are most closely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |