|
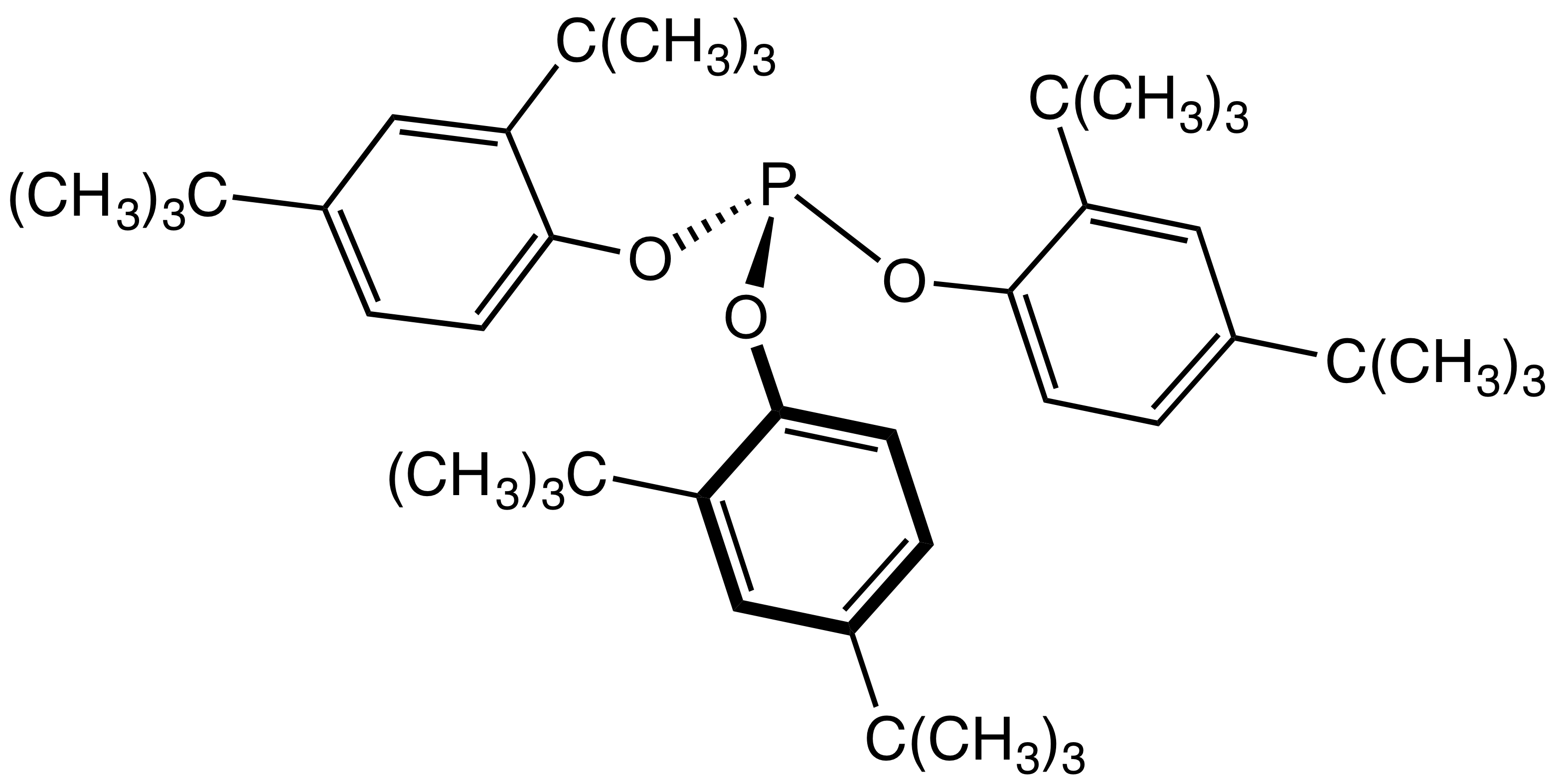
Triphenyl Phosphite Ozonide
Triphenyl phosphite ozonide (TPPO) is a chemical compound with the formula PO3(C6H5O)3 that is used to generate singlet oxygen. When TPPO is mixed with amines, the ozonide breaks down into singlet oxygen and leaves behind triphenyl phosphite. Pyridine is the only known amine that can effectively cause the break down of TPPO while not quenching any of the produced oxygen. Synthesis Triphenyl phosphite ozonide is created by bubbling dry ozone through dichloromethane Dichloromethane (DCM or methylene chloride, methylene bichloride) is an organochlorine compound with the formula . This colorless, volatile liquid with a chloroform-like, sweet odour is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible with ... with triphenyl phosphite being added dropwise at -78 °C. If triphenyl phosphite is added in excess in the synthesis, TPPO can be reduced to triphenyl phosphite oxide, PO(C6H5O)3, and oxygen gas. References Ozonides Organophosphites Phenol ethers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Singlet Oxygen
Singlet oxygen, systematically named dioxygen(singlet) and dioxidene, is a gaseous inorganic chemical with the formula O=O (also written as or ), which is in a quantum state where all electrons are spin paired. It is kinetically unstable at ambient temperature, but the rate of decay is slow. The lowest excited state of the diatomic oxygen molecule is a singlet state. It is a gas with physical properties differing only subtly from those of the more prevalent triplet ground state of O2. In terms of its chemical reactivity, however, singlet oxygen is far more reactive toward organic compounds. It is responsible for the photodegradation of many materials but can be put to constructive use in preparative organic chemistry and photodynamic therapy. Trace amounts of singlet oxygen are found in the upper atmosphere and also in polluted urban atmospheres where it contributes to the formation of lung-damaging nitrogen dioxide. It often appears and coexists confounded in environments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group (these may respectively be called alkylamines and arylamines; amines in which both types of substituent are attached to one nitrogen atom may be called alkylarylamines). Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline; Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine (). The substituent is called an amino group. Compounds with a nitrogen atom attached to a carbonyl group, thus having the structure , are called amides and have different chemical properties from amines. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number of substituents on nitrogen. Aliphatic amines contain only H and alkyl substituents. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozonide
Ozonide is the polyatomic anion . Cyclic organic compounds formed by the addition of ozone () to an alkene are also called ozonides. Ionic ozonides Inorganic ozonides are dark red salts. The anion has the bent shape of the ozone molecule. Inorganic ozonides are formed by burning potassium, rubidium, or caesium in ozone, or by treating the alkali metal hydroxide with ozone; this yields potassium ozonide, rubidium ozonide, and caesium ozonide respectively. They are very sensitive explosives that have to be handled at low temperatures in an atmosphere consisting of an inert gas. Lithium and sodium ozonide are extremely labile and must be prepared by low-temperature ion exchange starting from . Sodium ozonide, , which is prone to decomposition into NaOH and , was previously thought to be impossible to obtain in pure form. However, with the help of cryptands and methylamine, pure sodium ozonide may be obtained as red crystals isostructural to . Ionic ozonides are being investigate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triphenyl Phosphite
Triphenyl phosphite is the organophosphorus compound with the formula P(OC6H5)3. It is a colourless viscous liquid. Preparation Triphenylphosphite is prepared from phosphorus trichloride and phenol in the presence of a catalytic amount of base: :PCl3 + 3 HOC6H5 → P(OC6H5)3 + 3 HCl Reactions Triphenylphosphite is a precursor to trimethylphosphine, it serves as a source of P3+ that is less electrophilic than phosphorus trichloride: : (C6H5O)3P + 3CH3MgBr → P(CH3)3 + 3"MgBrOC6H5" Triphenylphosphite is quaternized by methyl iodide: : (C6H5O)3P + CH3I → H3(C6H5O)3Psup>+I− Coordination complexes Triphenylphosphite is a common ligand in coordination chemistry. It forms zero-valent complexes of the type M (OC6H5)3sub>4 (M = Ni, Pd, Pt). The nickel complex can be prepared by displacement of the diene from bis(cyclooctadiene)nickel Bis(cyclooctadiene)nickel(0) is the organonickel compound with the formula Ni(C8H12)2, also written Ni(cod)2. It is a diamagnetic coordinatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyridine-N-oxide
Pyridine-''N''-oxide is the heterocyclic compound with the formula C5H5NO. This colourless, hygroscopic solid is the product of the oxidation of pyridine. It was originally prepared using peroxyacids as the oxidising agent. The compound is used infrequently as an oxidizing reagent in organic synthesis. Structure The structure of pyridine-N-oxide is very similar to that of pyridine with respect to the parameters for the ring. The molecule is planar. The N-O distance is 1.34Å. The C-N-C angle is 124°, 7° wider than in pyridine. Synthesis The oxidation of pyridine can be achieved with a number of peracids including peracetic acid and perbenzoic acid. Oxidation can also be effected by a modified Dakin reaction using a urea-hydrogen peroxide complex, and sodium perborate or, using methylrhenium trioxide () as catalyst, with sodium percarbonate. Reactions Pyridine ''N''-oxide is five orders of magnitude less basic than pyridine, but it is isolable as a hydrochloride salt, 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozone
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lower atmosphere to (dioxygen). Ozone is formed from dioxygen by the action of ultraviolet (UV) light and electrical discharges within the Earth's atmosphere. It is present in very low concentrations throughout the latter, with its highest concentration high in the ozone layer of the stratosphere, which absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Ozone's odour is reminiscent of chlorine, and detectable by many people at concentrations of as little as in air. Ozone's O3 structure was determined in 1865. The molecule was later proven to have a bent structure and to be weakly diamagnetic. In standard conditions, ozone is a pale blue gas that condenses at cryogenic temperatures to a dark blue liquid and finally a violet-black soli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichloromethane
Dichloromethane (DCM or methylene chloride, methylene bichloride) is an organochlorine compound with the formula . This colorless, volatile liquid with a chloroform-like, sweet odour is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible with water, it is slightly polar, and miscible with many organic solvents.Rossberg, M. ''et al.'' (2006) "Chlorinated Hydrocarbons" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. . Occurrence Natural sources of dichloromethane include oceanic sources, macroalgae, wetlands, and volcanoes. However, the majority of dichloromethane in the environment is the result of industrial emissions. Production DCM is produced by treating either chloromethane or methane with chlorine gas at 400–500 °C. At these temperatures, both methane and chloromethane undergo a series of reactions producing progressively more chlorinated products. In this way, an estimated 400,000 tons were produced in the US, Europe, and Japan in 1993. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redox
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate (chemistry), substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of Electron, electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. There are two classes of redox reactions: * ''Electron-transfer'' – Only one (usually) electron flows from the reducing agent to the oxidant. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * ''Atom transfer'' – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides, other chemical species can serve the same function. In hydrogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozonides
Ozonide is the polyatomic anion . Cyclic organic compounds formed by the addition of ozone () to an alkene are also called ozonides. Ionic ozonides Inorganic ozonides are dark red salts. The anion has the bent shape of the ozone molecule. Inorganic ozonides are formed by burning potassium, rubidium, or caesium in ozone, or by treating the alkali metal hydroxide with ozone; this yields potassium ozonide, rubidium ozonide, and caesium ozonide respectively. They are very sensitive explosives that have to be handled at low temperatures in an atmosphere consisting of an inert gas. Lithium and sodium ozonide are extremely labile and must be prepared by low-temperature ion exchange starting from . Sodium ozonide, , which is prone to decomposition into NaOH and , was previously thought to be impossible to obtain in pure form. However, with the help of cryptands and methylamine, pure sodium ozonide may be obtained as red crystals isostructural to . Ionic ozonides are being investigate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organophosphites
The general structure of a phosphite ester showing the lone pairs on the P In organic chemistry, a phosphite ester or organophosphite usually refers to an organophosphorous compound with the formula P(OR)3. They can be considered as esters of an unobserved tautomer phosphorous acid, H3PO3, with the simplest example being trimethylphosphite, P(OCH3)3. Some phosphites can be considered esters of the dominant tautomer of phosphorous acid (HP(O)(OH)2). The simplest representative is dimethylphosphite with the formula HP(O)(OCH3)2. Both classes of phosphites are usually colorless liquids. Synthesis ;From PCl3 Phosphite esters are typically prepared by treating phosphorus trichloride with an alcohol. Depending on the synthetic details, this alcoholysis can give the diorganophosphites: :PCl3 + 3 C2H5OH → (C2H5O)2P(O)H + 2 HCl + C2H5Cl Alternatively, when the alcoholysis is conducted in the presence of proton acceptors, one obtains the C3-symmetric trialkoxy deriva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |