|
Typewriter-paired Keyboard
A bit-paired keyboard is a keyboard where the layout of shifted keys corresponds to columns in the ASCII (1963) table, archetypally the Teletype Model 33 (1963) keyboard. This was later contrasted with a typewriter-paired keyboard, where the layout of shifted keys corresponds to ''electric'' typewriter layouts, notably the IBM Selectric (1961). The difference is most visible in the digits row (top row): compared with mechanical typewriters, bit-paired keyboards remove the _ character from 6 and shift the remaining &*() from 7890 to 6789, while typewriter-paired keyboards replace 3 characters: from " to @ from _ to ^ and from ' to *. An important subtlety is that ASCII was based on mechanical typewriters, but electric typewriters became popular during the same period that ASCII was adopted, and made their own changes to layout. Thus differences between bit-paired and (electric) typewriter-paired keyboards are due to the differences of both of these from earlier mechanical typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary-coded Decimal
In computing and electronic systems, binary-coded decimal (BCD) is a class of binary encodings of decimal numbers where each digit is represented by a fixed number of bits, usually four or eight. Sometimes, special bit patterns are used for a sign or other indications (e.g. error or overflow). In byte-oriented systems (i.e. most modern computers), the term ''unpacked'' BCD usually implies a full byte for each digit (often including a sign), whereas ''packed'' BCD typically encodes two digits within a single byte by taking advantage of the fact that four bits are enough to represent the range 0 to 9. The precise 4-bit encoding, however, may vary for technical reasons (e.g. Excess-3). The ten states representing a BCD digit are sometimes called '' tetrades'' (for the nibble typically needed to hold them is also known as a tetrade) while the unused, don't care-states are named , ''pseudo-decimals'' or ''pseudo-decimal digits''. BCD's main virtue, in comparison to binary posit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Computer
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or technician. Unlike large, costly minicomputers and mainframes, time-sharing by many people at the same time is not used with personal computers. Primarily in the late 1970s and 1980s, the term home computer was also used. Institutional or corporate computer owners in the 1960s had to write their own programs to do any useful work with the machines. While personal computer users may develop their own applications, usually these systems run commercial software, free-of-charge software ("freeware"), which is most often proprietary, or free and open-source software, which is provided in "ready-to-run", or binary, form. Software for personal computers is typically developed and distributed independently from the hardware or operating system ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
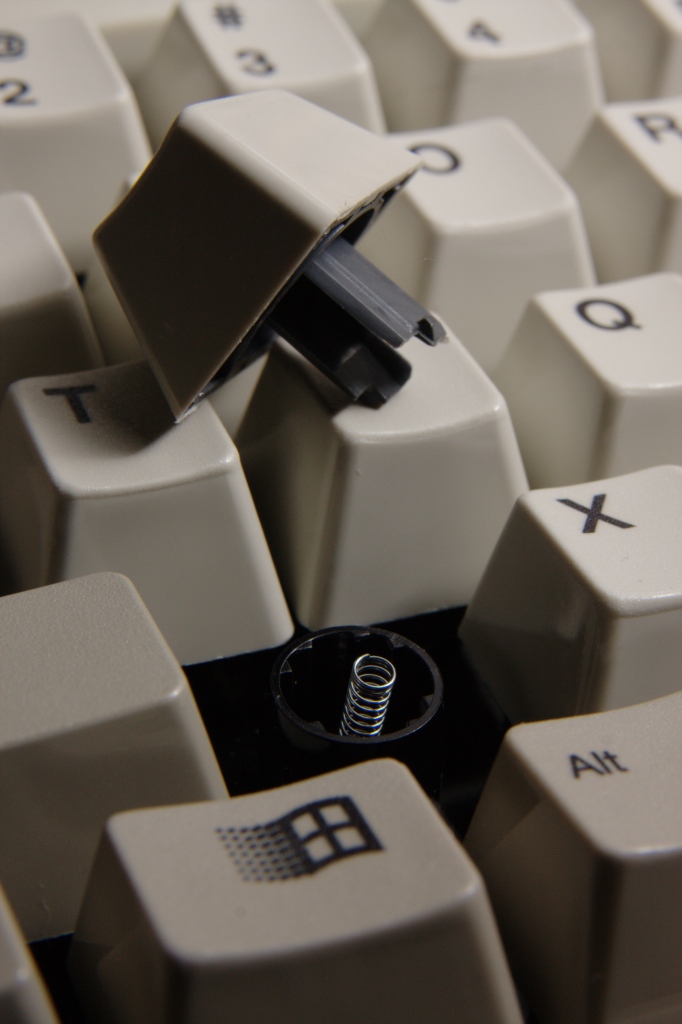
Model M
Model M designates a group of computer keyboards designed and manufactured by IBM starting in 1985, and later by Lexmark International, Maxi Switch, and Unicomp. The keyboard's many variations have their own distinct characteristics, with the vast majority having a buckling-spring key design and swappable keycaps. Model M keyboards have been praised by computer enthusiasts and frequent typists due to their durability and consistency, and the tactile and auditory feedback they provide. The popularity of the IBM PC and its successors made the Model M's design tremendously influential. Almost all later general-purpose computer keyboards mimicked its key layout and other aspects of its ergonomics. The layout was standardized by ISO in 1994 and ANSI in 1998, with minor additions—most notably the Windows key and Menu key. The Model M is regarded as a timeless and durable piece of hardware. Although the computers and computer peripherals produced concurrently with them are con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM PC
The IBM Personal Computer (model 5150, commonly known as the IBM PC) is the first microcomputer released in the IBM PC model line and the basis for the IBM PC compatible de facto standard. Released on August 12, 1981, it was created by a team of engineers and designers directed by Don Estridge in Boca Raton, Florida. The machine was based on open architecture and third-party peripherals. Over time, expansion cards and software technology increased to support it. The PC had a substantial influence on the personal computer market. The specifications of the IBM PC became one of the most popular computer design standards in the world. The only significant competition it faced from a non-compatible platform throughout the 1980s was from the Apple Macintosh product line. The majority of modern personal computers are distant descendants of the IBM PC. History Prior to the 1980s, IBM had largely been known as a provider of business computer systems. As the 1980s opened, their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VT52
The VT50 was a CRT-based computer terminal introduced by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) in July 1974. It provided a display with 12 rows and 80 columns of upper-case text, and used an expanded set of control characters and forward-only scrolling based on the earlier VT05. DEC documentation of the era refers to the terminals as the DECscope, a name that was otherwise almost never seen. The VT50 was sold only for a short period before it was replaced by the VT52 in September 1975. The VT52 provided a screen of 24 rows and 80 columns of text and supported all 95 ASCII characters as well as 32 graphics characters, bi-directional scrolling, and an expanded control character system. DEC produced a series of upgraded VT52's with additional hardware for various uses. The VT52 family was followed by the much more sophisticated VT100 in 1978. Description The VT50 supported asynchronous communication at baud rates up to 9600 bits per second and did not require any fill characters. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Equipment Corporation
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC ), using the trademark Digital, was a major American company in the computer industry from the 1960s to the 1990s. The company was co-founded by Ken Olsen and Harlan Anderson in 1957. Olsen was president until forced to resign in 1992, after the company had gone into precipitous decline. The company produced many different product lines over its history. It is best known for the work in the minicomputer market starting in the mid-1960s. The company produced a series of machines known as the PDP line, with the PDP-8 and PDP-11 being among the most successful minis in history. Their success was only surpassed by another DEC product, the late-1970s VAX "supermini" systems that were designed to replace the PDP-11. Although a number of competitors had successfully competed with Digital through the 1970s, the VAX cemented the company's place as a leading vendor in the computer space. As microcomputers improved in the late 1980s, especially wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple II
The Apple II (stylized as ) is an 8-bit home computer and one of the world's first highly successful mass-produced microcomputer products. It was designed primarily by Steve Wozniak; Jerry Manock developed the design of Apple II's foam-molded plastic case, Rod Holt developed the switching power supply, while Steve Jobs's role in the design of the computer was limited to overseeing Jerry Manock's work on the plastic case. It was introduced by Jobs and Wozniak at the 1977 West Coast Computer Faire, and marks Apple's first launch of a personal computer aimed at a consumer market—branded toward American households rather than businessmen or computer hobbyists. ''Byte'' magazine referred to the Apple II, Commodore PET 2001, and TRS-80 as the "1977 Trinity". As the Apple II had the defining feature of being able to display color graphics, the Apple logo was redesigned to have a spectrum of colors. The Apple II is the first model in the Apple II series, followed by Apple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HP 2640
The HP 2640A and other HP 264X models were block-mode "smart" and intelligent ASCII standard serial terminals produced by Hewlett-Packard using the Intel 8008 and 8080 microprocessors. History The HP 2640A was introduced in November 1974 at a list price of US$3000. Based on the Intel 8008 CPU, it had 8 KB of ROM firmware and came standard with 1 KB of RAM, expandable up to 8 KB (two 4 KB semiconductor RAM cards). In September 1975 Hewlett-Packard introduced the HP 2644A, which was an HP 2640A with mass storage (two mini-tape cartridges, 110 KB each), for US$5000. HP followed up in 1976 with the 2640B, an updated, cost-reduced version of the 2640A with a list price of US$2600, along with three international versions: the Cyrillic-oriented 2640C, the Swedish/Finnish-oriented 2640S, and the Danish/Norwegian-oriented 2640N. All of these early members of the 2640 series had the relatively slow 8008 CPU running at 700 kHz, and they were thus limited to speeds of 2400 baud. The 2640A an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecma International
Ecma International () is a nonprofit standards organization for information and communication systems. It acquired its current name in 1994, when the European Computer Manufacturers Association (ECMA) changed its name to reflect the organization's global reach and activities. As a consequence, the name is no longer considered an acronym and no longer uses full capitalization. The organization was founded in 1961 to standardize computer systems in Europe. Membership is open to large and small companies worldwide that produce, market, or develop computer or communication systems, and have interest and experience in the areas addressed by the group's technical bodies. It is located in Geneva. Aims Ecma aims to develop standards and technical reports to facilitate and standardize the use of information communication technology and consumer electronics; encourage the correct use of standards by influencing the environment in which they are applied; and publish these standards a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Standards Association
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private non-profit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards Standardization or standardisation is the process of implementing and developing technical standards based on the consensus of different parties that include firms, users, interest groups, standards organizations and governments. Standardization ... for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organization also coordinates U.S. standards with international standards so that American products can be used worldwide. ANSI accredits standards that are developed by representatives of other standards organizations, government agency, government agencies, consumer organization, consumer groups, companies, and others. These standards ensure that the characteristics and performance of products are consistent, that people use the same definitions and terms, and that products are tested the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromechanical
In engineering, electromechanics combines processes and procedures drawn from electrical engineering and mechanical engineering. Electromechanics focuses on the interaction of electrical and mechanical systems as a whole and how the two systems interact with each other. This process is especially prominent in systems such as those of DC or AC rotating electrical machines which can be designed and operated to generate power from a mechanical process (generator) or used to power a mechanical effect (motor). Electrical engineering in this context also encompasses electronics engineering. Electromechanical devices are ones which have both electrical and mechanical processes. Strictly speaking, a manually operated switch is an electromechanical component due to the mechanical movement causing an electrical output. Though this is true, the term is usually understood to refer to devices which involve an electrical signal to create mechanical movement, or vice versa mechanical movement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |