|
Triangulation (chess)
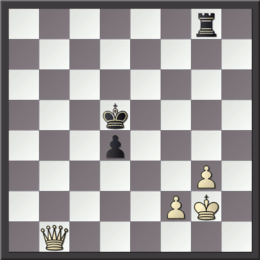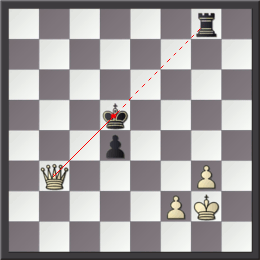
Triangulation is a tactic used in chess to put one's opponent in zugzwang (a position when it is a disadvantage to move). Triangulation is also called ''losing a tempo'' or ''losing a move''. Triangulation occurs most commonly in endgames with only kings and pawns when one king can maneuver on three adjacent squares in the shape of a triangle and maintain the basic position while the opposing king only has two such squares. Thus, if one king triangulates by using three moves to return to the original square and the opposing king cannot do the same, he has lost a crucial tempo and reached the same position with the other player to move. Triangulation can occur in other endgames and even in some middlegames. Example Consider this position, with White to move. Here, Black has the opposition and is keeping the white king out. However, if White had the opposition (i.e. it were Black's move in this position), the black king would have to move away from d7 and allow the white ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess Tactics
In chess, a tactic is a sequence of moves that each makes one or more immediate threats ─ that is, a Check (chess), check, a Glossary of chess#material, material threat, a Checkmate, checkmating sequence threat, or the threat of another tactic ─ which culminates in the opponent being unable to respond to all of the threats without conceding an immediate benefit to the opponent. Most often, the immediate benefit takes the form of a material advantage or checkmating attack; however, some tactics are used for defensive purposes and can salvage material that would otherwise be lost, or to induce stalemate in an otherwise lost position. Tactics are usually contrasted with Chess strategy, strategy, whereby the individual moves by themselves don't make indefensible threats, and the cumulative advantage of the moves takes longer to be capitalised on. In rough terms, the dichotomy can be summarised as tactics concerning short-term play and strategy concerning long-term play. Examples of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Chess Champion
The World Chess Championship is played to determine the world champion in chess. The current world champion is Magnus Carlsen of Norway, who has held the title since 2013. The first event recognized as a world championship was the 1886 match between the two leading players in the world, Wilhelm Steinitz and Johannes Zukertort. Steinitz won, becoming the first world champion. From 1886 to 1946, the champion set the terms, requiring any challenger to raise a sizable stake and defeat the champion in a match in order to become the new world champion. Following the death of reigning world champion Alexander Alekhine in 1946, FIDE (the International Chess Federation) took over administration of the World Championship, beginning with the 1948 World Championship tournament. From 1948 to 1993, FIDE organized a set of tournaments to choose a new challenger every three years. In 1993, reigning champion Garry Kasparov broke away from FIDE, which led to a rival claimant to the title of W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FIDE
The International Chess Federation or World Chess Federation, commonly referred to by its French acronym FIDE ( Fédération Internationale des Échecs), is an international organization based in Switzerland that connects the various national chess federations and acts as the governing body of international chess competition. FIDE was founded in Paris, France, on July 20, 1924.World Chess Federation FIDE (April 8, 2009). Retrieved on 2013-07-28. Its motto is ''Gens una sumus'', Latin for "We are one Family". In 1999, FIDE was recognized by the (IOC). As of May 2022, there are 200 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knight (chess)
The knight (♘, ♞) is a piece in the game of chess, represented by a horse's head and neck. It moves two squares vertically and one square horizontally, or two squares horizontally and one square vertically, jumping over other pieces. Each player starts the game with two knights on the b- and g-, each located between a rook and a bishop. Movement Compared to other chess pieces, the knight's movement is unique: it moves two squares vertically and one square horizontally, or two squares horizontally and one square vertically (with both forming the shape of a capital L). When moving, the knight can jump over pieces to reach its destination. Knights capture in the same way, replacing the enemy piece on the square and removing it from the board. A knight can have up to eight available moves at once. Knights and pawns are the only pieces that can be moved in the chess starting position. Value Knights and bishops, also known as , have a value of about three pawns. Bishops utili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop (chess)
The bishop (♗, ♝) is a piece in the game of chess. It moves and captures along without jumping over intervening pieces. Each player begins the game with two bishops. One starts between the and the king, the other between the and the queen. The starting squares are c1 and f1 for White's bishops, and c8 and f8 for Black's bishops. Placement and movement The king's bishop is placed between the king and the king's knight, f1 for White and f8 for Black; the queen's bishop is placed between the queen and the queen's knight, c1 for White and c8 for Black. The bishop has no restrictions in distance for each move but is limited to diagonal movement. It cannot jump over other pieces. A bishop captures by occupying the square on which an enemy piece stands. As a consequence of its diagonal movement, each bishop always remains on one square color. Due to this, it is common to refer to a bishop as a light-squared or dark-squared bishop. Comparison – other pieces Versus rook A r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zugzwang
Zugzwang (German for "compulsion to move", ) is a situation found in chess and other turn-based games wherein one player is put at a disadvantage because of their obligation to make a move; a player is said to be "in zugzwang" when any legal move will worsen their position. Although the term is used less precisely in games such as chess, it is used specifically in combinatorial game theory to denote a move that directly changes the outcome of the game from a win to a loss. Putting the opponent in zugzwang is a common way to help the superior side win a game, and in some cases it is necessary in order to make the win possible. The term ''zugzwang'' was used in German chess literature in 1858 or earlier, and the first known use of the term in English was by World Champion Emanuel Lasker in 1905. The concept of zugzwang was known to chess players many centuries before the term was coined, appearing in an endgame study published in 1604 by Alessandro Salvio, one of the first writers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philidor Position
The Philidor position (or Philidor's position) is a chess endgame involving a drawing technique for the defending side in the rook and pawn versus rook endgame. This technique is known as the ''third defense'' due to the positioning of the defending rook. It was analyzed by François-André Danican Philidor in 1777. Many rook and pawn versus rook endgames reach either the drawn Philidor position or the winning Lucena position. The defending side should try to reach the Philidor position; the attacking side should try to reach the Lucena position. Said grandmaster Jesús de la Villa, " he Lucena and Philidor positionsare the most important positions in this type of endgame ..and in endgame theory." Description The diagram shows an example of Philidor's position. The important characteristics of the position are (from the point of view of the defender): * The defending king (White in this diagram) is on the queening square of the pawn (or adjacent to it). The pawn can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rook (chess)
The rook (; ♖, ♜) is a piece in the game of chess. It may move any number of squares horizontally or vertically without jumping, and it may an enemy piece on its path; additionally, it may participate in castling. Each player starts the game with two rooks, one in each corner on their own side of the board. Formerly, the rook (from Persian رخ ''rokh''/''rukh'', meaning "chariot") was alternatively called the tower, marquess, rector, and comes (count or earl). The term "castle" is considered to be informal, incorrect, or old-fashioned. Placement and movement The white rooks start on squares a1 and h1, while the black rooks start on a8 and h8. The rook moves horizontally or vertically, through any number of unoccupied squares (see diagram). The rook cannot jump over pieces. The rook may capture an enemy piece by moving to the square on which the enemy piece stands, removing it from play. The rook also participates with the king in a special move called castling, wherein i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen (chess)
The queen (♕, ♛) is the most powerful chess piece, piece in the game of chess. It can move any number of squares vertically, horizontally or , combining the powers of the Rook (chess), rook and Bishop (chess), bishop. Each player starts the game with one queen, placed in the middle of the first next to the King (chess), king. Because the queen is the strongest piece, a pawn (chess), pawn is promotion (chess), promoted to a queen in the vast majority of cases. The predecessor to the queen is the ''Ferz (chess), ferz'', a weak piece only able to move or capture one step diagonally, originating from the Persian game of shatranj. The modern queen gained its power and its modern move in Spain in the 15th century during Isabella of Castile, Isabella I's reign, perhaps inspired by her great political power. Placement and movement The white queen starts on d1, while the black queen starts on d8. With the chessboard oriented correctly, the white queen starts on a white square a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Grischuk
Alexander Igorevich Grischuk (born October 31, 1983) is a Russian chess grandmaster. Grischuk was the Russian champion in 2009. He is also a three-time world blitz chess champion (in 2006, 2012 and 2015). He has competed in five Candidates Tournaments: in 2007, 2011 (when he reached the final), 2013, 2018 and 2020. He also reached the semifinals of the 2000 FIDE World Championship. Grischuk has won two team gold-medals, three team silvers, one team bronze, and one individual bronze medal at Chess Olympiads. He also holds three team gold medals, one team silver and individual gold, two silver and one bronze from the World Team Chess Championship. Chess career 1996 In 1996, Grischuk finished in 21st place in the Boys Under-14 section of the World Youth Festival and tied for third place in the same section of the Disney Rapid Chess Championships. 1998 By January 1998 Grischuk had become a FIDE Master, finished 24th in the Moscow leg of the Russian Cup with 6/9, and finish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexey Shirov
Alexei Shirov (, lv, Aleksejs Širovs; born 4 July 1972) is a Latvian and Spanish chess player. Shirov was ranked number two in the world in 1994. He won a match against Vladimir Kramnik in 1998 to qualify to play as challenger for the classical world championship match with Garry Kasparov; it never took place due to a lack of sponsorship. Career Shirov became the world under-16 champion in 1988 and was the runner-up at the World Junior Championship in 1990 (second on tiebreaks to Ilya Gurevich). In the same year, he achieved the title of Grandmaster. Shirov is the winner of numerous international tournaments: Biel 1991, Madrid 1997 (shared first place with Veselin Topalov), Ter Apel 1997, Monte Carlo 1998, Mérida 2000, Paul Keres Memorial Rapid Tournament in Tallinn (2004, 2005, 2011, 2012, 2013), Canadian Open Chess Championship 2005. He reached second on the FIDE rating list in January and July 1994, behind Anatoly Karpov, though Garry Kasparov was excluded from those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opposition (chess)
In chess, opposition (or direct opposition) is a situation in which two kings are two squares apart on the same or . Since kings cannot move adjacent to each other, each king prevents the other's advance, creating a mutual blockade. In this situation, the player not having to move is said to ''have the opposition''. It is a special type of zugzwang and most often occurs in endgames with only kings and pawns. The side with the move may have to move their king away, potentially allowing the opposing king access to important squares. Taking the opposition is a means to an end, normally to force the opponent's king to move to a weaker position, and is not always the best thing to do. There are extensions of direct opposition, such as diagonal opposition and distant opposition, which can be conducive to reaching direct opposition. All three types may be referred to simply as ''opposition'' if the type is unambiguous in context. Direct opposition ''Direct opposition'' is a posit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




