|
Ureterocoele
A ureterocele is a congenital abnormality found in the ureter. In this condition the distal ureter balloons at its opening into the bladder, forming a sac-like pouch. It is most often associated with a duplicated collection system, where two ureters drain their respective kidney instead of one. Simple ureterocele, where the condition involves only a single ureter, represents only twenty percent of cases. Since the advent of the ultrasound, most ureteroceles are diagnosed prenatally. The pediatric and adult conditions are often found incidentally, i.e. through diagnostic imaging performed for unrelated reasons. Classification ; Intravesical : Confined within the bladder ; Ectopic : Some part extends to the bladder neck or urethra ; Stenotic : Intravesical ureterocele with a narrow opening ; Sphincteric : Ectopic ureterocele with an orifice distal to the bladder neck ; Sphincterostenotic : Orifice is both stenotic and distal to the bladder neck ; Cecoureterocele : Ectopic ureteroce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ureter
The ureters are tubes made of smooth muscle that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In a human adult, the ureters are usually long and around in diameter. The ureter is lined by urothelial cells, a type of transitional epithelium, and has an additional smooth muscle layer that assists with peristalsis in its lowest third. The ureters can be affected by a number of diseases, including urinary tract infections and kidney stone. is when a ureter is narrowed, due to for example chronic inflammation. Congenital abnormalities that affect the ureters can include the development of two ureters on the same side or abnormally placed ureters. Additionally, reflux of urine from the bladder back up the ureters is a condition commonly seen in children. The ureters have been identified for at least two thousand years, with the word "ureter" stemming from the stem relating to urinating and seen in written records since at least the time of Hippocrates. It is, however, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showin ... associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues. Common causes of pain in the abdomen include gastroenteritis and irritable bowel syndrome. About 15% of people have a more serious underlying condition such as appendicitis, leaking or ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm, diverticulitis, or ectopic pregnancy. In a third of cases the exact cause is unclear. Given that a variety of diseases can cause some form of abdominal pain, a systematic approach to the examination of a person and the formulation of a differential diagnosis remains important. Differential diagnosis The most frequent reasons for abdominal pain are gastroenteritis (13%), irritable bowel syndr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seminal Vesicle
The seminal vesicles (also called vesicular glands, or seminal glands) are a pair of two convoluted tubular glands that lie behind the urinary bladder of some male mammals. They secrete fluid that partly composes the semen. The vesicles are 5–10 cm in size, 3–5 cm in diameter, and are located between the bladder and the rectum. They have multiple outpouchings which contain secretory glands, which join together with the vas deferens at the ejaculatory duct. They receive blood from the vesiculodeferential artery, and drain into the vesiculodeferential veins. The glands are lined with column-shaped and cuboidal cells. The vesicles are present in many groups of mammals, but not marsupials, monotremes or carnivores. Inflammation of the seminal vesicles is called seminal vesiculitis, most often is due to bacterial infection as a result of a sexually transmitted disease or following a surgical procedure. Seminal vesiculitis can cause pain in the lower abdomen, scrotum, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesonephric Duct
The mesonephric duct (also known as the Wolffian duct, archinephric duct, Leydig's duct or nephric duct) is a paired Organ (anatomy), organ that forms during the embryonic development of humans and other mammals and gives rise to male Sex organ, reproductive organs. Structure The mesonephric duct connects the primitive kidney, the ''mesonephros'', to the cloaca. It also serves as the primordium for male urogenital structures including the epididymis, vas deferens, and seminal vesicles. Development In both male and female the mesonephric duct develops into the trigone of urinary bladder, a part of the bladder wall, but the sexes differentiate in other ways during development of the Development of the urinary system, urinary and Development of the reproductive system, reproductive organs. Male In a male, it develops into a system of connected organs between the efferent ducts of the testis and the prostate, namely the epididymis, the vas deferens, and the seminal vesicle. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar working in the 19th century in Brno, was the first to study genetics scientifically. Mendel studied "trait inheritance", patterns in the way traits are handed down from parents to offspring over time. He observed that organisms (pea plants) inherit traits by way of discrete "units of inheritance". This term, still used today, is a somewhat ambiguous definition of what is referred to as a gene. Trait inheritance and molecular inheritance mechanisms of genes are still primary principles of genetics in the 21st century, but modern genetics has expanded to study the function and behavior of genes. Gene structure and function, variation, and distribution are studied within the context of the cell, the organism (e.g. dominance), and within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The uterus is a hormone-responsive sex organ that contains glands in its lining that secrete uterine milk for embryonic nourishment. In the human, the lower end of the uterus, is a narrow part known as the isthmus that connects to the cervix, leading to the vagina. The upper end, the body of the uterus, is connected to the fallopian tubes, at the uterine horns, and the rounded part above the openings to the fallopian tubes is the fundus. The connection of the uterine cavity with a fallopian tube is called the uterotubal junction. The fertilized egg is carried to the uterus along the fallopian tube. It will have divided on its journey to form a blastocyst that will implant itself into the lining of the uterus – the endometrium, where it will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uric Acid
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates, such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is a product of the metabolic breakdown of purine nucleotides, and it is a normal component of urine. High blood concentrations of uric acid can lead to gout and are associated with other medical conditions, including diabetes and the formation of ammonium acid urate kidney stones. Chemistry Uric acid was first isolated from kidney stones in 1776 by Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele. In 1882, the Ukrainian chemist Ivan Horbaczewski first synthesized uric acid by melting urea with glycine. Uric acid displays lactam–lactim tautomerism (also often described as keto–enol tautomerism). Although the lactim form is expected to possess some degree of aromaticity, uric acid crystallizes in the lactam form, with computational chemistry also indicating that tautomer to be the most s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney Stones
Kidney stone disease, also known as nephrolithiasis or urolithiasis, is a crystallopathy where a solid piece of material (kidney stone) develops in the urinary tract. Kidney stones typically form in the kidney and leave the body in the urine stream. A small stone may pass without causing symptoms. If a stone grows to more than , it can cause blockage of the ureter, resulting in sharp and severe pain in the lower back or abdomen. A stone may also result in blood in the urine, vomiting, or painful urination. About half of people who have had a kidney stone will have another within ten years. Most stones form by a combination of genetics and environmental factors. Risk factors include high urine calcium levels, obesity, certain foods, some medications, calcium supplements, hyperparathyroidism, gout and not drinking enough fluids. Stones form in the kidney when minerals in urine are at high concentration. The diagnosis is usually based on symptoms, urine testing, and medical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urolithiasis
Kidney stone disease, also known as nephrolithiasis or urolithiasis, is a crystallopathy where a solid piece of material (kidney stone) develops in the urinary tract. Kidney stones typically form in the kidney and leave the body in the urine stream. A small stone may pass without causing symptoms. If a stone grows to more than , it can cause blockage of the ureter, resulting in sharp and severe pain in the lower back or abdomen. A stone may also result in blood in the urine, vomiting, or painful urination. About half of people who have had a kidney stone will have another within ten years. Most stones form by a combination of genetics and environmental factors. Risk factors include high urine calcium levels, obesity, certain foods, some medications, calcium supplements, hyperparathyroidism, gout and not drinking enough fluids. Stones form in the kidney when minerals in urine are at high concentration. The diagnosis is usually based on symptoms, urine testing, and medical i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
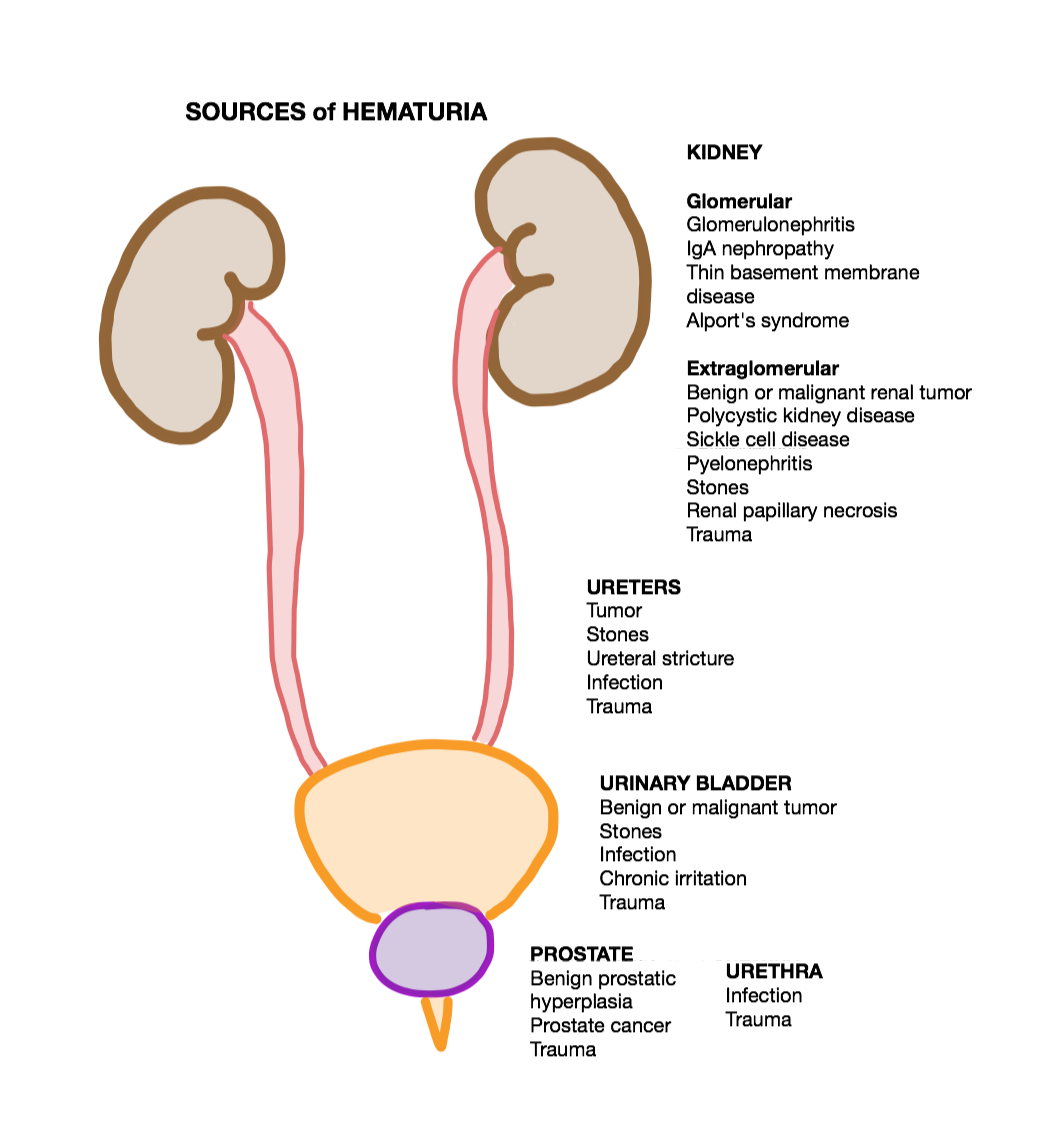
Hematuria
Hematuria or haematuria is defined as the presence of blood or red blood cells in the urine. “Gross hematuria” occurs when urine appears red, brown, or tea-colored due to the presence of blood. Hematuria may also be subtle and only detectable with a microscope or laboratory test. Blood that enters and mixes with the urine can come from any location within the urinary system, including the kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra, and in men, the prostate. Common causes of hematuria include urinary tract infection (UTI), kidney stones, viral illness, trauma, bladder cancer, and exercise. These causes are grouped into glomerular and non-glomerular causes, depending on the involvement of the glomerulus of the kidney. But not all red urine is hematuria. Other substances such as certain medications and foods (e.g. blackberries, beets, food dyes) can cause urine to appear red. Menstruation in women may also cause the appearance of hematuria and may result in a positive urine dipstick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, acid–base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hydrogen, ammonium, potassium and uric acid. The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. Each adult human kidney contains around 1 million nephrons, while a mouse kidney contains on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Failure To Thrive
Failure to thrive (FTT), also known as weight faltering or faltering growth, indicates insufficient weight gain or absence of appropriate physical growth in children. FTT is usually defined in terms of weight, and can be evaluated either by a low weight for the child's age, or by a low rate of increase in the weight. The term "failure to thrive" has been used in different ways, as there is no objective standard or universally accepted definition for when to diagnose FTT. One definition describes FTT as a fall in one or more weight centile spaces on a World Health Organization (WHO) growth chart depending on birth weight or when weight is below the 2nd percentile of weight for age irrespective of birth weight. Another definition of FTT is a weight for age that is consistently below the 5th percentile or weight for age that falls by at least two major percentile lines on a growth chart. While weight loss after birth is normal and most babies return to their birth weight by three wee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |