|
Umbrella Antenna
An umbrella antenna is a capacitively top-loaded wire monopole antenna, consisting in most cases of a mast fed at the ground end, to which a number of radial wires are connected at the top, sloping downwards. They are used as transmitting antennas below 1 MHz, in the MF, LF and particularly the VLF bands, at frequencies sufficiently low that it is impractical or infeasible to build a full size quarter-wave monopole antenna. The outer end of each radial wire, sloping down from the top of the antenna, is connected by an insulator to a supporting rope or (usually) insulated cable anchored to the ground; the radial wires can also support the mast as guy wires. The radial wires make the antenna look like the wire frame of a giant umbrella (without the cloth) hence the name. Design The antenna is supported by a central steel tubular or lattice mast. The top of the mast is attached to a ring of equally spaced radial wires extending diagonally to near the ground, where each is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monopole Antenna
A monopole antenna is a class of radio antenna consisting of a straight rod-shaped conductor, often mounted perpendicularly over some type of conductive surface, called a ground plane. The driving signal from the transmitter is applied, or for receiving antennas the output signal to the receiver is taken, between the lower end of the monopole and the ground plane. One side of the antenna feedline is attached to the lower end of the monopole, and the other side is attached to the ground plane, which is often the Earth. This contrasts with a dipole antenna which consists of two identical rod conductors, with the signal from the transmitter applied between the two halves of the antenna. The monopole is often used as a resonant antenna; the rod functions as an open resonator for radio waves, oscillating with standing waves of voltage and current along its length. Therefore the length of the antenna is determined by the wavelength of the radio waves it is used with. The most co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Réunion Island
Réunion (; french: La Réunion, ; previously ''Île Bourbon''; rcf, label= Reunionese Creole, La Rényon) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas department and region of France. It is located approximately east of the island of Madagascar and southwest of the island of Mauritius. , it had a population of 868,846. Like the other four overseas departments, Réunion also holds the status of a region of France, and is an integral part of the French Republic. Réunion is an outermost region of the European Union and is part of the eurozone. Réunion and the fellow French overseas department of Mayotte are the only eurozone regions located in the Southern Hemisphere. As in the rest of France, the official language of Réunion is French. In addition, a majority of the region's population speaks Réunion Creole. Toponymy When France took possession of the island in the seventeenth century, it was named Bourbon, after the dynasty that then ruled France. To break ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuned Circuit
An LC circuit, also called a resonant circuit, tank circuit, or tuned circuit, is an electric circuit consisting of an inductor, represented by the letter L, and a capacitor, represented by the letter C, connected together. The circuit can act as an electrical resonator, an electrical analogue of a tuning fork, storing energy oscillating at the circuit's resonant frequency. LC circuits are used either for generating signals at a particular frequency, or picking out a signal at a particular frequency from a more complex signal; this function is called a bandpass filter. They are key components in many electronic devices, particularly radio equipment, used in circuits such as oscillators, filters, tuners and frequency mixers. An LC circuit is an idealized model since it assumes there is no dissipation of energy due to resistance. Any practical implementation of an LC circuit will always include loss resulting from small but non-zero resistance within the components and conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loading Coil
A loading coil or load coil is an inductor that is inserted into an electronic circuit to increase its inductance. The term originated in the 19th century for inductors used to prevent signal distortion in long-distance telegraph transmission cables. The term is also used for inductors in radio antennas, or between the antenna and its feedline, to make an electrically short antenna resonant at its operating frequency. The concept of loading coils was discovered by Oliver Heaviside in studying the problem of slow signalling speed of the first transatlantic telegraph cable in the 1860s. He concluded additional inductance was required to prevent amplitude and time delay distortion of the transmitted signal. The mathematical condition for distortion-free transmission is known as the Heaviside condition. Previous telegraph lines were overland or shorter and hence had less delay, and the need for extra inductance was not as great. Submarine communications cables are particularly sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inductor
An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when electric current flows through it. An inductor typically consists of an insulated wire wound into a coil. When the current flowing through the coil changes, the time-varying magnetic field induces an electromotive force (''emf'') (voltage) in the conductor, described by Faraday's law of induction. According to Lenz's law, the induced voltage has a polarity (direction) which opposes the change in current that created it. As a result, inductors oppose any changes in current through them. An inductor is characterized by its inductance, which is the ratio of the voltage to the rate of change of current. In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of inductance is the henry (H) named for 19th century American scientist Joseph Henry. In the measurement of magnetic circuits, it is equivalent to . Inductors have values that typically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capacitive Reactance
In electrical circuits, reactance is the opposition presented to alternating current by inductance or capacitance. Greater reactance gives smaller current for the same applied voltage. Reactance is similar to resistance in this respect, but does not lead to dissipation of electrical energy as heat; instead, energy is momentarily stored in the reactance, and a quarter-cycle later returned to the circuit. Reactance is used to compute amplitude and phase changes of sinusoidal alternating current going through a circuit element. Like resistance, reactance is measured in ohms, with positive values indicating ''inductive'' reactance and negative indicating ''capacitive'' reactance. It is denoted by the symbol X. An ideal resistor has zero reactance, whereas ideal inductors and capacitors have zero resistance. As frequency increases, inductive reactance increases and capacitive reactance decreases. Comparison to resistance Reactance is similar to resistance in that larger react ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capacitance
Capacitance is the capability of a material object or device to store electric charge. It is measured by the change in charge in response to a difference in electric potential, expressed as the ratio of those quantities. Commonly recognized are two closely related notions of capacitance: ''self capacitance'' and ''mutual capacitance''. An object that can be electrically charged exhibits self capacitance, for which the electric potential is measured between the object and ground. Mutual capacitance is measured between two components, and is particularly important in the operations of the capacitor, a device designed for this purpose as an elementary Linear circuit, linear electronic component. Capacitance is a function only of the geometry of the design of the capacitor, e.g., the opposing surface area of the plates and the distance between them, and the permittivity of the dielectric material between the plates. For many dielectric materials, the permittivity and thus the capaci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
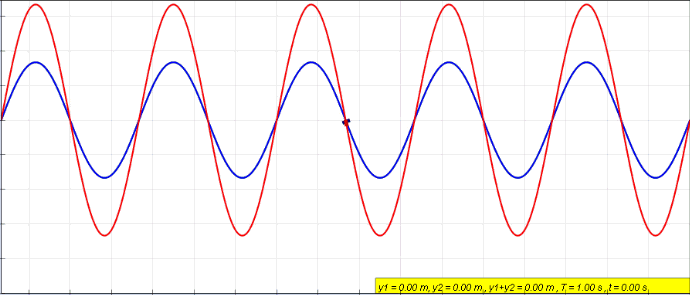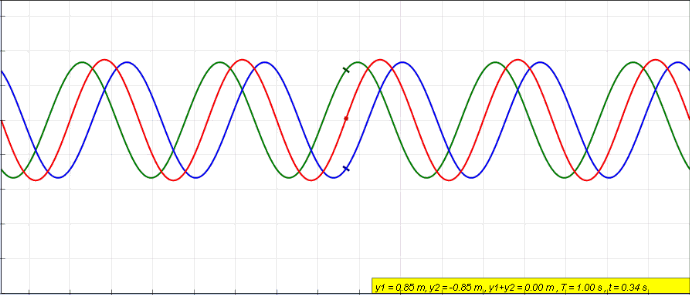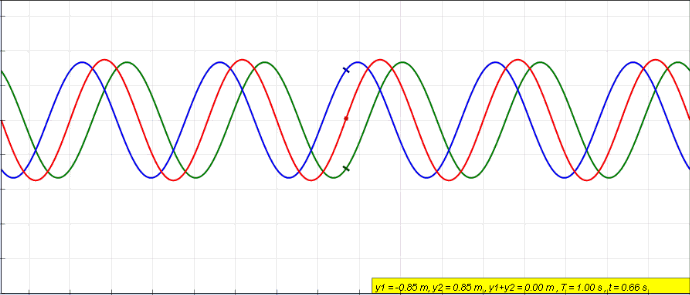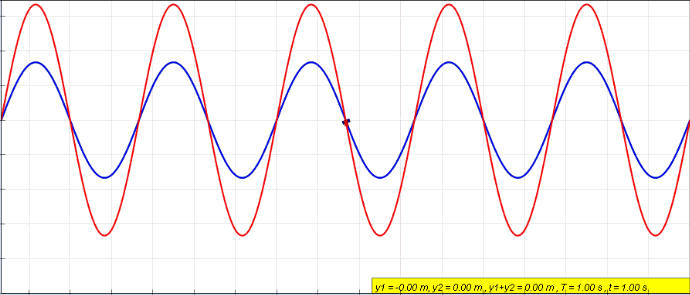
Sine Wave
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or just sinusoid is a curve, mathematical curve defined in terms of the ''sine'' trigonometric function, of which it is the graph of a function, graph. It is a type of continuous wave and also a Smoothness, smooth periodic function. It occurs often in mathematics, as well as in physics, engineering, signal processing and many other fields. Formulation Its most basic form as a function of time (''t'') is: y(t) = A\sin(2 \pi f t + \varphi) = A\sin(\omega t + \varphi) where: * ''A'', ''amplitude'', the peak deviation of the function from zero. * ''f'', ''frequency, ordinary frequency'', the ''Real number, number'' of oscillations (cycles) that occur each second of time. * ''ω'' = 2''f'', ''angular frequency'', the rate of change of the function argument in units of radians per second. * \varphi, ''phase (waves), phase'', specifies (in radians) where in its cycle the oscillation is at ''t'' = 0. When \varphi is non-zero, the entire waveform appears to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standing Wave
In physics, a standing wave, also known as a stationary wave, is a wave that oscillates in time but whose peak amplitude profile does not move in space. The peak amplitude of the wave oscillations at any point in space is constant with respect to time, and the oscillations at different points throughout the wave are in phase. The locations at which the absolute value of the amplitude is minimum are called nodes, and the locations where the absolute value of the amplitude is maximum are called antinodes. Standing waves were first noticed by Michael Faraday in 1831. Faraday observed standing waves on the surface of a liquid in a vibrating container. Franz Melde coined the term "standing wave" (German: ''stehende Welle'' or ''Stehwelle'') around 1860 and demonstrated the phenomenon in his classic experiment with vibrating strings. This phenomenon can occur because the medium is moving in the direction opposite to the movement of the wave, or it can arise in a stationary medium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Resistance
Radiation resistance, \ R_\mathsf\ or \ R_\mathsf\ , is proportional to the part of an antenna's feedpoint electrical resistance that is caused by power loss from the emission of radio waves from the antenna. Radiation resistance is an ''effective'' resistance, due to the power carried away from the antenna as radio waves. Unlike conventional resistance or " Ohmic resistance", radiation resistance is ''not'' due to the opposition to current (resistivity) of the imperfect conducting materials the antenna is made of. The radiation resistance (\ R_\mathsf\ ) is conventionally defined as the value of loss resistance that ''would'' dissipate the same amount of power as heat, as is dissipated by the radio waves emitted from the antenna, when fed at a minimum-voltage / maximum-current point ("voltage node"). From Joule's law, it is equal to the total power \ P_\mathsf\ radiated as radio waves by the antenna, divided by the square of the current \ I_\mathsf\ into the antenna termina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Lengthening
In electrical engineering, electrical length is a dimensionless parameter equal to the physical length of an electrical conductor such as a cable or wire, divided by the wavelength of alternating current at a given frequency traveling through the conductor. ANSI (American National Standards Institute) accredited definition In other words, it is the length of the conductor measured in wavelengths. It can alternately be expressed as an angle, in radians or degrees, equal to the phase shift the alternating current experiences traveling through the conductor. Electrical length is defined for a conductor operating at a specific frequency or narrow band of frequencies. It is determined by the construction of the cable, so different cables of the same length operating at the same frequency can have different electrical lengths. A conductor is called ''electrically long'' if it has an electrical length much greater than one; that is it is much longer than the wavelength of the alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. The inverse of the wavelength is called the spatial frequency. Wavelength is commonly designated by the Greek letter ''lambda'' (λ). The term ''wavelength'' is also sometimes applied to modulated waves, and to the sinusoidal envelopes of modulated waves or waves formed by interference of several sinusoids. Assuming a sinusoidal wave moving at a fixed wave speed, wavelength is inversely proportional to frequency of the wave: waves with higher frequencies have shorter wavelengths, and lower frequencies have longer wavelengths. Wavelength depends on the medium (for example, vacuum, air, or water) that a wav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |