|
Tungsten(II) Chloride
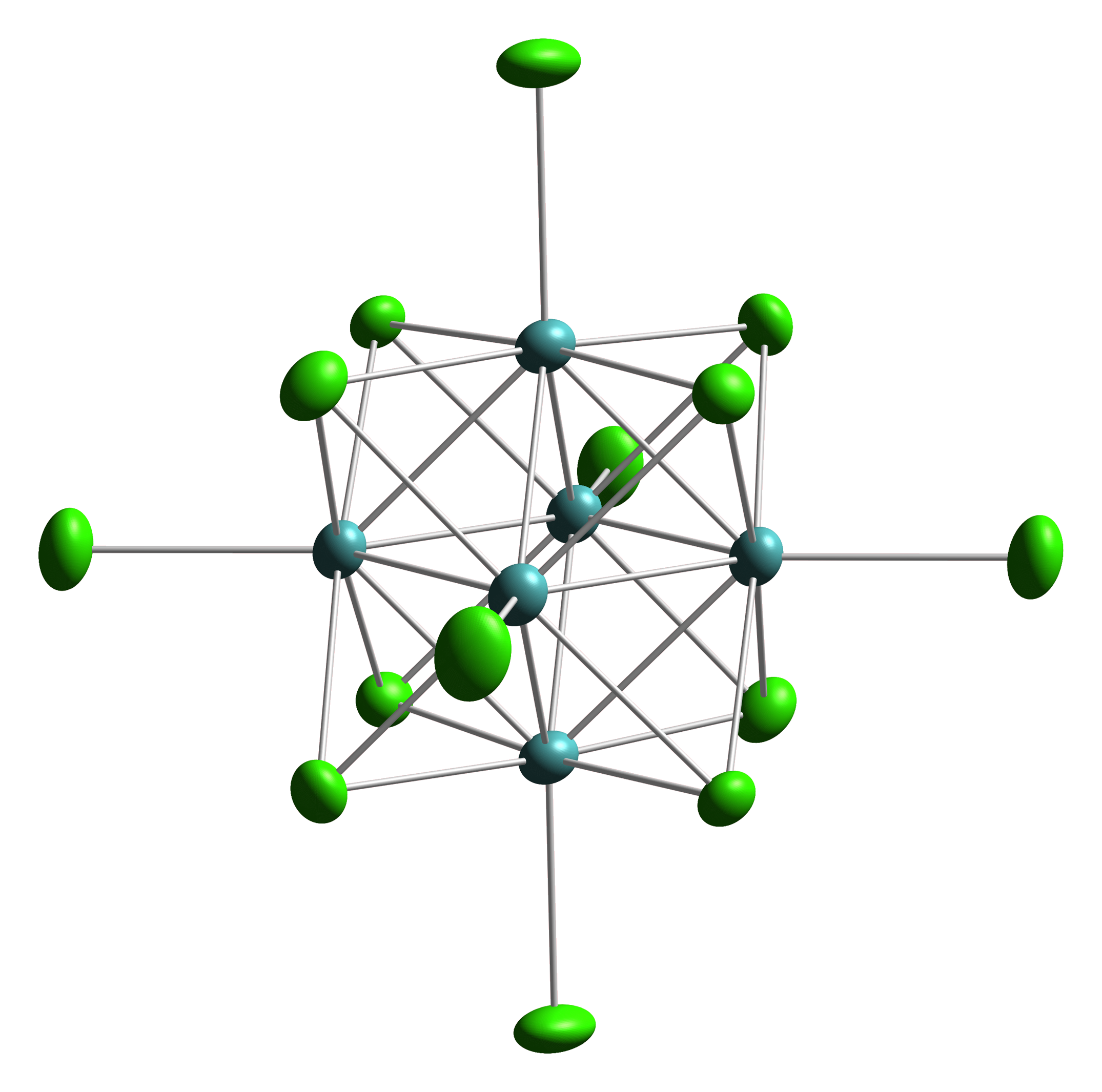
Tungsten(II) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula W6Cl12. It is a polymeric cluster compound. The material dissolves in concentrated hydrochloric acid, forming (H3O)2 6Cl14H2O)x. Heating this salt gives yellow-brown W6Cl12. The structural chemistry resembles that observed for molybdenum(II) chloride Molybdenum dichloride describes chemical compounds with the empirical formula MoCl2. At least two forms are known, and both have attracted much attention from academic researchers because of the unexpected structures seen for these compounds and t .... Tungsten(II) chloride is prepared by reduction of the hexachloride. Bismuth is a typical reductant: :6 WCl6 + 8 Bi → W6Cl12 + 8 BiCl3 :. References {{Chlorides Tungsten halides Chlorides Octahedral compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compound
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation. Some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, etc.), carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbides, and the following salts of inorganic anions: carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, and thiocyanates. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it does not occur within living things. History Friedrich Wöhler's conversion of ammonium cyanate into urea in 1828 is often cited as the starting point of modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part") is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals. The term "polymer" derives from the Greek word πολύς (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and μέρος (''meros'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octahedral Cluster
Octahedral clusters are inorganic or organometallic cluster compounds composed of six metals in an octahedral array.Eric J. Welch and Jeffrey R. Long ''Atomlike Building Units of Adjustable Character: Solid-State and Solution Routes to Manipulating Hexanuclear Transition Metal Chalcohalide Clusters'' in Progress in Inorganic Chemistry, Volume 54 Kenneth D. Karlin 2005''Link/ref> Many types of compounds are known, but all are synthetic. Octahedral chalcogenide and halide clusters These compounds are bound together by metal-metal bonding as well as two kinds of ligands. Ligands that span the faces or edges of the M6 core are labeled Li, for ''inner'' (innen in the original German description), and those ligands attached only to one metal are labeled outer, or La for ''ausser''. Typically, the outer ligands can be exchanged whereas the bridging ligands are more inert toward substitution. Face-capped halide clusters The premier example is of the class is Mo6Cl142−. This dianion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochloric Acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbolised by the chemical formula HA, to dissociate into a proton, H+, and an anion, A-. The dissociation of a strong acid in solution is effectively complete, except in its most concentrated solutions .... It is a component of the gastric acid in the digestive systems of most animal species, including humans. Hydrochloric acid is an important laboratory reagent and industrial chemical. History In the early tenth century, the Persian physician and alchemist Abu Bakr al-Razi ( 865–925, Latin: Rhazes) conducted experiments with sal ammoniac (ammonium chloride) and vitriol (hydrated sulfates of various metals), which he distilled together, thus producing the gas hydrogen chloride. In doing so, al-Razi may have stumbled upon a primitive method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molybdenum(II) Chloride
Molybdenum dichloride describes chemical compounds with the empirical formula MoCl2. At least two forms are known, and both have attracted much attention from academic researchers because of the unexpected structures seen for these compounds and the fact that they give rise to hundreds of derivatives. The form discussed here is Mo6Cl12. The other molybdenum(II) chloride is potassium octachlorodimolybdate. Structure Rather than adopting a close-packed structure typical of metal dihalides, e.g., cadmium chloride, molybdenum(II) chloride forms a structure based on clusters. Molybdenum(II), which is a rather large ion, prefers to form compounds with metal-metal bonds, i.e. metal clusters. In fact all "lower halides" (i.e. where halide/M ratio is 2−. In this anion, each Mo bears one terminal chloride but is otherwise part of an Mo6 octahedron embedded inside a cube defined by eight chloride centers. Thus, the coordination environment of each Mo is four triply bridging chloride l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungsten Halides
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isolated as a metal in 1783. Its important ores include scheelite and wolframite, the latter lending the element its alternate name. The free element is remarkable for its robustness, especially the fact that it has the highest melting point of all known elements barring carbon (which sublimes at normal pressure), melting at . It also has the highest boiling point, at . Its density is , comparable with that of uranium and gold, and much higher (about 1.7 times) than that of lead. Polycrystalline tungsten is an intrinsically brittle and hard material (under standard conditions, when uncombined), making it difficult to work. However, pure single-crystalline tungsten is more ductile and can be cut with a hard-steel hacksaw. Tungsten occurs in many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorides
The chloride ion is the anion (negatively charged ion) Cl−. It is formed when the element chlorine (a halogen) gains an electron or when a compound such as hydrogen chloride is dissolved in water or other polar solvents. Chloride salts such as sodium chloride are often very soluble in water.Green, John, and Sadru Damji. "Chapter 3." ''Chemistry''. Camberwell, Vic.: IBID, 2001. Print. It is an essential electrolyte located in all body fluids responsible for maintaining acid/base balance, transmitting nerve impulses and regulating liquid flow in and out of cells. Less frequently, the word ''chloride'' may also form part of the "common" name of chemical compounds in which one or more chlorine atoms are covalently bonded. For example, methyl chloride, with the standard name chloromethane (see IUPAC books) is an organic compound with a covalent C−Cl bond in which the chlorine is not an anion. Electronic properties A chloride ion (diameter 167 pm) is much larger than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

2Mo6Cl14.jpg)

