|
Trengestone
Trengestone, sold under the brand names Reteroid, Retroid, and Retrone, is a progestin medication which was formerly used to treat menstrual disorders but is now no longer marketed.http://www.micromedexsolutions.com It is taken by mouth. Side effects of trengestone include headache, fatigue, and breast tenderness among others. Trengestone is a progestin, or a synthetic progestogen, and hence is an agonist of the progesterone receptor, the biological target of progestogens like progesterone. It is not androgenic or estrogenic. Trengestone was introduced for medical use in 1974. It is no longer available. Medical uses Trengestone was used in the treatment of menstrual disorders. It has also been used to induce ovulation, with about a 50% success rate on average. Side effects Side effects of trengestone include headache, fatigue, and breast tenderness among others. It is not androgenic and does not cause masculinization. Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics Trengestone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
20α-Dihydrotrengestone
20α-Dihydrotrengestone (20α-DHTG), also known as 20α-hydroxytrengestone, as well as 6-chloro-20(''S'')-hydroxy-9β,10α-pregna-1,4,6-trien-3-one, is a progestin and the major active metabolite of trengestone. It appears that trengestone is a prodrug of 20α-DHTG, as it is largely transformed into this metabolite when given orally in humans. 20α-DHTG has potent progestogenic activity similarly to trengestone. See also * 20α-Dihydrodydrogesterone * 20α-Dihydroprogesterone 20α-Dihydroprogesterone (20α-DHP), also known as 20α-hydroxyprogesterone (20α-OHP), is a naturally occurring, endogenous progestogen. It is a metabolite of progesterone, formed by the 20α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (20α-HSDs) AKR1C1 ... References Secondary alcohols Chloroarenes Human drug metabolites Enones Pregnanes Progestogens Conjugated dienes {{Genito-urinary-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dydrogesterone
Dydrogesterone, sold under the brand name Duphaston & Dydroboon among others, is a progestin medication which is used for a variety of indications, including threatened or recurrent miscarriage during pregnancy, dysfunctional bleeding, infertility due to luteal insufficiency, dysmenorrhea, endometriosis, secondary amenorrhea, irregular cycles, premenstrual syndrome, and as a component of menopausal hormone therapy. It is taken by mouth. Side effects of dydrogesterone include menstrual irregularities, headache, nausea, breast tenderness, and others. Dydrogesterone is a progestin, or a synthetic progestogen, and hence is an agonist of the progesterone receptor, the biological target of progestogens like progesterone. The medication is an atypical progestogen and does not inhibit ovulation. It has weak antimineralocorticoid activity and no other important hormonal activity. Dydrogesterone was developed in the 1950s and introduced for medical use in 1961. It is available widely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progestin
A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural product, natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a ''synthetic compound, synthetic'' progestogen. Progestogens are used most commonly in hormonal contraception, hormonal birth control and menopausal hormone therapy. They can also be used in the treatment of gynecological conditions, to support fertility and pregnancy, to lower sex hormone levels for various purposes, and for other indications. Progestogens are used alone or in combination with estrogen (medication), estrogens. They are available in a wide variety of drug formulation, formulations and for use by many different route of administration, routes of administration. Examples of progestogens include natural or bioidentical progesterone (medication), progesterone as well as progestins such as medroxyprogesterone acetate and norethisterone. Side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progestogen (medication)
A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural product, natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a ''synthetic compound, synthetic'' progestogen. Progestogens are used most commonly in hormonal contraception, hormonal birth control and menopausal hormone therapy. They can also be used in the treatment of gynecological conditions, to support fertility and pregnancy, to lower sex hormone levels for various purposes, and for other indications. Progestogens are used alone or in combination with estrogen (medication), estrogens. They are available in a wide variety of drug formulation, formulations and for use by many different route of administration, routes of administration. Examples of progestogens include natural or bioidentical progesterone (medication), progesterone as well as progestins such as medroxyprogesterone acetate and norethisterone. Side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progestogen (medication)
A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural product, natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a ''synthetic compound, synthetic'' progestogen. Progestogens are used most commonly in hormonal contraception, hormonal birth control and menopausal hormone therapy. They can also be used in the treatment of gynecological conditions, to support fertility and pregnancy, to lower sex hormone levels for various purposes, and for other indications. Progestogens are used alone or in combination with estrogen (medication), estrogens. They are available in a wide variety of drug formulation, formulations and for use by many different route of administration, routes of administration. Examples of progestogens include natural or bioidentical progesterone (medication), progesterone as well as progestins such as medroxyprogesterone acetate and norethisterone. Side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progestin
A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural product, natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a ''synthetic compound, synthetic'' progestogen. Progestogens are used most commonly in hormonal contraception, hormonal birth control and menopausal hormone therapy. They can also be used in the treatment of gynecological conditions, to support fertility and pregnancy, to lower sex hormone levels for various purposes, and for other indications. Progestogens are used alone or in combination with estrogen (medication), estrogens. They are available in a wide variety of drug formulation, formulations and for use by many different route of administration, routes of administration. Examples of progestogens include natural or bioidentical progesterone (medication), progesterone as well as progestins such as medroxyprogesterone acetate and norethisterone. Side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
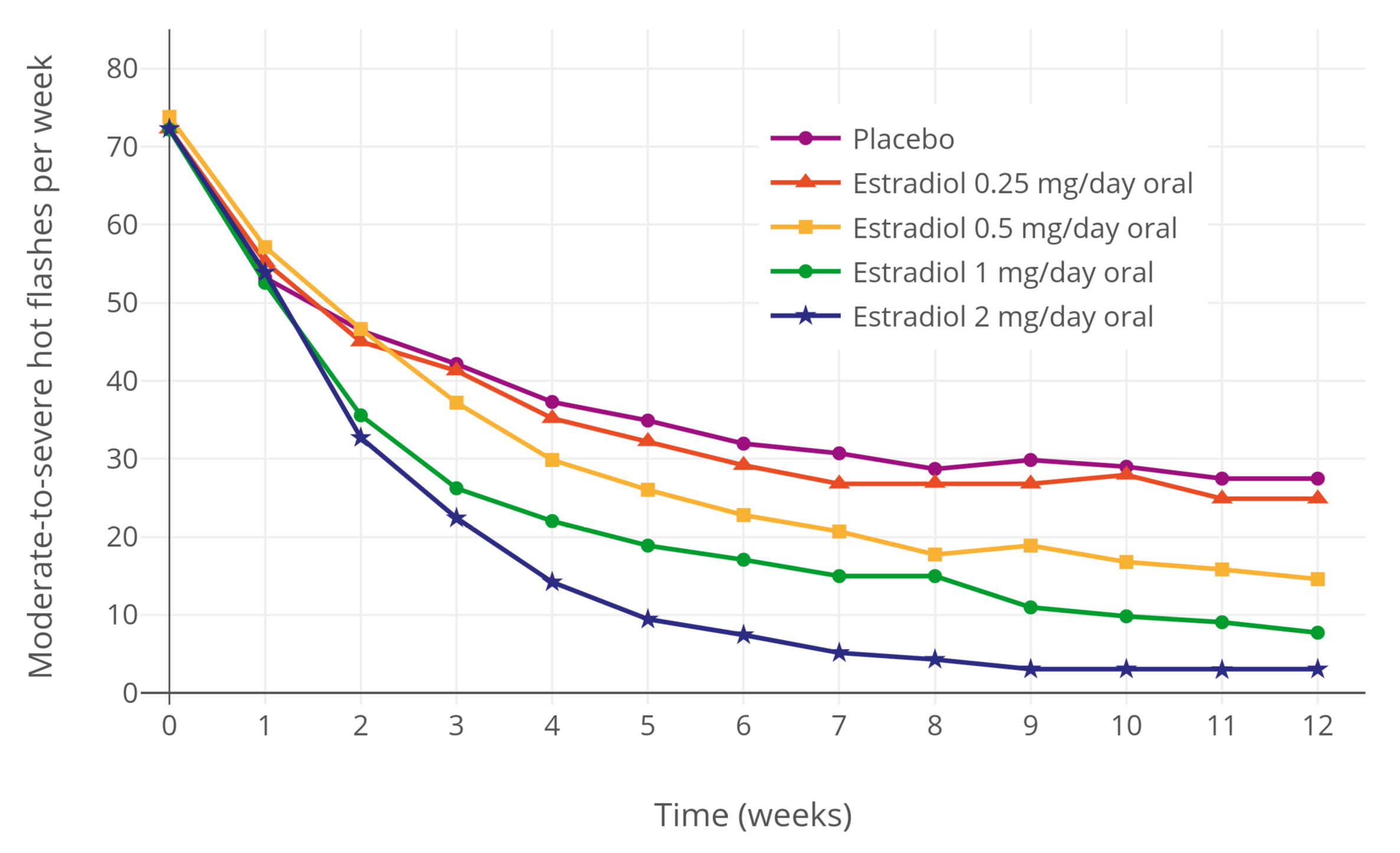
Estrogen (medication)
An estrogen (E) is a type of medication which is used most commonly in hormonal birth control and menopausal hormone therapy, and as part of feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women. They can also be used in the treatment of hormone-sensitive cancers like breast cancer and prostate cancer and for various other indications. Estrogens are used alone or in combination with progestogens. They are available in a wide variety of formulations and for use by many different routes of administration. Examples of estrogens include bioidentical estradiol, natural conjugated estrogens, synthetic steroidal estrogens like ethinylestradiol, and synthetic nonsteroidal estrogens like diethylstilbestrol. Estrogens are one of three types of sex hormone agonists, the others being androgens/anabolic steroids like testosterone and progestogens like progesterone. Side effects of estrogens include breast tenderness, breast enlargement, headache, nausea, fluid retention, and edema among other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovulation Induction
Ovulation induction is the stimulation of ovulation by medication. It is usually used in the sense of stimulation of the development of ovarian follicles Ovulation Induction Retrieved on Mars 7, 2010 to reverse anovulation or oligoovulation. Scope The term ''ovulation induction'' can potentially also be used for: *Final maturation induction, in the sense of triggering ''oocyte release'' from relatively mature ovarian follicles during late follicular phase. In any case, ovarian stimulation (in the sense of stimulating the development of oocytes) is often used in conjunction with triggering oocyte release, such as for proper timing of artificial insemination. *Controlled ovarian hyperstimulation (stimulating the development of multiple follicles of the ovaries in one single cycle), has also appeared in the scope of ovulation induction.IVF.com > Ovulation Induction Retrieved on Mars 7, 2010 Controlled ovarian hyperstimulation is generally part of in vitro fertilization, and the aim i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virilization
Virilization or masculinization is the biological development of adult male characteristics in young males or females. Most of the changes of virilization are produced by androgens. Virilization is most commonly used in three medical and biology of sex contexts: prenatal biological sexual differentiation, the postnatal changes of typical chromosomal male (46, XY) puberty, and excessive androgen effects in typical chromosomal females (46, XX). It is also the intended result of androgen replacement therapy in males with delayed puberty and low testosterone. Prenatal virilization In the prenatal period, virilization refers to closure of the perineum, thinning and wrinkling (rugation) of the scrotum, growth of the penis, and closure of the urethral groove to the tip of the penis. In this context, ''masculinization'' is synonymous with ''virilization.'' Prenatal virilization of genetic females and undervirilization of genetic males are common causes of ambiguous genitalia and inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperthermia
Hyperthermia, also known simply as overheating, is a condition in which an individual's body temperature is elevated beyond normal due to failed thermoregulation. The person's body produces or absorbs more heat than it dissipates. When extreme temperature elevation occurs, it becomes a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment to prevent disability or death. Almost half a million deaths are recorded every year from hyperthermia. The most common causes include heat stroke and adverse reactions to drugs. Heat stroke is an body temperature, acute temperature elevation caused by exposure to excessive heat, or combination of heat and humidity, that overwhelms the heat-regulating mechanisms of the body. The latter is a relatively rare side effect of many drugs, particularly those that affect the central nervous system. Malignant hyperthermia is a rare complication of some types of general anesthesia. Hyperthermia can also be caused by a traumatic brain injury. Hyperthermia di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Temperature
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even when the surrounding temperature is very different. A thermoconforming organism, by contrast, simply adopts the surrounding temperature as its own body temperature, thus avoiding the need for internal thermoregulation. The internal thermoregulation process is one aspect of homeostasis: a state of dynamic stability in an organism's internal conditions, maintained far from thermal equilibrium with its environment (the study of such processes in zoology has been called physiological ecology). If the body is unable to maintain a normal temperature and it increases significantly above normal, a condition known as hyperthermia occurs. Humans may also experience lethal hyperthermia when the wet bulb temperature is sustained above for six hours. The opposite condition, when body temperature decreases below normal levels, is known as hypothermia. It results when the homeostatic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |