|
Trench Nephritis
Trench nephritis, also known as war nephritis, is a kidney infection, first recognised by medical officers as a new disease during the early part of the First World War and distinguished from the then-understood acute nephritis by also having bronchitis and frequent relapses. Trench nephritis was the major kidney problem of the war. The cause was not established at the time, treatments were ineffective, and the condition led to 35,000 British and 2,000 American casualties. The term ''trench nephritis'' was coined by Nathan Raw and was first reported in the ''British Medical Journal'' in 1915 as affecting soldiers of the British Expeditionary Force in Flanders. Soldiers presented with sudden-onset albuminuria, casts in urine, high blood pressure, swelling of legs or face, headache, sore throat and difficulty breathing and bronchitis. Pathology suggested an underlying inflammation of the small blood vessels of the kidneys. Later evidence showed that trench nephritis may have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nephrology
Nephrology (from Greek'' nephros'' "kidney", combined with the suffix ''-logy'', "the study of") is a specialty of adult internal medicine and pediatric medicine that concerns the study of the kidneys, specifically normal kidney function (renal physiology) and kidney disease (renal pathophysiology), the preservation of kidney health, and the treatment of kidney disease, from diet and medication to renal replacement therapy ( dialysis and kidney transplantation). The word “renal” is an adjective meaning “relating to the kidneys”, and its roots are French or late Latin. Whereas according to some opinions, "renal" and "nephro" should be replaced with "kidney" in scientific writings such as "kidney medicine" (instead of nephrology) or "kidney replacement therapy", other experts have advocated preserving the use of renal and nephro as appropriate including in "nephrology" and "renal replacement therapy", respectively. Nephrology also studies systemic conditions that aff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthohantavirus
''Orthohantavirus'' is a genus of single-stranded, enveloped, negative-sense RNA viruses in the family ''Hantaviridae'' within the order ''Bunyavirales''. Members of this genus may be called orthohantaviruses or simply hantaviruses. Orthohantaviruses typically cause chronic asymptomatic infection in rodents. Humans may become infected with hantaviruses through contact with rodent urine, saliva, or feces. Some strains cause potentially fatal diseases in humans, such as hantavirus hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS), or hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS), also known as hantavirus cardiopulmonary syndrome (HCPS), while others have not been associated with known human disease (e.g. Prospect Hill virus). HPS (HCPS) is a "rare respiratory illness associated with the inhalation of aerosolized rodent excreta (urine and feces) contaminated by hantavirus particles." Human infections of hantaviruses have almost entirely been linked to human contact with rodent excrement; however, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proceedings Of The Royal Society Of Medicine
The ''Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine'' is a peer-reviewed medical journal. It is the flagship journal of the Royal Society of Medicine with full editorial independence. Its continuous publication history dates back to 1809. Since July 2005 the editor-in-chief is Kamran Abbasi, who succeeded Robin Fox who was editor for almost 10 years. History The journal was established in 1806 as the ''Medico-Chirurgical Transactions'' published by the Royal Medical and Chirurgical Society of London. It was renamed to ''Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine'' in 1907, following the merger that led to the formation of the Royal Society of Medicine and with volume numbering restarting at 1, before obtaining its current name in 1978. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in MEDLINE/PubMed, Science Citation Index, EMBASE, CAB International, and Elsevier Biobase. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 18.000. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Culture
A blood culture is a medical laboratory test used to detect bacteria or fungi in a person's blood. Under normal conditions, the blood does not contain microorganisms: their presence can indicate a bloodstream infection such as bacteremia or fungemia, which in severe cases may result in sepsis. By culturing the blood, microbes can be identified and tested for resistance to antimicrobial drugs, which allows clinicians to provide an effective treatment. To perform the test, blood is drawn into bottles containing a liquid formula that enhances microbial growth, called a culture medium. Usually, two containers are collected during one draw, one of which is designed for aerobic organisms that require oxygen, and one of which is for anaerobic organisms, that do not. These two containers are referred to as a ''set'' of blood cultures. Two sets of blood cultures are sometimes collected from two different blood draw sites. If an organism only appears in one of the two sets, it is more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Medicine
The Royal Society of Medicine (RSM) is a medical society in the United Kingdom, headquartered in London. History The Society was established in 1805 as Medical and Chirurgical Society of London, meeting in two rooms in barristers’ chambers at Gray's Inn and then moving to Lincoln's Inn Fields where it stayed for 25 years. In 1834 the Society moved to Berners Street and was granted a Royal Charter by King William IV. In 1889 under the leadership of Sir John MacAlister, a Building Committee chaired by Timothy Holmes supervised the move of the quarters of the Society from Berners Street to 20 Hanover Square. In 1905 an eleven-member committee headed by Sir Richard Douglas Powell organised the celebration of the Society's centenary. Two years later the Royal Medical and Chirurgical Society of London came together with seventeen specialist medical societies and, with a supplementary Royal Charter granted by Edward VII, became the Royal Society of Medicine. In 1910 the Society ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Bartholomew's Hospital
St Bartholomew's Hospital, commonly known as Barts, is a teaching hospital located in the City of London. It was founded in 1123 and is currently run by Barts Health NHS Trust. History Early history Barts was founded in 1123 by Rahere (died 1144, and entombed in the nearby Priory Church of St Bartholomew the Great), a favourite courtier of King Henry I. The dissolution of the monasteries did not affect the running of Barts as a hospital, but left it in a precarious position by removing its income. It was refounded by King Henry VIII in December 1546, on the signing of an agreement granting the hospital to the Corporation of London.''St Bartholomew's Hospital'' ''Old and New London'': Volume 2 (1878), pp. 359–363. Retrieved 30 January 2009 The hospital became legally styled as the "House of the Poore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Research Council (United Kingdom)
The Medical Research Council (MRC) is responsible for co-coordinating and funding medical research in the United Kingdom. It is part of United Kingdom Research and Innovation (UKRI), which came into operation 1 April 2018, and brings together the UK's seven research councils, Innovate UK and Research England. UK Research and Innovation is answerable to, although politically independent from, the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy. The MRC focuses on high-impact research and has provided the financial support and scientific expertise behind a number of medical breakthroughs, including the development of penicillin and the discovery of the structure of DNA. Research funded by the MRC has produced 32 Nobel Prize winners to date. History The MRC was founded as the Medical Research Committee and Advisory Council in 1913, with its prime role being the distribution of medical research funds under the terms of the National Insurance Act 1911. This was a consequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Oliver (physician)
Sir Thomas Oliver, (1853–1942) was a Scottish physician and expert on industrial hygiene, particularly in the mining industry and antimony workers. He was President of the College of Medicine 1926 to 1934 and President of the Royal Institute of Public Health and Hygiene from 1937 to 1942. Life He was born in St Quivox in Ayrshire on 2 March 1853 the son of James Oliver and his wife, Margaret McMurtrie. He was educated at Ayr Academy then studied medicine at Glasgow University graduating MB ChM in 1874. He undertook some practical experience at Glasgow Royal Infirmary then went to Paris to undertake further postgraduate studies.http://munksroll.rcplondon.ac.uk/Biography/Details/3378 Returning to Britain he worked in Preston Hospital 1875 to 1879. In 1880 he began lecturing at the Medical School of Durham University. In 1889 he was created Professor of Medicine. In 1892 he became a member of the White Lead Commission and was instrumental in banning females from being employed i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scarlet Fever
Scarlet fever, also known as Scarlatina, is an infectious disease caused by ''Streptococcus pyogenes'' a Group A streptococcus (GAS). The infection is a type of Group A streptococcal infection (Group A strep). It most commonly affects children between five and 15 years of age. The signs and symptoms include a sore throat, fever, headache, swollen lymph nodes, and a characteristic rash. The face is flushed and the rash is red and blanching. It typically feels like sandpaper and the tongue may be red and bumpy. The rash occurs as a result of capillary damage by exotoxins produced by ''S.pyogenes''. On darker pigmented skin the rash may be hard to discern. Scarlet fever affects a small number of people who have strep throat or streptococcal skin infections. The bacteria are usually spread by people coughing or sneezing. It can also be spread when a person touches an object that has the bacteria on it and then touches their mouth or nose. The diagnosis is typically confirmed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beriberi
Thiamine deficiency is a medical condition of low levels of thiamine (Vitamin B1). A severe and chronic form is known as beriberi. The two main types in adults are wet beriberi and dry beriberi. Wet beriberi affects the cardiovascular system, resulting in a fast heart rate, shortness of breath, and leg swelling. Dry beriberi affects the nervous system, resulting in numbness of the hands and feet, confusion, trouble moving the legs, and pain. A form with loss of appetite and constipation may also occur. Another type, acute beriberi, found mostly in babies, presents with loss of appetite, vomiting, lactic acidosis, changes in heart rate, and enlargement of the heart. Risk factors include a diet of mostly white rice, alcoholism, dialysis, chronic diarrhea, and taking high doses of diuretics. In rare cases, it may be due to a genetic condition that results in difficulties absorbing thiamine found in food. Wernicke encephalopathy and Korsakoff syndrome are forms of dry beriberi. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
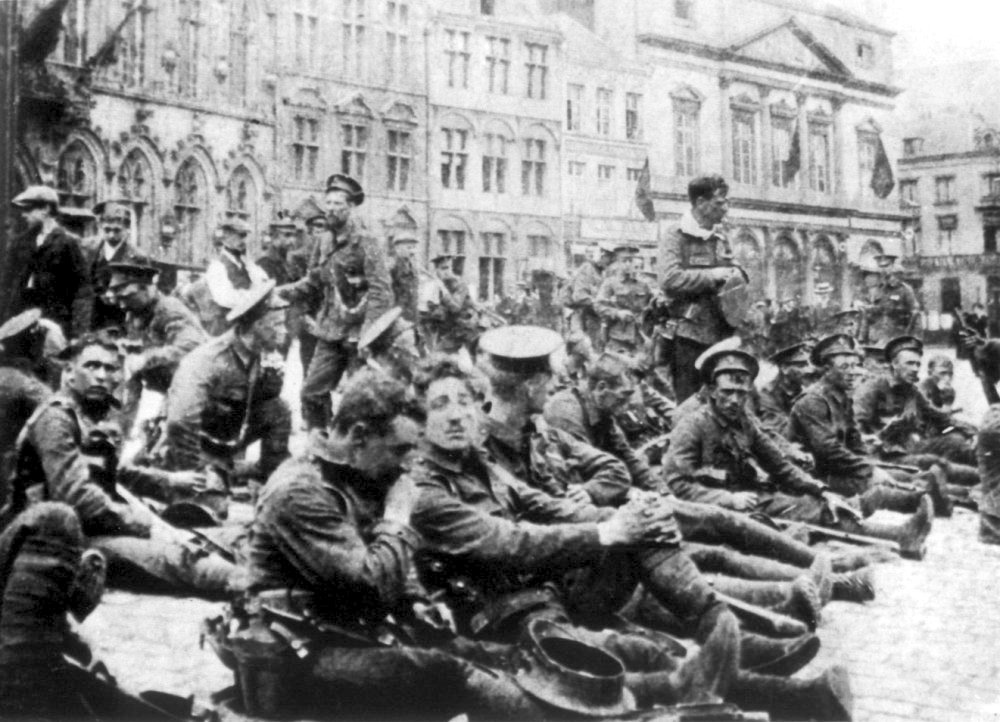
British Expeditionary Force (World War I)
The British Expeditionary Force (BEF) was the six-divisions the British Army sent to the Western Front during the First World War. Planning for a British Expeditionary Force began with the 1906–1912 Haldane reforms of the British Army carried out by the Secretary of State for War Richard Haldane following the Second Boer War (1899–1902). The term ''British Expeditionary Force'' is often used to refer only to the forces present in France prior to the end of the First Battle of Ypres on 22 November 1914. By the end of 1914—after the battles of Mons, Le Cateau, the Aisne and Ypres—the existent BEF had been almost exhausted, although it helped stop the German advance.Chandler (2003), p. 211 An alternative endpoint of the BEF was 26 December 1914, when it was divided into the First and Second Armies (a Third, Fourth and Fifth being created later in the war). "British Expeditionary Force" remained the official name of the British armies in France and Flanders thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
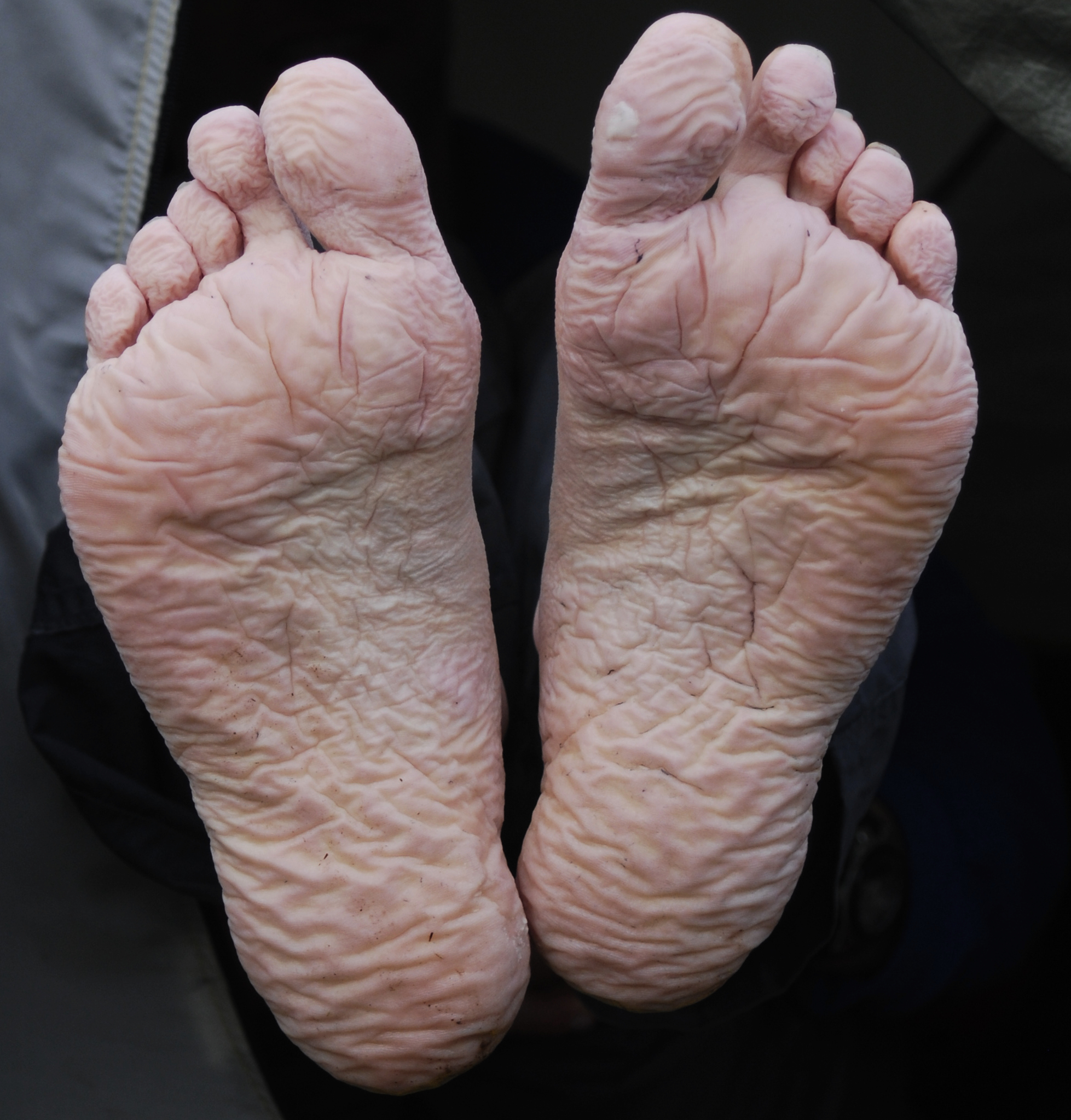
Trench Foot
Trench foot is a type of foot damage due to moisture. Initial symptoms often include tingling or itching which can progress to numbness. The feet may become red or bluish in color. As the condition worsens the feet can start to swell and smell of decay. Complications may include skin breakdown or infection. Trench foot occurs due to prolonged exposure of the feet to cold, damp, and often unsanitary conditions. Unlike frostbite, trench foot usually occurs at temperatures above freezing, and can be classed as a form of non-freezing cold injury. Onset can be as rapid as 10 hours. Risk factors include overly tight boots and not moving. The underlying mechanism is believed to involve constriction of blood vessels resulting in insufficient blood flow to the feet. Diagnosis is based on symptoms and examination. Prevention involves keeping the feet warm, dry, and clean. After the condition has occurred, pain medications may be required during the gradual rewarming process. Pain m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |