|
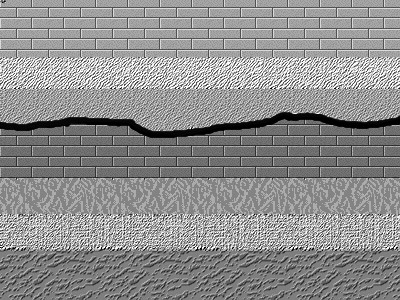
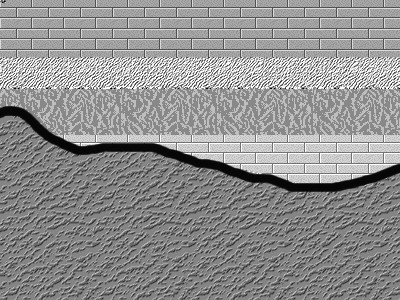
Unconformities
An unconformity is a buried erosional or non-depositional surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval of time before deposition of the younger layer, but the term is used to describe any break in the sedimentary geologic record. The significance of angular unconformity (see below) was shown by James Hutton, who found examples of Hutton's Unconformity at Jedburgh in 1787 and at Siccar Point in 1788. The rocks above an unconformity are younger than the rocks beneath (unless the sequence has been overturned). An unconformity represents time during which no sediments were preserved in a region or were subsequently eroded before the next deposition. The local record for that time interval is missing and geologists must use other clues to discover that part of the geologic history of that area. The interval of geologic time not represented is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hutton's Unconformity
Hutton's Unconformity is a name given to various notable geological sites in Scotland identified by the 18th-century Scottish geologist James Hutton as places where the junction between two types of rock formations can be seen. This geological phenomenon marks the location where rock formations created at different times and by different forces adjoin. For Hutton, such an unconformity provided evidence for his Plutonist theories of uniformitarianism and the age of Earth. An unconformity is any break in the normal progression of sedimentary deposits, which are laid the newer on top of the older. In his search, Hutton and colleagues examined rock outcrops and cliffs, both riverside and sea, and found several locations where two adjoining rock types had been laid bare, the most noted being at Siccar Point on the coast of Berwickshire. Theory of rock formations Hutton hit on a variety of ideas to explain the rock formations he saw, and, after a quarter century of work, he read h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraconformity
An unconformity is a buried erosional or non-depositional surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval of time before deposition of the younger layer, but the term is used to describe any break in the sedimentary geologic record. The significance of angular unconformity (see below) was shown by James Hutton, who found examples of Hutton's Unconformity at Jedburgh in 1787 and at Siccar Point in 1788. The rocks above an unconformity are younger than the rocks beneath (unless the sequence has been overturned). An unconformity represents time during which no sediments were preserved in a region or were subsequently eroded before the next deposition. The local record for that time interval is missing and geologists must use other clues to discover that part of the geologic history of that area. The interval of geologic time not represented is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Unconformity
An unconformity is a buried erosion surface, erosional or non-depositional surface separating two Rock (geology), rock masses or Stratum, strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval of time before deposition of the younger layer, but the term is used to describe any break in the Sedimentary rocks, sedimentary geologic record. The significance of angular unconformity (see below) was shown by James Hutton, who found examples of Hutton's Unconformity at Jedburgh in 1787 and at Siccar Point in 1788. The rocks above an unconformity Law of superposition, are younger than the rocks beneath (unless the sequence has been overturned). An unconformity represents Geologic time, time during which no sediments were preserved in a region or were subsequently eroded before the next deposition. The local record for that time interval is missing and geologists must use other clues to discover th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erosion Surface
In geology and geomorphology, an erosion surface is a surface of rock or regolith that was formed by erosion and not by construction (e.g. lava flows, sediment deposition) nor fault displacement. Erosional surfaces within the stratigraphic record are known as unconformities, but not all unconformities are buried erosion surfaces. Erosion surfaces vary in scale and can be formed on a mountain range or a rock. Particularly large and flat erosion surfaces receive the names of peneplain, paleoplain, planation surface or pediplain. An example of erosion surface is road surface erosion which is caused by natural and anthropogenic factors. Erosion surface can be measured through direct, contact measurement methods and indirect, non-contact measurement methods. Road surface erosion Just like mountains and rocks, erosion can also occur on unsealed roads due to natural and anthropogenic factors. Road surface erosion could be caused by snowfall, rainfall and wind. The material and hydr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disconformity
An unconformity is a buried erosional or non-depositional surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval of time before deposition of the younger layer, but the term is used to describe any break in the sedimentary geologic record. The significance of angular unconformity (see below) was shown by James Hutton, who found examples of Hutton's Unconformity at Jedburgh in 1787 and at Siccar Point in 1788. The rocks above an unconformity are younger than the rocks beneath (unless the sequence has been overturned). An unconformity represents time during which no sediments were preserved in a region or were subsequently eroded before the next deposition. The local record for that time interval is missing and geologists must use other clues to discover that part of the geologic history of that area. The interval of geologic time not represented is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Hutton
James Hutton (; 3 June O.S.172614 June 1726 New Style. – 26 March 1797) was a Scottish geologist, agriculturalist, chemical manufacturer, naturalist and physician. Often referred to as the father of modern geology, he played a key role in establishing geology as a modern science. Hutton advanced the idea that the physical world's remote history can be inferred from evidence in present-day rocks. Through his study of features in the landscape and coastlines of his native Scottish lowlands, such as Salisbury Crags or Siccar Point, he developed the theory that geological features could not be static but underwent continuing transformation over indefinitely long periods of time. From this he argued, in agreement with many other early geologists, that the Earth could not be young. He was one of the earliest proponents of what in the 1830s became known as uniformitarianism, the science which explains features of the Earth's crust as the outcome of continuing natural processes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologic Time
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronology (scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontologists, geophysicists, geochemists, and paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithologies, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardized international units of geologic time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), a constituent body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), whose primary objective is to precisely define ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siccar Point
Siccar Point is a rocky promontory in the county of Berwickshire on the east coast of Scotland. It is famous in the history of geology for Hutton's Unconformity found in 1788, which James Hutton regarded as conclusive proof of his uniformitarian theory of geological development. History Siccar Point was the site of a dun, or small hill fort, in the territory of the ancient Britons. Siccar Point is now in the parish of Cockburnspath but was formerly in the parish of Old Cambus, from which the ancient parish church of St Helen's Chapel survives as a ruin about one kilometre to the west of the point. The church is built in a Romanesque style, in a mixture of Old Red Sandstone believed to have been quarried from the nearby Greenheugh Bay and of the greywacke rock also used in the drystone dyke forming the field boundaries. It is likely that the medieval village of Old Cambus was nearer to Siccar Point than the extant hamlet of Old Cambus. To the south of the point twentieth-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentary Rocks
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles to settle in place. The particles that form a sedimentary rock are called sediment, and may be composed of geological detritus (minerals) or biological detritus (organic matter). The geological detritus originated from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus was formed by bodies and parts (mainly shells) of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies (marine snow). Sedimentation may also occur as dissolved minerals precipitate from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diastem
In geology, a diastem (plural: diastems) is a short interruption in sedimentation with little or no erosion. They can also be described as very short unconformities (more precisely as very short paraconformities).In 1917 Joseph barrel of USA estimated the rate of deposition of succession from the available radiometric age. His accumulation showed that the strata accumulation was at the rate of thousands of years per foot rather than hundreds. He stated that diastems are universal in sedimentary rocks and explain them as a product of fluctuation of base level. Definition The International Commission on Stratigraphy defines a diastem as " short interruption in deposition with little or no erosion before resumption of sedimentation" Duration Studies indicate that the age contained in diastems ranges from a few hundred to a few thousand years in shelf settings as well as throughout the Paleozoic The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentary Rocks
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles to settle in place. The particles that form a sedimentary rock are called sediment, and may be composed of geological detritus (minerals) or biological detritus (organic matter). The geological detritus originated from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus was formed by bodies and parts (mainly shells) of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies (marine snow). Sedimentation may also occur as dissolved minerals precipitate from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphic Rocks
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causing profound physical or chemical changes. During this process, the rock remains mostly in the solid state, but gradually recrystallizes to a new texture or mineral composition. The protolith may be an igneous, sedimentary, or existing metamorphic rock. Metamorphic rocks make up a large part of the Earth's crust and form 12% of the Earth's land surface. They are classified by their protolith, their chemical and mineral makeup, and their texture. They may be formed simply by being deeply buried beneath the Earth's surface, where they are subject to high temperatures and the great pressure of the rock layers above. They can also form from tectonic processes such as continental collisions, which cause horizontal pressure, friction, and distort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





%2C_Sunset.jpg)