|
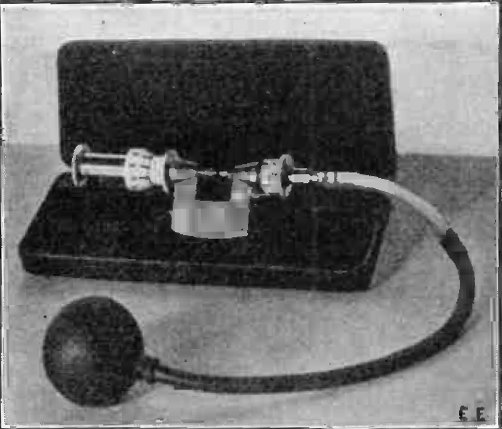
Ultrasound Scanner
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies from person to person and is approximately 20 kilohertz (20,000 hertz) in healthy young adults. Ultrasound devices operate with frequencies from 20 kHz up to several gigahertz. Ultrasound is used in many different fields. Ultrasonic devices are used to detect objects and measure distances. Ultrasound imaging or sonography is often used in medicine. In the nondestructive testing of products and structures, ultrasound is used to detect invisible flaws. Industrially, ultrasound is used for cleaning, mixing, and accelerating chemical processes. Animals such as bats and porpoises use ultrasound for locating prey and obstacles. History Acoustics, the science of sound, starts as far back as Pythagoras in the 6th century BC, who wrot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRL Crown Rump Length 12 Weeks Ecografia Dr
CRL may refer to: Organisations Science and technology research * Chalk River Laboratories, a Canadian nuclear research center * Charles River Laboratories, an American biomedical company * Computational Research Laboratories, an Indian computer company Sports leagues * California Rugby League, governing body for rugby league football in California and surrounding West Coast states in the US * Canada Rugby League, the governing body for rugby league football in Canada * Championship Racing League, a co-sanctioning arrangement between CART and USAC for the 1980 CART PPG Indy Car World Series * Country Rugby League, governing body for rugby league football in rural New South Wales, Australia Other organizations * Canons Regular of the Lateran, a Catholic religious order * Center for Research Libraries, a consortium of North American universities, colleges, and independent research libraries * Co-operative Retail Logistics, part of the Co-operative Group * Corsair International, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
String Instrument
String instruments, stringed instruments, or chordophones are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer plays or sounds the strings in some manner. Musicians play some string instruments by plucking the strings with their fingers or a plectrum—and others by hitting the strings with a light wooden hammer or by rubbing the strings with a bow. In some keyboard instruments, such as the harpsichord, the musician presses a key that plucks the string. Other musical instruments generate sound by striking the string. With bowed instruments, the player pulls a rosined horsehair bow across the strings, causing them to vibrate. With a hurdy-gurdy, the musician cranks a wheel whose rosined edge touches the strings. Bowed instruments include the string section instruments of the orchestra in Western classical music (violin, viola, cello and double bass) and a number of other instruments (e.g., viols and gambas used in early music from the Baro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasound Range Diagram
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies from person to person and is approximately 20 kilohertz (20,000 hertz) in healthy young adults. Ultrasound devices operate with frequencies from 20 kHz up to several gigahertz. Ultrasound is used in many different fields. Ultrasonic devices are used to detect objects and measure distances. Ultrasound imaging or sonography is often used in medicine. In the nondestructive testing of products and structures, ultrasound is used to detect invisible flaws. Industrially, ultrasound is used for cleaning, mixing, and accelerating chemical processes. Animals such as bats and porpoises use ultrasound for locating prey and obstacles. History Acoustics, the science of sound, starts as far back as Pythagoras in the 6th century BC, who wrote o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transducer
A transducer is a device that converts energy from one form to another. Usually a transducer converts a signal in one form of energy to a signal in another. Transducers are often employed at the boundaries of automation, measurement, and control systems, where electrical signals are converted to and from other physical quantities (energy, force, torque, light, motion, position, etc.). The process of converting one form of energy to another is known as transduction. Types * Mechanical transducers, so-called as they convert physical quantities into mechanical outputs or vice versa; * Electrical transducers however convert physical quantities into electrical outputs or signals. Examples of these are: ** a thermocouple that changes temperature differences into a small voltage; ** a linear variable differential transformer (LVDT), used to measure displacement (position) changes by means of electrical signals. Sensors, actuators and transceivers Transducers can be categorized by wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Curie
Pierre Curie ( , ; 15 May 1859 – 19 April 1906) was a French physicist, a pioneer in crystallography, magnetism, piezoelectricity, and radioactivity. In 1903, he received the Nobel Prize in Physics with his wife, Marie Curie, and Henri Becquerel, "in recognition of the extraordinary services they have rendered by their joint researches on the radiation phenomena discovered by Professor Henri Becquerel". With their win, the Curies became the first ever married couple to win the Nobel Prize, launching the Curie family legacy of five Nobel Prizes. Early life Born in Paris on 15 May 1859, Pierre Curie was the son of Eugène Curie (1827–1910), a doctor of French Catholic origin from Alsace, and Sophie-Claire Curie (née Depouilly; 1832–1897). He was educated by his father and in his early teens showed a strong aptitude for mathematics and geometry. When he was 16, he earned his Bachelor of Science in mathematics. By the age of 18, he earned his license, the equivalent of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Curie
Jacques Curie (29 October 1855 – 19 February 1941) was a French physicist and professor of mineralogy at the University of Montpellier. Along with his younger brother, Pierre Curie, he studied pyroelectricity in the 1880s, leading to their discovery of some of the mechanisms behind piezoelectricity. He is buried in the Saint-Lazare cemetery in Montpellier. Biography In 1883, Jacques Curie was appointed professor of mineralogy at the University of Montpellier. This appointment marked the end of his collaboration with his brother Pierre. He remained in Montpellier until his death in 1941 with the exception of the years 1887–1889, which he spent in Algeria, teaching at the School of Science of Algiers and conducting his research. It was not until 1903 that he was appointed to the chair of physics, a position he retained until his retirement in 1925. His son Maurice Curie was a physicist. Research and discoveries The major legacy of Jacques Curie is the discovery of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piezoelectric Effect
Piezoelectricity (, ) is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solid materials—such as crystals, certain ceramics, and biological matter such as bone, DNA, and various proteins—in response to applied Stress (mechanics), mechanical stress. The word ''piezoelectricity'' means electricity resulting from pressure and latent heat. It is derived from the Greek language, Greek word ; ''piezein'', which means to squeeze or press, and ''ēlektron'', which means amber, an ancient source of electric charge. The piezoelectric effect results from the linear electromechanical interaction between the mechanical and electrical states in crystalline materials with no Centrosymmetry, inversion symmetry. The piezoelectric effect is a reversible process (thermodynamics), reversible process: List of piezoelectric materials, materials exhibiting the piezoelectric effect also exhibit the reverse piezoelectric effect, the internal generation of a mechanical strain resulting from an appli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Langevin
Paul Langevin (; ; 23 January 1872 – 19 December 1946) was a French physicist who developed Langevin dynamics and the Langevin equation. He was one of the founders of the ''Comité de vigilance des intellectuels antifascistes'', an anti-fascist organization created after the 6 February 1934 far right riots. Being a public opponent of fascism in the 1930s resulted in his arrest and being held under house arrest by the Vichy government for most of World War II. Langevin was also president of the Human Rights League (LDH) from 1944 to 1946, having recently joined the French Communist Party. He was a doctoral student of Pierre Curie and later a lover of widowed Marie Curie. He is also known for his two US patents with Constantin Chilowsky in 1916 and 1917 involving ultrasonic submarine detection. He is entombed at the Panthéon. Life Langevin was born in Paris, and studied at the '' École de Physique et Chimie'' and the ''École Normale Supérieure''. He then went to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely operated vehicles and Autonomous underwater vehicle, robots, as well as medium-sized or smaller vessels, such as the midget submarine and the wet sub. Submarines are referred to as ''boats'' rather than ''ships'' irrespective of their size. Although experimental submarines had been built earlier, submarine design took off during the 19th century, and they were adopted by several navies. They were first widely used during World War I (1914–1918), and are now used in many navy, navies, large and small. Military uses include attacking enemy surface ships (merchant and military) or other submarines, and for aircraft carrier protection, Blockade runner, blockade running, Ballistic missile submarine, nuclear deterrence, reconnaissance, conventio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whistle
A whistle is an instrument which produces sound from a stream of gas, most commonly air. It may be mouth-operated, or powered by air pressure, steam, or other means. Whistles vary in size from a small slide whistle or nose flute type to a large multi-piped church organ. Whistles have been around since early humans first carved out a gourd or branch and found they could make sound with it. In prehistoric Egypt, small shells were used as whistles. Many present day wind instruments are inheritors of these early whistles. With the rise of more mechanical power, other forms of whistles have been developed. One characteristic of a whistle is that it creates a pure, or nearly pure, tone. The conversion of flow energy to sound comes from an interaction between a solid material and a fluid stream. The forces in some whistles are sufficient to set the solid material in motion. Classic examples are Aeolian tones that result in galloping power lines, or the Tacoma Narrows Bridge (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dog Whistle
A dog whistle (also known as silent whistle or Galton's whistle) is a type of whistle that emits sound in the ultrasonic range, which humans cannot hear but some other animals can, including dogs and domestic cats, and is used in their training. It was invented in 1876 by Francis Galton and is mentioned in his book ''Inquiries into Human Faculty and Its Development'',Galton, Francis (1883) ''Inquiries into Human Faculty and Its Development'' pp. 26-27. in which he describes experiments to test the range of frequencies that could be heard by various animals, such as a house cat. The upper limit of the human hearing range is about 20 kilohertz (kHz) for children, declining to 15–17 kHz for middle-age adults. The top end of a dog's hearing range is about 45 kHz, while a cat's is 64 kHz. It is thought that the wild ancestors of cats and dogs evolved this higher hearing range in order to hear high-frequency sounds made by their preferred prey, small rodents. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |