|
Uroporphyrinogen
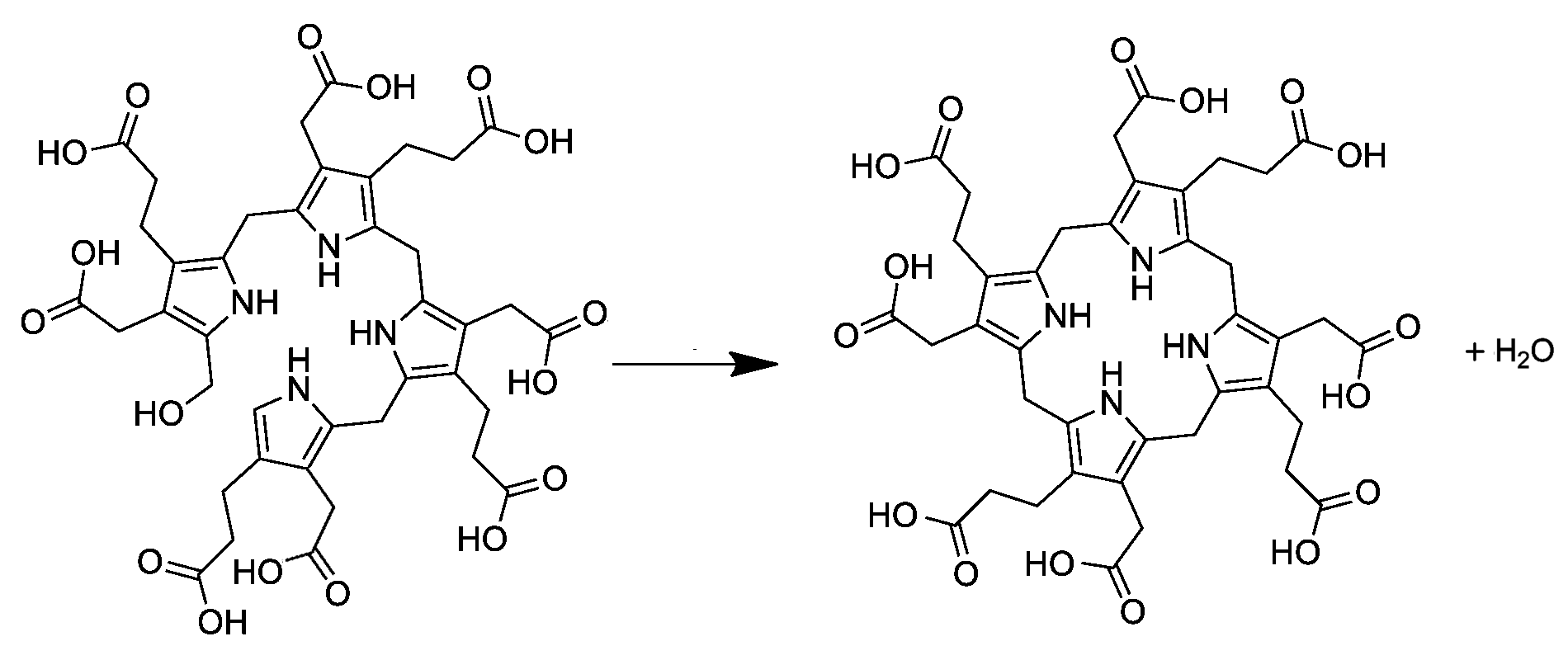
Uroporphyrinogens are cyclic tetrapyrroles with four propionic acid groups ("P" groups) and four acetic acid groups ("A" groups). There are four forms, which vary based upon the arrangements of the "P" and "A" groups (in clockwise order): * In the "I" variety (i.e. uroporphyrinogen I), the order repeats four times: AP-AP-AP-AP. * In the "III" variety (i.e. uroporphyrinogen III), the fourth is reversed: AP-AP-AP-PA. *:This is the most common form. In the synthesis of porphyrin, it is created from the linear tetrapyrrole hydroxymethylbilane by the enzyme uroporphyrinogen III synthase, and is further converted into coproporphyrinogen III Coproporphyrinogen III is a metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of many compounds that are critical for living organisms, such as hemoglobin and chlorophyll. It is a colorless solid. The compound is a porphyrinogen, a class of compounds ... by the enzyme uroporphyrinogen III decarboxylase. * The "II" and "IV" varieties can be created syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uroporphyrinogen III Decarboxylase
Uroporphyrinogen III decarboxylase (uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase, or UROD) is an enzyme () that in humans is encoded by the ''UROD'' gene. Function Uroporphyrinogen III decarboxylase is a homodimeric enzyme () that catalyzes the fifth step in heme biosynthesis, which corresponds to the elimination of carboxyl groups from the four acetate side chains of uroporphyrinogen III to yield coproporphyrinogen III: :uroporphyrinogen III \rightleftharpoons coproporphyrinogen III + 4 CO2 Clinical significance Mutations and deficiency in this enzyme are known to cause familial porphyria cutanea tarda Porphyria cutanea tarda is the most common subtype of porphyria. The disease is named because it is a porphyria that often presents with skin manifestations later in life. The disorder results from low levels of the enzyme responsible for the fift ... and hepatoerythropoietic porphyria. At least 65 disease-causing mutations in this gene have been discovered. Mechanism At low substr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uroporphyrinogen I
Uroporphyrinogen I is an isomer of uroporphyrinogen III, a metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of heme. A type of porphyria is caused by production of uroporphyrinogen I instead of III. Biosynthesis and metabolism In living organisms, uroporphyrinogen I occurs as a side branch of the main porphyrin synthesis pathway. In the normal pathway, the linear tetrapyrrole precursor preuroporphyrinogen (a substituted hydroxymethylbilane) is converted by the enzyme uroporphyrinogen-III cosynthase into the cyclic uroporphyrinogen III; which is then converted to coproporphyrinogen III on the way to porphyrins like heme. Uroporphyrinogen I is instead produced spontaneously from preuroporphyrinogen when the enzyme is not present. The difference between the I and III forms is the arrangement of the four carboxyethyl groups (propionic acid, "P") and the four carboxymethyl groups (acetic acid, "A"). The non-enzymatic conversion to uroporphyrinogen I results in the sequence AP-AP-AP-AP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uroporphyrinogen III
Uroporphyrinogen III is a tetrapyrrole, the first macrocyclic intermediate in the biosynthesis of heme, chlorophyll, vitamin B12, and siroheme. It is a colorless compound, like other porphyrinogens. Structure The molecular structure of uroporphyrinogen III can be described as a hexahydroporphine core, where each pyrrole ring has the hydrogen atoms on its two outermost carbons replaced by an acetic acid group (, "A") and a propionic acid group (, "P"). The groups are attached in an asymmetric way: going around the macrocycle, the order is AP-AP-AP-PA. Biosynthesis and metabolism In the general porphyrin biosynthesis pathway, uroporphyrinogen III is derived from the linear tetrapyrrole preuroporphyrinogen (a substituted hydroxymethylbilane) by the action of the enzyme uroporphyrinogen-III cosynthase. The conversion entails a reversal of the last pyrrole unit (thus swapping the acetic and propionic acid groups) and a condensation reaction that closes the macrocycle by eliminati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxymethylbilane
Hydroxymethylbilane, also known as preuroporphyrinogen, is an organic compound that occurs in living organisms during the synthesis of porphyrins, a group of critical substances that include haemoglobin, myoglobin, and chlorophyll. The name is often abbreviated as HMB. The compound is a substituted bilane, a chain of four pyrrole rings interconnected by methylene bridges . The chain starts with a hydroxymethyl group and ends with an hydrogen, in place of the respective methylene bridges. The other two carbon atoms of each pyrrole cycle are connected to an acetic acid group and a propionic acid group , in that order. The compound is generated from four molecules of porphobilinogen by the enzyme porphobilinogen deaminase: The enzyme uroporphyrinogen III synthase closes the chain to form a porphyrinogen a class of compounds with the hexahydroporphine macrocycle; specifically, uroporphyrinogen III. In the absence of the enzyme, the compound undergoes spontaneous cyclization a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uroporphyrinogen III Synthase
Uroporphyrinogen III synthase () is an enzyme involved in the metabolism of the cyclic tetrapyrrole compound porphyrin. It is involved in the conversion of hydroxymethyl bilane into uroporphyrinogen III. This enzyme catalyses the inversion of the final pyrrole unit (ring D) of the linear tetrapyrrole molecule, linking it to the first pyrrole unit (ring A), thereby generating a large macrocyclic structure, uroporphyrinogen III. The enzyme folds into two alpha/beta domains connected by a beta-ladder, the active site being located between the two domains. Pathology A deficiency is associated with Gunther's disease, also known as congenital erythropoietic porphyria (CEP). This is an autosomal recessive In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and t ... inborn error of metaboli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coproporphyrinogen III
Coproporphyrinogen III is a metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of many compounds that are critical for living organisms, such as hemoglobin and chlorophyll. It is a colorless solid. The compound is a porphyrinogen, a class of compounds characterized by a hexahydroporphine core with various side chains. The coproporphyrinogens have the outermost hydrogen atoms of the core replaced by four methyl groups (M) and four propionic acid Propionic acid (, from the Greek words πρῶτος : ''prōtos'', meaning "first", and πίων : ''píōn'', meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula CH3CH2CO2H. It is a liq ... groups (P). In coproporphyrogen III, the order around the outer ring is MP-MP-MP-PM. For comparison, coproporphyrinogen I has them in the sequence MP-MP-MP-MP. heme. Biosynthesis and metabolism In the main Porphyrin#Synthesis, porphyrin biosynthesis pathway, coproporphyrinogen III is derived f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapyrroles
Tetrapyrroles are a class of chemical compounds that contain four pyrrole or pyrrole-like rings. The pyrrole/pyrrole derivatives are linked by ( =- or -- units), in either a linear or a cyclic fashion. Pyrroles are a five-atom ring with four carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom. Tetrapyrroles are common cofactors in biochemistry and their biosynthesis and degradation feature prominently in the chemistry of life. Some tetrapyrroles form the active core of compounds with crucial biochemical roles in living systems, such as hemoglobin and chlorophyll. In these two molecules, in particular, the pyrrole macrocycle ring frames a metal atom, that forms a coordination compound with the pyrroles and plays a central role in the biochemical function of those molecules. Structure Linear tetrapyrroles (called bilanes) include: *Heme breakdown products (e.g., bilirubin, biliverdin) * Phycobilins (found in cyanobacteria) *Luciferins as found in dinoflagellates and euphausiid shrimps (krill) F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyrin
Porphyrins ( ) are a group of heterocyclic macrocycle organic compounds, composed of four modified pyrrole subunits interconnected at their α carbon atoms via methine bridges (=CH−). The parent of porphyrin is porphine, a rare chemical compound of exclusively theoretical interest. Substituted porphines are called porphyrins. With a total of 26 π-electrons, of which 18 π-electrons form a planar, continuous cycle, the porphyrin ring structure is often described as aromatic. One result of the large conjugated system is that porphyrins typically absorb strongly in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum, i.e. they are deeply colored. The name "porphyrin" derives from the Greek word πορφύρα (''porphyra''), meaning ''purple''. Complexes of porphyrins Concomitant with the displacement of two N-''H'' protons, porphyrins bind metal ions in the N4 "pocket". The metal ion usually has a charge of 2+ or 3+. A schematic equation for these syntheses is shown: :H2porp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propionic Acid
Propionic acid (, from the Greek words πρῶτος : ''prōtos'', meaning "first", and πίων : ''píōn'', meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula CH3CH2CO2H. It is a liquid with a pungent and unpleasant smell somewhat resembling body odor. The anion CH3CH2CO2− as well as the salts and esters of propionic acid are known as propionates or propanoates. History Propionic acid was first described in 1844 by Johann Gottlieb, who found it among the degradation products of sugar. Over the next few years, other chemists produced propionic acid by different means, none of them realizing they were producing the same substance. In 1847, French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas established all the acids to be the same compound, which he called propionic acid, from the Greek words πρῶτος (prōtos), meaning ''first'', and πίων (piōn), meaning ''fat'', because it is the smallest H(CH2)''n''COOH acid that exhib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetic Acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water and other trace elements. Acetic acid is the second simplest carboxylic acid (after formic acid). It is an important Reagent, chemical reagent and industrial chemical, used primarily in the production of cellulose acetate for photographic film, polyvinyl acetate for wood Adhesive, glue, and synthetic fibres and fabrics. In households, diluted acetic acid is often used in descaling agents. In the food industry, acetic acid is controlled by the E number, food additive code E260 as an acidity regulator and as a condiment. In biochemistry, the acetyl group, derived from acetic acid, is fundamental to all forms of life. When bound to coenzyme A, it is central to the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats. The global ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |