|
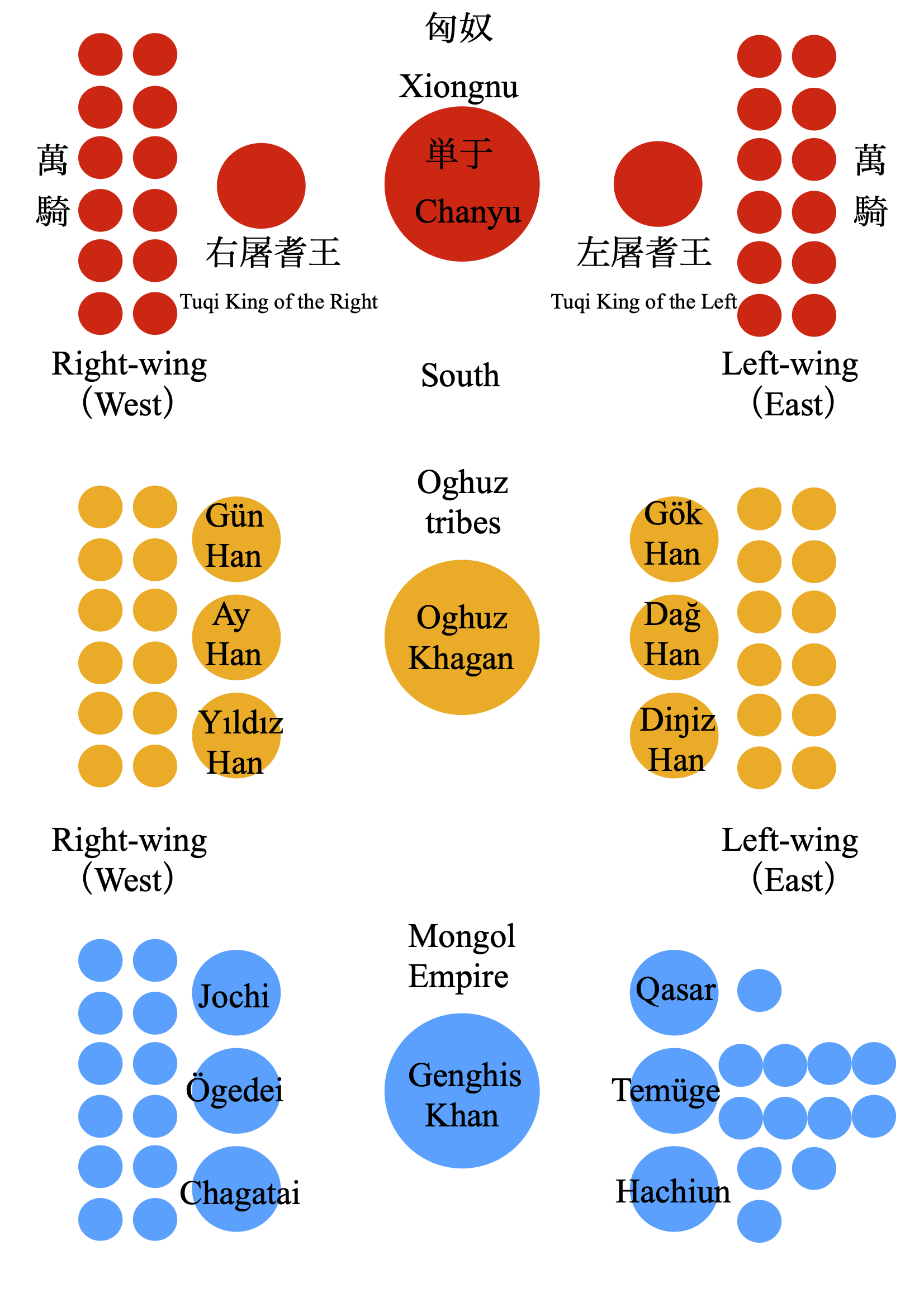
Tuqi
The Tuqi King () was a high office of the Xiongnu, a title also known to the Chinese as "worthy/wise prince/king".Chen (1999), p. 237–277Ma (2005), p. 397–411 In the 6th to 8th centuries, Chinese annalists used the expression 贤王 ''Xian wang'' only in reference to the Eastern Turkic Khaganate. The Tuqi King of the Left was generally designated as the successor of the chanyu. Two titles were awarded with each of them a commander-in-chief who derived his power from the eastern and western territories respectively. These served as two wings alongside the chanyu's main domain. The Chinese annalistic explanation was a "Worthy Prince of the Left (East)" and "Worthy Prince of the Right (West)". This organization of the state was traditional for the Eurasian nomadic states from the Huns to the Turkic Khanates. Etymology N.Ya. Bichurin, using the pronunciation of the Qing dynasty, phoneticized 屠耆 as (russian: Чжуки), which is a direct rendering of the Turkic "wise", maki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 BC, founded the Xiongnu Empire. After their previous rivals, the Yuezhi, migrated west into Central Asia during the 2nd century BC, the Xiongnu became a dominant power on the steppes of East Asia, centred on the Mongolian Plateau. The Xiongnu were also active in areas now part of Siberia, Inner Mongolia, Gansu and Xinjiang. Their relations with adjacent Chinese dynasties to the south-east were complex—alternating between various periods of peace, war, and subjugation. Ultimately, the Xiongnu were defeated by the Han dynasty in a centuries-long conflict, which led to the confederation splitting in two, and forcible resettlement of large numbers of Xiongnu within Han borders. During the Sixteen Kingdoms era, as one of the "Five B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xubu
The Xubu (; LHC: *''sio-pok'') was a tribe of the Xiongnu tribe that flourished between 3rd century BCE to 4th century CE. Chinese annals noted that the Xubu tribe replaced the Huyan tribe, which was an earlier maternal dynastic tribe of the dynastic union with the paternal dynastic tribe Luandi. The traditional system of conjugal unions is a form of the nomadic exogamic society. The male members of the maternal dynastic line were not eligible for the Chanyu throne, only the male members of the Luandi line, whose father was a Luanti Chanyu, and mother was a Xubu Khatun (Queen) were eligible for the supreme throne. A Xubu could only become a Chanyu after a palace coup. The tribe Huyan moved from the Right (Western) Wing, where the maternal dynastic tribe is traditionally assigned, to the Left (Eastern) Wing. The later Hou Hanshu chapter 89, l. 7b) stated that of the noble tribes other than Luanti, Huyan, Xubu, Qiulin and Lan, Huyan already belonged to the dominating Left Wing, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chanyu
Chanyu () or Shanyu (), short for Chengli Gutu Chanyu (), was the title used by the supreme rulers of Inner Asian nomads for eight centuries until superseded by the title "''Khagan''" in 402 CE. The title was most famously used by the ruling Luandi clan of the Xiongnu during the Qin dynasty (221–206 BCE) and Han dynasty (206 BCE–220 CE). It was later also used infrequently by the Chinese as a reference to Gokturk leaders. Etymology According to the ''Book of Han'', "the Xiongnu called the Tian, Heaven (天) ''Tengri, Chēnglí'' (撐犁) and they called a child (子) ''gūtú'' (孤塗). As for ''Chányú'' (單于), it is a "vast [and] great appearance" (廣大之貌).". L. Rogers and Edwin G. Pulleyblank argue that the title ''chanyu'' may be equivalent to the later attested title ''tarkhan'', suggesting that the Chinese pronunciation was originally ''dān-ĥwāĥ'', an approximation for ''*darxan''.Universität Bonn. Seminar für Sprach- und Kulturwissenschaft Zentra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chanyu
Chanyu () or Shanyu (), short for Chengli Gutu Chanyu (), was the title used by the supreme rulers of Inner Asian nomads for eight centuries until superseded by the title "''Khagan''" in 402 CE. The title was most famously used by the ruling Luandi clan of the Xiongnu during the Qin dynasty (221–206 BCE) and Han dynasty (206 BCE–220 CE). It was later also used infrequently by the Chinese as a reference to Gokturk leaders. Etymology According to the ''Book of Han'', "the Xiongnu called the Tian, Heaven (天) ''Tengri, Chēnglí'' (撐犁) and they called a child (子) ''gūtú'' (孤塗). As for ''Chányú'' (單于), it is a "vast [and] great appearance" (廣大之貌).". L. Rogers and Edwin G. Pulleyblank argue that the title ''chanyu'' may be equivalent to the later attested title ''tarkhan'', suggesting that the Chinese pronunciation was originally ''dān-ĥwāĥ'', an approximation for ''*darxan''.Universität Bonn. Seminar für Sprach- und Kulturwissenschaft Zentra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huyan
The Huyan (; LHC: *''ha(C)-jan'' < (~200 BCE): *''hɑ-janH/B'') was a noble house that led the last remnants of the to during the second century after the . The House of Huyan emerged during the political organization that came under 's reign which saw the Xiongnu reach i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)