|
Undervirilization
Undervirilization is a medical term describing the state of a male whose body, especially the genitalia, shows evidence of below-normal prenatal (less commonly pubertal) androgen effects. See virilization for a more detailed description of the normal process and newborn status. See also * Sexual differentiation * Defeminization and masculinization * Defeminization * Feminization Feminization most commonly refers to: * Feminization (biology), the hormonally induced development of female sexual characteristics * Feminization (activity), a sexual or lifestyle practice where a person assumes a female role * Feminization (soci ... References Medical terminology {{endocrine-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virilization
Virilization or masculinization is the biological development of adult male characteristics in young males or females. Most of the changes of virilization are produced by androgens. Virilization is most commonly used in three medical and biology of sex contexts: prenatal biological sexual differentiation, the postnatal changes of typical chromosomal male (46, XY) puberty, and excessive androgen effects in typical chromosomal females (46, XX). It is also the intended result of androgen replacement therapy in males with delayed puberty and low testosterone. Prenatal virilization In the prenatal period, virilization refers to closure of the perineum, thinning and wrinkling (rugation) of the scrotum, growth of the penis, and closure of the urethral groove to the tip of the penis. In this context, ''masculinization'' is synonymous with ''virilization.'' Prenatal virilization of genetic females and undervirilization of genetic males are common causes of ambiguous genitalia and inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genitalia
A sex organ (or reproductive organ) is any part of an animal or plant that is involved in sexual reproduction. The reproductive organs together constitute the reproductive system. In animals, the testis in the male, and the ovary in the female, are called the ''primary sex organs''. All others are called ''secondary sex organs'', divided between the external sex organs—the genitals or external genitalia, visible at birth in both sexes—and the internal sex organs. Mosses, ferns, and some similar plants have gametangia for reproductive organs, which are part of the gametophyte. The flowers of flowering plants produce pollen and egg cells, but the sex organs themselves are inside the gametophytes within the pollen and the ovule. Coniferous plants likewise produce their sexually reproductive structures within the gametophytes contained within the cones and pollen. The cones and pollen are not themselves sexual organs. Terminology The ''primary sex organs'' are the gonads, a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
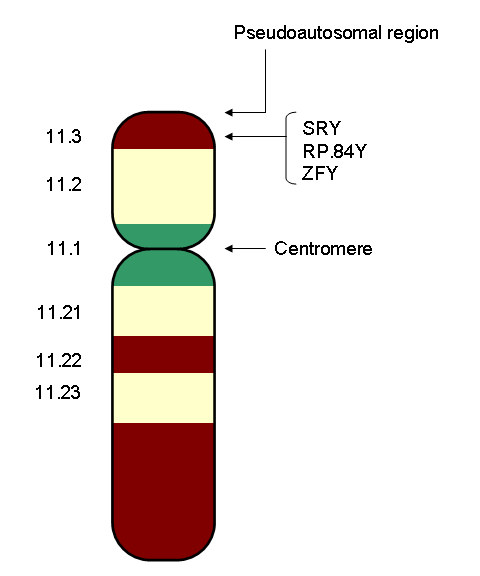
Androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning "man") is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This includes the embryological development of the primary male sex organs, and the development of male secondary sex characteristics at puberty. Androgens are synthesized in the testes, the ovaries, and the adrenal glands. Androgens increase in both males and females during puberty. The major androgen in males is testosterone. Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and androstenedione are of equal importance in male development. DHT ''in utero'' causes differentiation of the penis, scrotum and prostate. In adulthood, DHT contributes to balding, prostate growth, and sebaceous gland activity. Although androgens are commonly thought of only as male sex hormones, females also have them, but at lower levels: they function in libido and sexual arousal. Also, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Differentiation
Sexual differentiation is the process of development of the sex differences between males and females from an undifferentiated zygote. Sex determination is often distinct from sex differentiation; sex determination is the designation for the development stage towards either male or female, while sex differentiation is the pathway towards the development of the phenotype. In many species, testicular or ovarian differentiation begins with appearance of Sertoli cells in males and granulosa cells in females. As male and female individuals develop from embryos into mature adults, sex differences at many levels develop, such as genes, chromosomes, gonads, hormones, anatomy, and psyche. Beginning with determination of sex by genetic and/or environmental factors, humans and other organisms proceed down different pathways of differentiation as they grow and develop. These processes are not fixed, and can change over one organism's lifetime or over many generations evolutionarily. Sex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defeminization And Masculinization
In developmental biology and zoology, defeminization is an aspect of the process of sexual differentiation by which a potential female-specific structure, function, or behavior is changed by one of the processes of male development. Although the term might seem to imply "removal" of female characteristics, in nearly all biological contexts it refers to ''prevention'' of an aspect of female development from manifesting. In human biology of gender, the best known example of this is the prevention of development of the müllerian duct derivatives by anti-müllerian hormone (AMH) in the 3rd and 4th months of fetal development, though the term is not commonly used in discussions of human development. In a number of non-human mammals, there is evidence that hormones produced by the testes act directly on the brain to prevent development of female characteristics, especially female reproductive behavior. In humans, defeminization may be triggered by loss of estrogens or by increased a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defeminization
In developmental biology and zoology, defeminization is an aspect of the process of sexual differentiation by which a potential female-specific structure, function, or behavior is changed by one of the processes of male development. Although the term might seem to imply "removal" of female characteristics, in nearly all biological contexts it refers to ''prevention'' of an aspect of female development from manifesting. In human biology of gender, the best known example of this is the prevention of development of the müllerian duct derivatives by anti-müllerian hormone (AMH) in the 3rd and 4th months of fetal development, though the term is not commonly used in discussions of human development. In a number of non-human mammals, there is evidence that hormones produced by the testes act directly on the brain to prevent development of female characteristics, especially female reproductive behavior. In humans, defeminization may be triggered by loss of estrogens or by increased and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feminization (biology)
In biology and medicine, feminization is the development in an organism of physical characteristics that are usually unique to the female of the species. This may represent a normal developmental process, contributing to sexual differentiation. Feminization can also be induced by environmental factors, and this phenomenon has been observed in several animal species. In the case of transgender hormone therapy, it is intentionally induced artificially. Pathological feminization In animals, when feminization occurs in a male, or at an inappropriate developmental age, it is often due to a genetic or acquired disorder of the endocrine system. In humans, one of the more common manifestations of abnormal feminization is gynecomastia, the inappropriate development of breasts which may result from elevated levels of feminizing hormones such as estrogens. Deficiency or blockage of virilizing hormones (androgens) can also contribute to feminization. In some cases, ''high'' levels of androgen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |