|
Utility Poles
A utility pole is a column or post typically made out of wood used to support overhead power lines and various other public utilities, such as electrical cable, fiber optic cable, and related equipment such as transformers and street lights. It can be referred to as a transmission pole, telephone pole, telecommunication pole, power pole, hydro pole, telegraph pole, or telegraph post, depending on its application. A Stobie pole is a multi-purpose pole made of two steel joists held apart by a slab of concrete in the middle, generally found in South Australia. Electrical wires and cables are routed overhead on utility poles as an inexpensive way to keep them insulated from the ground and out of the way of people and vehicles. Utility poles can be made of wood, metal, concrete, or composites like fiberglass. They are used for two different types of power lines: ''sub transmission lines'', which carry higher voltage power between substations, and ''distribution lines'', which distrib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hv Braunschweig20
HV or Hv is a two-letter acronym which may refer to: In militaries: * Heimevernet, a Norwegian military force * Hemvärnet, a Swedish military force * Hrvatska Vojska, the Croatian army * , the Danish home guard Places: * Burkina Faso (WMO country code HV, from the former French name, "Haute Volta") * Hudson Valley, New York, US In science and technology: * Absolute visual magnitude, or V-band magnitude, HV * Mitochondrial DNA Haplogroup HV * Hasselblad HV, a digital system camera based on the Sony α SLT-A99V * High voltage, in electricity distribution * Hybrid vehicles, which use two or more distinct types of power *Hydrogen vehicle, powered by hydrogen * Hypervelocity star, an astronomical object or as a designation of such in a star catalogue * hν, light, in chemistry shorthand * Vickers Hardness, a hardness test Other uses: * Holcomb Valley Scout Ranch * Holiday village, a holiday resort where the visitors stay in villas. * Home video, pre-recorded media for home entertainm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood Preservation
Wood easily degrades without sufficient preservation. Apart from structural wood preservation measures, there are a number of different chemical preservatives and processes (also known as "timber treatment", "lumber treatment" or "pressure treatment") that can extend the life of wood, timber, and their associated products, including engineered wood. These generally increase the durability and resistance from being destroyed by insects or fungi. History As proposed by Richardson, treatment of wood has been practiced for almost as long as the use of wood itself. There are records of wood preservation reaching back to ancient Greece during Alexander the Great's rule, where bridge wood was soaked in olive oil. The Romans protected their ship hulls by brushing the wood with tar. During the Industrial Revolution, wood preservation became a cornerstone of the wood processing industry. Inventors and scientists such as Bethell, Boucherie, Burnett and Kyan made historic developments in wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Fire Protection Association
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) is an international nonprofit organization devoted to eliminating death, injury, property and economic loss due to fire, electrical and related hazards. As of 2018, the NFPA claims to have 50,000 members and 9,000 volunteers working with the organization through its 250 technical committees. History In 1895, a Committee on Automatic Sprinkler Protection was formed in Massachusetts by men affiliated with several fire insurance companies and a pipe manufacturer to develop a uniform standard for the design and installation of fire sprinkler systems. At the time, there were nine such standards in effect within of Boston, Massachusetts, and such diversity was causing great difficulties for plumbers working in the New England region. The next year, the committee published its initial report on a uniform standard, and went on to form the NFPA in late 1896. The committee's initial report evolved into NFPA 13, ''Standard for the Installat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Electrical Code
The National Electrical Code (NEC), or NFPA 70, is a regionally adoptable standard for the safe installation of electrical wiring and equipment in the United States. It is part of the National Fire Code series published by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), a private trade association. Despite the use of the term "national", it is not a Law of the United States, federal law. It is typically adopted by U.S. state, states and municipalities in an effort to standardize their enforcement of safe electrical practices. In some cases, the NEC is amended, altered and may even be rejected in lieu of regional regulations as voted on by local governing bodies. The "authority having jurisdiction" inspects for compliance with these standards. The NEC should not be confused with the National Electrical Safety Code (NESC) published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). The NESC is used for electric power and communication utility systems including overh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Electrical And Electronics Engineers
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is a 501(c)(3) professional association for electronic engineering and electrical engineering (and associated disciplines) with its corporate office in New York City and its operations center in Piscataway, New Jersey. The mission of the IEEE is ''advancing technology for the benefit of humanity''. The IEEE was formed from the amalgamation of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers and the Institute of Radio Engineers in 1963. Due to its expansion of scope into so many related fields, it is simply referred to by the letters I-E-E-E (pronounced I-triple-E), except on legal business documents. , it is the world's largest association of technical professionals with more than 423,000 members in over 160 countries around the world. Its objectives are the educational and technical advancement of electrical and electronic engineering, telecommunications, computer engineering and similar disciplines. History Origins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Electrical Safety Code
The National Electrical Safety Code (NESC) or ANSI Standard C2 is a United States standard of the safe installation, operation, and maintenance of electric power and communication utility systems including power substations, power and communication overhead lines, and power and communication underground lines. It is published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). "National Electrical Safety Code" and "NESC" are registered trademarks of the IEEE. The NESC should not be confused with the National Electrical Code (NEC) published by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA). The NEC is used for residential, commercial, and industrial building wiring. General Access to the NESC The NESC is written as a voluntary standard. It is typically adopted as law by individual states or other governmental authorities. To determine the legal status of the NESC, the state public service commission, public utility commission, or other governmental authority should be c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steel Utility Pole
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant typically need an additional 11% chromium. Because of its high tensile strength and low cost, steel is used in buildings, infrastructure, tools, ships, trains, cars, machines, electrical appliances, weapons, and rockets. Iron is the base metal of steel. Depending on the temperature, it can take two crystalline forms (allotropic forms): body-centred cubic and face-centred cubic. The interaction of the allotropes of iron with the alloying elements, primarily carbon, gives steel and cast iron their range of unique properties. In pure iron, the crystal structure has relatively little resistance to the iron atoms slipping past one another, and so pure iron is quite ductile, or soft and easily formed. In steel, small amounts of carbon, other ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
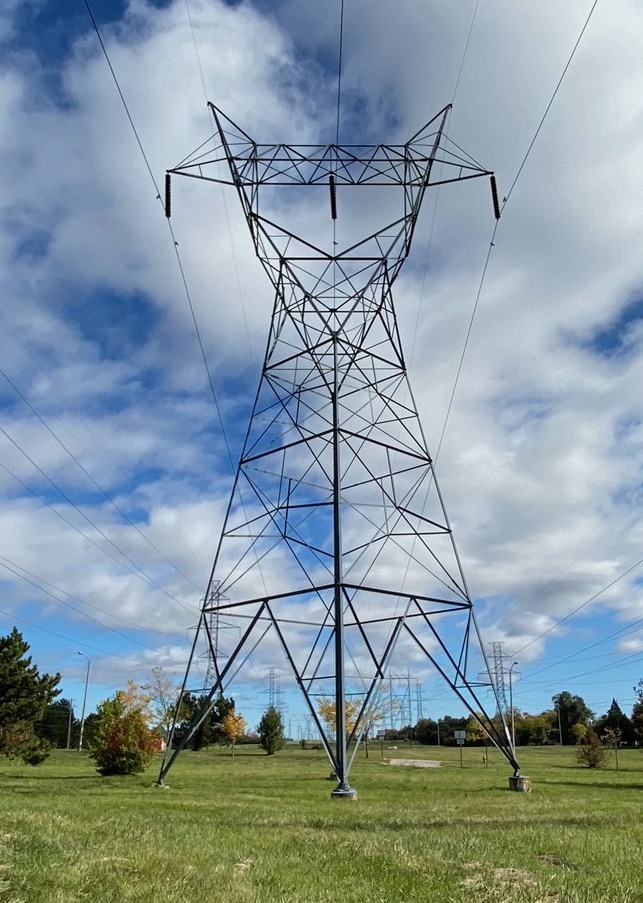
Transmission Tower
A transmission tower, also known as an electricity pylon or simply a pylon in British English and as a hydro tower in Canadian English, is a tall structure, usually a steel lattice tower, used to support an overhead power line. In electrical grids, they are generally used to carry high-voltage transmission lines that transport bulk electric power from generating stations to electrical substations; utility poles are used to support lower-voltage subtransmission and distribution lines that transport power from substations to electric customers. They come in a wide variety of shapes and sizes. Typical height ranges from , though the tallest are the towers of a span between the islands Jintang and Cezi in China's Zhejiang province. The longest span of any hydroelectric crossing ever built belongs to Ameralik Span, the powerline crossing of Ameralik fjord with a length of . In addition to steel, other materials may be used, including concrete and wood. There are four major categ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission Line
In electrical engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable or other structure designed to conduct electromagnetic waves in a contained manner. The term applies when the conductors are long enough that the wave nature of the transmission must be taken into account. This applies especially to radio-frequency engineering because the short wavelengths mean that wave phenomena arise over very short distances (this can be as short as millimetres depending on frequency). However, the theory of transmission lines was historically developed to explain phenomena on very long telegraph lines, especially submarine telegraph cables. Transmission lines are used for purposes such as connecting radio transmitters and receivers with their antennas (they are then called feed lines or feeders), distributing cable television signals, trunklines routing calls between telephone switching centres, computer network connections and high speed computer data buses. RF engineers commonly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Service Drop
In electric power distribution, a service drop is an overhead electrical line running from a utility pole, to a customer's building or other premises. It is the point where electric utilities provide power to their customers.Carson Dunlop "Electrical Systems" Dearborn Real Estate, 2003 page 24 The customer connection to an underground distribution system is usually called a "service lateral". Conductors of a service drop or lateral are usually owned and maintained by the utility company, but some industrial drops are installed and owned by the customer. At the customer's premises, the wires usually enter the building through a weatherhead that protects against entry of rain and snow, and drop down through conduit to an electric meter which measures and records the power used for billing purposes, then enters the main service panel. The utility's portion of the system ends, and the customer's wiring begins, at the output socket of the electric meter. The service panel will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827). Definition One volt is defined as the electric potential between two points of a conducting wire when an electric current of one ampere dissipates one watt of power between those points. Equivalently, it is the potential difference between two points that will impart one joule of energy per coulomb of charge that passes through it. It can be expressed in terms of SI base units ( m, kg, second, s, and ampere, A) as : \text = \frac = \frac = \frac. It can also be expressed as amperes times ohms (current times resistance, Ohm's law), webers per second (magnetic flux per time), watts per ampere (power per current), or joules per coulomb (energy per charge), which is also equivalent to electronvolts per elementary charge: : \text = \tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |