|
Unprovable
In mathematical logic, independence is the unprovability of a sentence from other sentences. A sentence σ is independent of a given first-order theory ''T'' if ''T'' neither proves nor refutes σ; that is, it is impossible to prove σ from ''T'', and it is also impossible to prove from ''T'' that σ is false. Sometimes, σ is said (synonymously) to be undecidable from ''T''; this is not the same meaning of " decidability" as in a decision problem. A theory ''T'' is independent if each axiom in ''T'' is not provable from the remaining axioms in ''T''. A theory for which there is an independent set of axioms is independently axiomatizable. Usage note Some authors say that σ is independent of ''T'' when ''T'' simply cannot prove σ, and do not necessarily assert by this that ''T'' cannot refute σ. These authors will sometimes say "σ is independent of and consistent with ''T''" to indicate that ''T'' can neither prove nor refute σ. Independence results in set theory Many inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zermelo–Fraenkel Set Theory
In set theory, Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory, named after mathematicians Ernst Zermelo and Abraham Fraenkel, is an axiomatic system that was proposed in the early twentieth century in order to formulate a theory of sets free of paradoxes such as Russell's paradox. Today, Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory, with the historically controversial axiom of choice (AC) included, is the standard form of axiomatic set theory and as such is the most common foundation of mathematics. Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory with the axiom of choice included is abbreviated ZFC, where C stands for "choice", and ZF refers to the axioms of Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory with the axiom of choice excluded. Informally, Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory is intended to formalize a single primitive notion, that of a hereditary well-founded set, so that all entities in the universe of discourse are such sets. Thus the axioms of Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory refer only to pure sets and prevent its models from containing u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
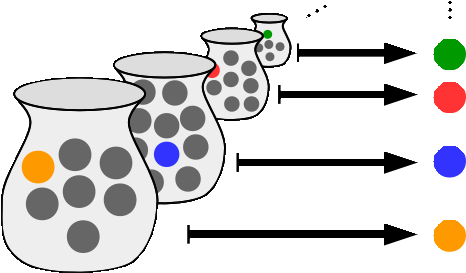
Axiom Of Choice
In mathematics, the axiom of choice, or AC, is an axiom of set theory equivalent to the statement that ''a Cartesian product of a collection of non-empty sets is non-empty''. Informally put, the axiom of choice says that given any collection of sets, each containing at least one element, it is possible to construct a new set by arbitrarily choosing one element from each set, even if the collection is infinite. Formally, it states that for every indexed family (S_i)_ of nonempty sets, there exists an indexed set (x_i)_ such that x_i \in S_i for every i \in I. The axiom of choice was formulated in 1904 by Ernst Zermelo in order to formalize his proof of the well-ordering theorem. In many cases, a set arising from choosing elements arbitrarily can be made without invoking the axiom of choice; this is, in particular, the case if the number of sets from which to choose the elements is finite, or if a canonical rule on how to choose the elements is available – some distinguishin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Logic
Mathematical logic is the study of logic, formal logic within mathematics. Major subareas include model theory, proof theory, set theory, and recursion theory. Research in mathematical logic commonly addresses the mathematical properties of formal systems of logic such as their expressive or deductive power. However, it can also include uses of logic to characterize correct mathematical reasoning or to establish foundations of mathematics. Since its inception, mathematical logic has both contributed to and been motivated by the study of foundations of mathematics. This study began in the late 19th century with the development of axiomatic frameworks for geometry, arithmetic, and Mathematical analysis, analysis. In the early 20th century it was shaped by David Hilbert's Hilbert's program, program to prove the consistency of foundational theories. Results of Kurt Gödel, Gerhard Gentzen, and others provided partial resolution to the program, and clarified the issues involved in pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strongly Inaccessible Cardinal
In set theory, an uncountable cardinal is inaccessible if it cannot be obtained from smaller cardinals by the usual operations of cardinal arithmetic. More precisely, a cardinal is strongly inaccessible if it is uncountable, it is not a sum of fewer than cardinals smaller than , and \alpha < \kappa implies . The term "inaccessible cardinal" is ambiguous. Until about 1950, it meant "weakly inaccessible cardinal", but since then it usually means "strongly inaccessible cardinal". An uncountable cardinal is weakly inaccessible if it is a regular . It is strongly inaccessible, or just inaccessible, if it is a regular strong limit cardinal (this is equivalent to the definition given above). Some authors do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Logic
Mathematical logic is the study of logic, formal logic within mathematics. Major subareas include model theory, proof theory, set theory, and recursion theory. Research in mathematical logic commonly addresses the mathematical properties of formal systems of logic such as their expressive or deductive power. However, it can also include uses of logic to characterize correct mathematical reasoning or to establish foundations of mathematics. Since its inception, mathematical logic has both contributed to and been motivated by the study of foundations of mathematics. This study began in the late 19th century with the development of axiomatic frameworks for geometry, arithmetic, and Mathematical analysis, analysis. In the early 20th century it was shaped by David Hilbert's Hilbert's program, program to prove the consistency of foundational theories. Results of Kurt Gödel, Gerhard Gentzen, and others provided partial resolution to the program, and clarified the issues involved in pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decision Problem
In computability theory and computational complexity theory, a decision problem is a computational problem that can be posed as a yes–no question of the input values. An example of a decision problem is deciding by means of an algorithm whether a given natural number is prime. Another is the problem "given two numbers ''x'' and ''y'', does ''x'' evenly divide ''y''?". The answer is either 'yes' or 'no' depending upon the values of ''x'' and ''y''. A method for solving a decision problem, given in the form of an algorithm, is called a decision procedure for that problem. A decision procedure for the decision problem "given two numbers ''x'' and ''y'', does ''x'' evenly divide ''y''?" would give the steps for determining whether ''x'' evenly divides ''y''. One such algorithm is long division. If the remainder is zero the answer is 'yes', otherwise it is 'no'. A decision problem which can be solved by an algorithm is called ''decidable''. Decision problems typically appear in mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Journal Of Physics
''New Journal of Physics'' is an online-only, open-access, peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in all aspects of physics, as well as interdisciplinary topics where physics forms the central theme. The journal was established in 1998 and is a joint publication of the Institute of Physics and the Deutsche Physikalische Gesellschaft. It is published by IOP Publishing. The editor-in-chief An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The highest-ranking editor of a publication may also be titled editor, managing ... is Andreas Buchleitner ( Albert Ludwigs University). ''New Journal of Physics'' is part of the SCOAP3 initiative. Abstracting and indexing The journal is indexed and abstracted in: References External links * {{Official website, http://iopscience.iop.org/1367-2630 Open access journals Physics journals IOP Publishing academic j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addison-Wesley
Addison-Wesley is an American publisher of textbooks and computer literature. It is an imprint of Pearson PLC, a global publishing and education company. In addition to publishing books, Addison-Wesley also distributes its technical titles through the O'Reilly Online Learning e-reference service. Addison-Wesley's majority of sales derive from the United States (55%) and Europe (22%). The Addison-Wesley Professional Imprint produces content including books, eBooks, and video for the professional IT worker including developers, programmers, managers, system administrators. Classic titles include ''The Art of Computer Programming'', ''The C++ Programming Language'', ''The Mythical Man-Month'', and ''Design Patterns''. History Lew Addison Cummings and Melbourne Wesley Cummings founded Addison-Wesley in 1942, with the first book published by Addison-Wesley being Massachusetts Institute of Technology professor Francis Weston Sears' ''Mechanics''. Its first computer book was ''Progra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer-Verlag
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationally, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chapman & Hall
Chapman & Hall is an imprint owned by CRC Press, originally founded as a British publishing house in London in the first half of the 19th century by Edward Chapman and William Hall. Chapman & Hall were publishers for Charles Dickens (from 1840 until 1844 and again from 1858 until 1870), Thomas Carlyle, William Thackeray, Elizabeth Barrett Browning, Anthony Trollope, Eadweard Muybridge and Evelyn Waugh. History Upon Hall's death in 1847, Chapman's cousin Frederic Chapman began his progress through the ranks of the company and eventually becoming a partner in 1858 and sole proprietor on Edward Chapman's retirement from Chapman & Hall in 1866. In 1868 author Anthony Trollope bought a third of the company for his son, Henry Merivale Trollope. From 1902 to 1930 the company's managing director was Arthur Waugh. In the 1930s the company merged with Methuen, a merger which, in 1955, participated in forming the Associated Book Publishers. The latter was acquired by The Thomson Corp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is called a ''geometer''. Until the 19th century, geometry was almost exclusively devoted to Euclidean geometry, which includes the notions of point, line, plane, distance, angle, surface, and curve, as fundamental concepts. During the 19th century several discoveries enlarged dramatically the scope of geometry. One of the oldest such discoveries is Carl Friedrich Gauss' ("remarkable theorem") that asserts roughly that the Gaussian curvature of a surface is independent from any specific embedding in a Euclidean space. This implies that surfaces can be studied ''intrinsically'', that is, as stand-alone spaces, and has been expanded into the theory of manifolds and Riemannian geometry. Later in the 19th century, it appeared that geometries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Postulate
In geometry, the parallel postulate, also called Euclid's fifth postulate because it is the fifth postulate in Euclid's ''Elements'', is a distinctive axiom in Euclidean geometry. It states that, in two-dimensional geometry: ''If a line segment intersects two straight lines forming two interior angles on the same side that are less than two right angles, then the two lines, if extended indefinitely, meet on that side on which the angles sum to less than two right angles.'' This postulate does not specifically talk about parallel lines; it is only a postulate related to parallelism. Euclid gave the definition of parallel lines in Book I, Definition 23 just before the five postulates. ''Euclidean geometry'' is the study of geometry that satisfies all of Euclid's axioms, ''including'' the parallel postulate. The postulate was long considered to be obvious or inevitable, but proofs were elusive. Eventually, it was discovered that inverting the postulate gave valid, albeit differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |