|
Trimethylsilyl Chloride
Trimethylsilyl chloride, also known as chlorotrimethylsilane is an organosilicon compound (silyl halide), with the formula (CH3)3SiCl, often abbreviated Me3SiCl or TMSCl. It is a colourless volatile liquid that is stable in the absence of water. It is widely used in organic chemistry. Preparation TMSCl is prepared on a large scale by the ''direct process'', the reaction of methyl chloride with a silicon-copper alloy. The principal target of this process is dimethyldichlorosilane, but substantial amounts of the trimethyl and monomethyl products are also obtained. The relevant reactions are (Me = CH3): : x MeCl + Si → Me3SiCl, Me2SiCl2, MeSiCl3, other products Typically about 2–4% of the product stream is the monochloride, which forms an azeotrope with MeSiCl3. Reactions and uses TMSCl is reactive toward nucleophiles, resulting in the replacement of the chloride. In a characteristic reaction of TMSCl, the nucleophile is water, resulting in hydrolysis to give the hexamethy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetal
In organic chemistry, an acetal is a functional group with the connectivity . Here, the R groups can be organic fragments (a carbon atom, with arbitrary other atoms attached to that) or hydrogen, while the R' groups must be organic fragments not hydrogen. The two R' groups can be equivalent to each other (a "symmetric acetal") or not (a "mixed acetal"). Acetals are formed from and convertible to aldehydes or ketones and have the same oxidation state at the central carbon, but have substantially different chemical stability and reactivity as compared to the analogous carbonyl compounds. The central carbon atom has four bonds to it, and is therefore saturated and has tetrahedral geometry. The term ketal is sometimes used to identify structures associated with ketones (both R groups organic fragments rather than hydrogen) rather than aldehydes and, historically, the term acetal was used specifically for the aldehyde-related cases (having at least one hydrogen in place of an R on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight, where it is used to make cellulose in cell walls, the most abundant carbohydrate in the world. In energy metabolism, glucose is the most important source of energy in all organisms. Glucose for metabolism is stored as a polymer, in plants mainly as starch and amylopectin, and in animals as glycogen. Glucose circulates in the blood of animals as blood sugar. The naturally occurring form of glucose is -glucose, while -glucose is produced synthetically in comparatively small amounts and is less biologically active. Glucose is a monosaccharide containing six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group, and is therefore an aldohexose. The glucose molecule can exist in an open-chain (acyclic) as well as ring (cyclic) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Chromatography
Gas chromatography (GC) is a common type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without decomposition. Typical uses of GC include testing the purity of a particular substance, or separating the different components of a mixture. In preparative chromatography, GC can be used to prepare pure compounds from a mixture. Gas chromatography is also sometimes known as vapor-phase chromatography (VPC), or gas–liquid partition chromatography (GLPC). These alternative names, as well as their respective abbreviations, are frequently used in scientific literature. Gas chromatography is the process of separating compounds in a mixture by injecting a gaseous or liquid sample into a mobile phase, typically called the carrier gas, and passing the gas through a stationary phase. The mobile phase is usually an inert gas or an unreactive gas such as helium, argon, nitrogen or hydrogen. The stationary phase is a microscopic l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimethylsilyl
A trimethylsilyl group (abbreviated TMS) is a functional group in organic chemistry. This group consists of three methyl groups bonded to a silicon atom minus;Si(CH3)3 which is in turn bonded to the rest of a molecule. This structural group is characterized by chemical inertness and a large molecular volume, which makes it useful in a number of applications. A trimethylsilyl group bonded to a methyl group forms tetramethylsilane, which is abbreviated as TMS as well. Compounds with trimethylsilyl groups are not normally found in nature. Chemists sometimes use a trimethylsilylating reagent to derivatize rather non-volatile compounds such as certain alcohols, phenols, or carboxylic acids by substituting a trimethylsilyl group for a hydrogen in the hydroxyl groups on the compounds. This way trimethylsiloxy groups minus;O-Si(CH3)3are formed on the molecule. A couple of examples of trimethylsilylating agents include trimethylsilyl chloride and bis(trimethylsilyl)acetamide. Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lability
Lability refers to something that is constantly undergoing change or is likely to undergo change. Biochemistry In reference to biochemistry, this is an important concept as far as kinetics is concerned in metalloproteins. This can allow for the rapid synthesis and degradation of substrates in biological systems. Biology Cells Labile cells refer to cells that constantly divide by entering and remaining in the cell cycle. These are contrasted with "stable cells" and "permanent cells". An important example of this is in the epithelium of the cornea, where cells divide at the basal level and move upwards, and the topmost cells die and fall off. Proteins In medicine, the term "labile" means susceptible to alteration or destruction. For example, a heat-labile protein is one that can be changed or destroyed at high temperatures. The opposite of labile in this context is "stable". Soils Compounds or materials that are easily transformed (often by biological activity) are termed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
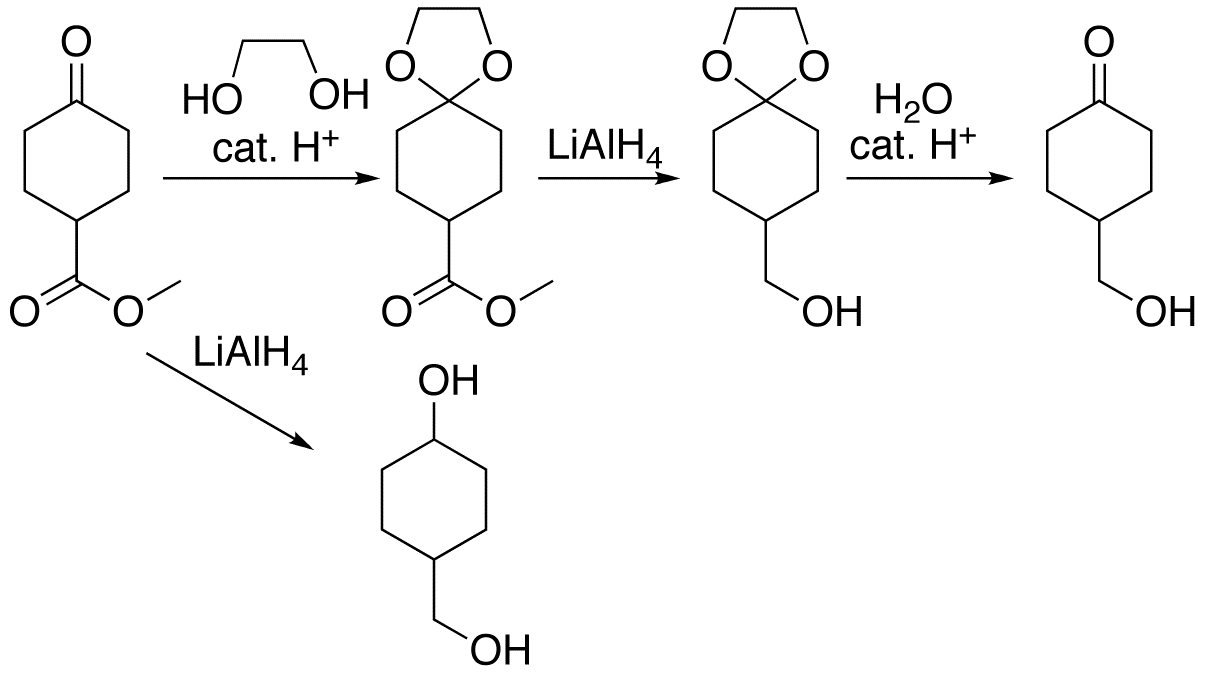
Protecting Group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis. In many preparations of delicate organic compounds, some specific parts of their molecules cannot survive the required reagents or chemical environments. Then, these parts, or groups, must be protected. For example, lithium aluminium hydride is a highly reactive but useful reagent capable of reducing esters to alcohols. It will always react with carbonyl groups, and this cannot be discouraged by any means. When a reduction of an ester is required in the presence of a carbonyl, the attack of the hydride on the carbonyl has to be prevented. For example, the carbonyl is converted into an acetal, which does not react with hydrides. The acetal is then called a protecting group for the carbonyl. After the step involving the hydride is complete, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimethylsilyl
A trimethylsilyl group (abbreviated TMS) is a functional group in organic chemistry. This group consists of three methyl groups bonded to a silicon atom minus;Si(CH3)3 which is in turn bonded to the rest of a molecule. This structural group is characterized by chemical inertness and a large molecular volume, which makes it useful in a number of applications. A trimethylsilyl group bonded to a methyl group forms tetramethylsilane, which is abbreviated as TMS as well. Compounds with trimethylsilyl groups are not normally found in nature. Chemists sometimes use a trimethylsilylating reagent to derivatize rather non-volatile compounds such as certain alcohols, phenols, or carboxylic acids by substituting a trimethylsilyl group for a hydrogen in the hydroxyl groups on the compounds. This way trimethylsiloxy groups minus;O-Si(CH3)3are formed on the molecule. A couple of examples of trimethylsilylating agents include trimethylsilyl chloride and bis(trimethylsilyl)acetamide. Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silyl Ether
Silyl ethers are a group of chemical compounds which contain a silicon atom covalently bonded to an alkoxy group. The general structure is R1R2R3Si−O−R4 where R4 is an alkyl group or an aryl group. Silyl ethers are usually used as protecting groups for alcohols in organic synthesis. Since R1R2R3 can be combinations of differing groups which can be varied in order to provide a number of silyl ethers, this group of chemical compounds provides a wide spectrum of selectivity for protecting group chemistry. Common silyl ethers are: trimethylsilyl (TMS), ''tert''-butyldiphenylsilyl (TBDPS), ''tert''-butyldimethylsilyl (TBS/TBDMS) and triisopropylsilyl (TIPS). They are particularly useful because they can be installed and removed very selectively under mild conditions. Common silyl ethers Formation Commonly silylation of alcohols requires a silyl chloride and an amine base. One reliable and rapid procedure is the Corey protocol in which the alcohol is reacted with a silyl c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group (these may respectively be called alkylamines and arylamines; amines in which both types of substituent are attached to one nitrogen atom may be called alkylarylamines). Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline; Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine (). The substituent is called an amino group. Compounds with a nitrogen atom attached to a carbonyl group, thus having the structure , are called amides and have different chemical properties from amines. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number of substituents on nitrogen. Aliphatic amines contain only H and alkyl substituen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohols
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula . Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (), secondary () and tertiary () alcohols. The suffix ''-ol'' appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority. When a higher priority group is present in the compound, the prefix ''hydroxy-'' is used in its IUPAC name. The suffix ''-ol'' in non-IUPAC names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance is an alcohol. However, some compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silylation
Silylation is the introduction of one or more (usually) substituted silyl groups (R3Si) to a molecule. The process is the basis of organosilicon chemistry. Of organic compounds Alcohols, carboxylic acids, amines, thiols, and phosphates can be silylated. The process involves the replacement of a proton with a trialkylsilyl group, typically trimethylsilyl (-SiMe3). Generally the substrate is deprotonated with a suitable strong base followed by treatment with a silyl chloride (e.g. trimethylsilyl chloride). Often strong bases such butyl lithium or a Grignard reagent are used, as illustrated by the synthesis of a trimethylsilyl ethers as protecting groups from an alcohol: :ROH + BuLi → ROLi + BuH :ROLi + Me3SiCl → ROSiMe3 + LiCl Bis(trimethylsilyl)acetamide ("BSA", Me3SiNC(OSiMe3)Me is an efficient silylation agent used for the derivatisation of compounds. The reaction of BSA with alcohols gives the corresponding trimethylsilyl ether, together with N-(trimethylsilyl)acetamide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


silyl.png)

