|
Upper Structure
In jazz, the term upper structure or "upper structure triad" refers to a voicing approach developed by jazz pianists and arrangers defined by the sounding of a major or minor triad in the uppermost pitches of a more complex harmony.Ellenberger, Kurt. ''Materials and Concepts in Jazz Improvisation'', p.20. Examples Example 1: Below, a common voicing used by jazz pianists is given for the chord C79 (C major chord with a minor 7th, and extended with an augmented 9th). In the lower stave the notes E and B are given. These form a tritone which defines the dominant sound, and are the major 3rd and minor 7th of the C79 chord. In the upper stave the notes E, G, and B are given together: these form an E major triad. This E major triad is what would be called the upper structure. Considered in relation to the root C, the notes of this E major triad function, respectively, as the sharpened ninth (the root of the E major chord), fifth, and seventh in relation to that root. (Note: th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a major form of musical expression in traditional and popular music. Jazz is characterized by swing and blue notes, complex chords, call and response vocals, polyrhythms and improvisation. Jazz has roots in European harmony and African rhythmic rituals. As jazz spread around the world, it drew on national, regional, and local musical cultures, which gave rise to different styles. New Orleans jazz began in the early 1910s, combining earlier brass band marches, French quadrilles, biguine, ragtime and blues with collective polyphonic improvisation. But jazz did not begin as a single musical tradition in New Orleans or elsewhere. In the 1930s, arranged dance-oriented swing big bands, Kansas City jazz (a hard-swinging, bluesy, improvisationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voicing (music)
In music theory, voicing refers to two closely related concepts: # How a musician or group distributes, or spaces, notes and chords on one or more instruments # The simultaneous vertical placement of notes in relation to each other; this relates to the concepts of spacing and doubling It includes the instrumentation and vertical spacing and ordering of the musical notes in a chord: which notes are on the top or in the middle, which ones are doubled, which octave each is in, and which instruments or voices perform each note. Vertical placement The following three chords are all C-major triads in root position with different voicings. The first is in close position (the most compact voicing), while the second and third are in open position (that is, with wider spacing). Notice also that the G is doubled at the octave in the third chord; that is, it appears in two different octaves. : Examples Many composers, as they developed and gained experience, became more enter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrangement
In music, an arrangement is a musical adaptation of an existing composition. Differences from the original composition may include reharmonization, melodic paraphrasing, orchestration, or formal development. Arranging differs from orchestration in that the latter process is limited to the assignment of notes to instruments for performance by an orchestra, concert band, or other musical ensemble. Arranging "involves adding compositional techniques, such as new thematic material for introductions, transitions, or modulations, and endings. Arranging is the art of giving an existing melody musical variety".(Corozine 2002, p. 3) In jazz, a memorized (unwritten) arrangement of a new or pre-existing composition is known as a ''head arrangement''. Classical music Arrangement and transcriptions of classical and serious music go back to the early history of this genre. Eighteenth century J.S. Bach frequently made arrangements of his own and other composers' piec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triad (music)
In music, a triad is a set of three notes (or "pitch classes") that can be stacked vertically in thirds.Ronald Pen, ''Introduction to Music'' (New York: McGraw-Hill, 1992): 81. . "A triad is a set of notes consisting of three notes built on successive intervals of a third. A triad can be constructed upon any note by adding alternating notes drawn from the scale.... In each case the note that forms the foundation pitch is called the ''root'', the middle tone of the triad is designated the ''third'' (because it is separated by the interval of a third from the root), and the top tone is referred to as the ''fifth'' (because it is a fifth away from the root)." Triads are the most common chords in Western music. When stacked in thirds, notes produce triads. The triad's members, from lowest-pitched tone to highest, are called: * the root **Note: Inversion does not change the root. (The third or fifth can be the lowest note.) * the third – its interval above the root being a minor thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominant Chord
In music, the dominant is the fifth scale degree () of the diatonic scale. It is called the ''dominant'' because it is second in importance to the first scale degree, the tonic. In the movable do solfège system, the dominant note is sung as "So(l)". The triad built on the dominant note is called the dominant chord. This chord is said to have dominant function, which means that it creates an instability that requires the tonic for resolution. Dominant triads, seventh chords, and ninth chords typically have dominant function. Leading-tone triads and leading-tone seventh chords may also have dominant function. Dominant chords In music theory, the dominant triad is a major chord, symbolized by the Roman numeral "V" in the major scale. In the natural minor scale, the triad is a minor chord, denoted by "v". However, in a minor key, the seventh scale degree is often raised by a half step ( to ), creating a major chord. These chords may also appear as seventh chords: typi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Structure Triad 1
Upper may refer to: * Shoe upper or ''vamp'', the part of a shoe on the top of the foot * Stimulant, drugs which induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical function or both * ''Upper'', the original film title for the 2013 found footage film ''The Upper Footage ''The Upper Footage'' (also known as ''Upper'') is a 2013 found footage film written and directed by Justin Cole. First released on January 31, 2013 to a limited run of midnight theatrical screenings at Landmark’s Sunshine Cinema in New York Cit ...'' See also {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Structure Triad 2
Upper may refer to: * Shoe upper or ''vamp'', the part of a shoe on the top of the foot * Stimulant, drugs which induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical function or both * ''Upper'', the original film title for the 2013 found footage film ''The Upper Footage ''The Upper Footage'' (also known as ''Upper'') is a 2013 found footage film written and directed by Justin Cole. First released on January 31, 2013 to a limited run of midnight theatrical screenings at Landmark’s Sunshine Cinema in New York Cit ...'' See also {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enharmonic
In modern musical notation and tuning, an enharmonic equivalent is a note, interval, or key signature that is equivalent to some other note, interval, or key signature but "spelled", or named differently. The enharmonic spelling of a written note, interval, or chord is an alternative way to write that note, interval, or chord. The term is derived from Latin ''enharmonicus'', from Late Latin ''enarmonius'', from Ancient Greek ἐναρμόνιος (''enarmónios''), from ἐν (''en'') and ἁρμονία (''harmonía''). Definition For example, in any twelve-tone equal temperament (the predominant system of musical tuning in Western music), the notes C and D are ''enharmonic'' (or ''enharmonically equivalent'') notes. Namely, they are the same key on a keyboard, and thus they are identical in pitch, although they have different names and different roles in harmony and chord progressions. Arbitrary amounts of accidentals can produce further enharmonic equivalents, such as B (me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
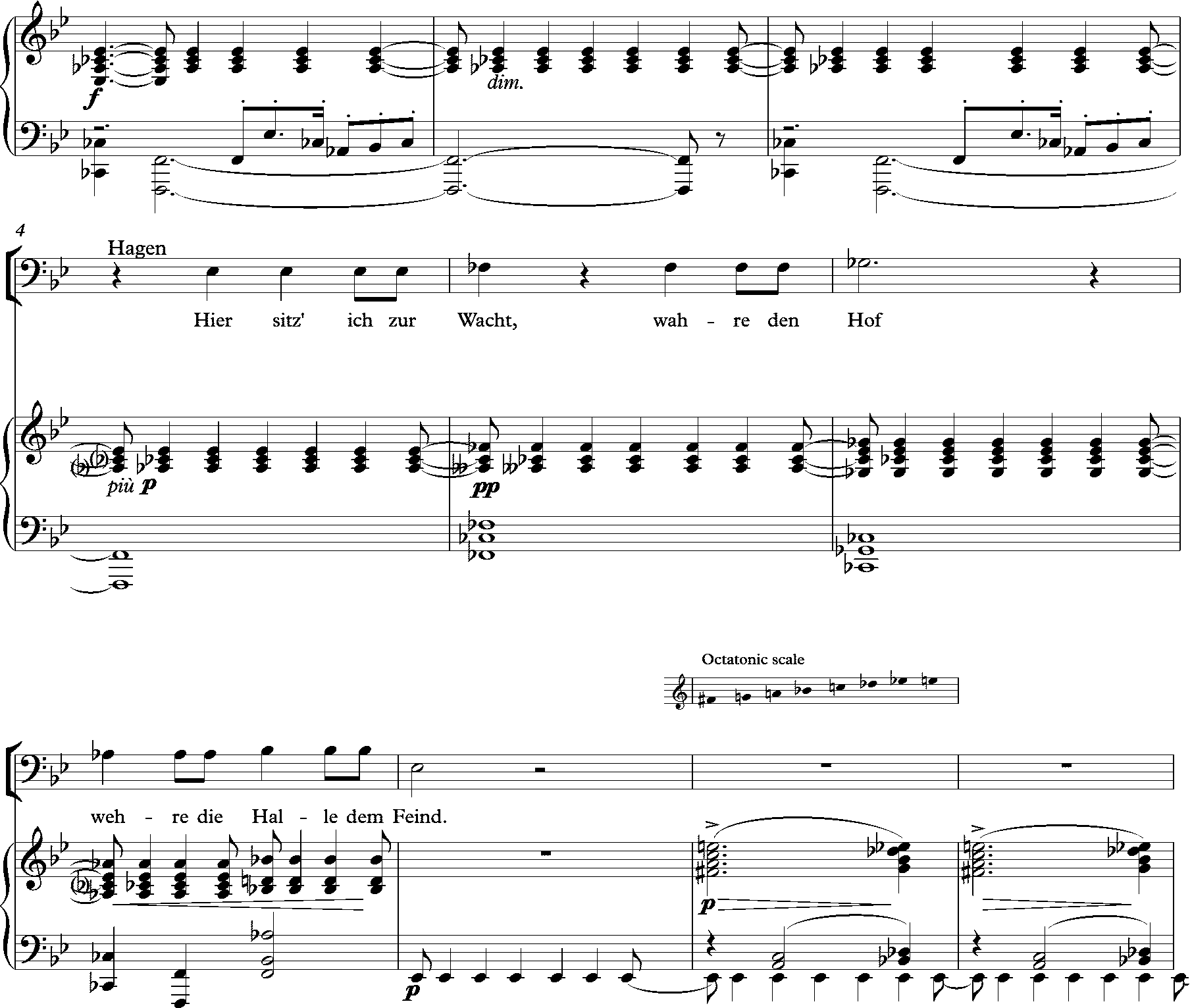
Octatonic Scale
An octatonic scale is any eight-note musical scale. However, the term most often refers to the symmetric scale composed of alternating whole and half steps, as shown at right. In classical theory (in contrast to jazz theory), this symmetrical scale is commonly called the ''octatonic scale'' (or the ''octatonic collection''), although there are a total of 42 enharmonically non-equivalent, transpositionally non-equivalent eight-note sets. The earliest systematic treatment of the octatonic scale was in Edmond de Polignac's unpublished treatise "Étude sur les successions alternantes de tons et demi-tons (Et sur la gamme dite majeure-mineure)" (''Study of the Succession of Alternating Whole Tones and Semitones (and of the so-called Major-Minor Scale)'') from c. 1879, which preceded Vito Frazzi's ''Scale alternate per pianoforte'' of 1930 by a full half-century. Nomenclature In Saint Petersburg at the turn of the 20th century, this scale had become so familiar in the circle of comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extended Harmony
In music, extended chords are certain chords (built from thirds) or triads with notes ''extended'', or added, beyond the seventh. Ninth, eleventh, and thirteenth chords are extended chords. The thirteenth is the farthest extension diatonically possible as, by that point, all seven tonal degrees are represented within the chord (the next extension, the fifteenth, is the same as the root of the chord). In practice however, extended chords do not typically use all the chord members; when it is not altered, the fifth is often omitted, as are notes between the seventh and the highest note (i.e., the ninth is often omitted in an eleventh chord; the ninth and eleventh are usually omitted in a thirteenth chord), unless they are altered to give a special texture. Chords extended beyond the seventh are rarely seen in the Baroque era, and are used more frequently in the Classical era. The Romantic era saw greatly increased use of extended harmony. Extended harmony prior to the 20th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jazz Chord
Jazz chords are chords, chord voicings and chord symbols that jazz musicians commonly use in composition, improvisation, and harmony. In jazz chords and theory, most triads that appear in lead sheets or fake books can have sevenths added to them, using the performer's discretion and ear. For example, if a tune is in the key of C, if there is a G chord, the chord-playing performer usually voices this chord as G7. While the notes of a G7 chord are G–B–D–F, jazz often omits the fifth of the chord—and even the root if playing in a group. However, not all jazz pianists leave out the root when they play voicings: Bud Powell, one of the best-known of the bebop pianists, and Horace Silver, whose quintet included many of jazz's biggest names from the 1950s to the 1970s, included the root note in their voicings. Improvising chord-playing musicians who omit the root and fifth are given the option to play other notes. For example, if a seventh chord, such as G7, appears in a lead sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jazz Scale
A jazz scale is any musical scale used in jazz. Many "jazz scales" are common scales drawn from Western European classical music, including the diatonic, whole-tone, octatonic (or diminished), and the modes of the ascending melodic minor. All of these scales were commonly used by late nineteenth and early twentieth-century composers such as Rimsky-Korsakov, Debussy, Ravel and Stravinsky, often in ways that directly anticipate jazz practice. Some jazz scales, such as the bebop scales, add additional chromatic passing tones to the familiar diatonic scales. Theory One important feature of jazz is what theorists call "the principles of chord-scale compatibility": the idea that a sequence of chords will generate a sequence of compatible scales. In classical major-mode harmony, chords typically belong to the same scale. For example, a ii–V–I progression in C major will typically use only the notes of the C diatonic collection. In jazz, a four-chord progression may use four di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |