|
Transfer Conductance
Transconductance (for transfer conductance), also infrequently called mutual conductance, is the electrical characteristic relating the current through the output of a device to the voltage across the input of a device. Conductance is the reciprocal of resistance. Transadmittance (or transfer admittance) is the AC equivalent of transconductance. Definition Transconductance is very often denoted as a conductance, ''g''m, with a subscript, m, for ''mutual''. It is defined as follows: :g_m = \frac For small signal alternating current, the definition is simpler: :g_m = \frac The SI unit for transconductance is the siemens, with the symbol S, as in conductance. Transresistance Transresistance (for transfer resistance), also infrequently referred to as mutual resistance, is the dual of transconductance. It refers to the ratio between a change of the voltage at two output points and a related change of current through two input points, and is notated as ''r''m: :r_m = \frac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Conductance
The electrical resistance of an object is a measure of its opposition to the flow of electric current. Its reciprocal quantity is , measuring the ease with which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with mechanical friction. The SI unit of electrical resistance is the ohm (), while electrical conductance is measured in siemens (S) (formerly called the 'mho' and then represented by ). The resistance of an object depends in large part on the material it is made of. Objects made of electrical insulators like rubber tend to have very high resistance and low conductance, while objects made of electrical conductors like metals tend to have very low resistance and high conductance. This relationship is quantified by resistivity or conductivity. The nature of a material is not the only factor in resistance and conductance, however; it also depends on the size and shape of an object because these properties are extensive rather than inten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which determines the conductivity of the device. This ability to change conductivity with the amount of applied voltage can be used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. A metal-insulator-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MISFET) is a term almost synonymous with MOSFET. Another synonym is IGFET for insulated-gate field-effect transistor. The basic principle of the field-effect transistor was first patented by Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925.Lilienfeld, Julius Edgar (1926-10-08) "Method and apparatus for controlling electric currents" upright=1.6, Two power MOSFETs in V_in_the_''off''_state,_and_can_conduct_a_continuous_current_of_30 surface-mount_packages._Operating_as_switches,_each_of_these_components_can_su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operational Amplifier
An operational amplifier (often op amp or opamp) is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op amp produces an output potential (relative to circuit ground) that is typically 100,000 times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals. The operational amplifier traces its origin and name to analog computers, where they were used to perform mathematical operations in linear, non-linear, and frequency-dependent circuits. The popularity of the op amp as a building block in analog circuits is due to its versatility. By using negative feedback, the characteristics of an op-amp circuit, its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth etc. are determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or engineering tolerance in the op amp itself. Op amps are used widely in electronic devices today, including a vast array of consumer, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
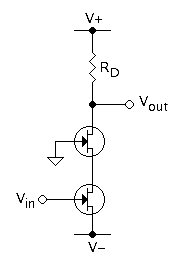
Cascode
The cascode is a two-stage amplifier that consists of a common-emitter stage feeding into a common-base stage. Compared to a single amplifier stage, this combination may have one or more of the following characteristics: higher input–output isolation, higher input impedance, high output impedance, higher bandwidth. In modern circuits, the cascode is often constructed from two transistors (BJTs or FETs), with one operating as a common emitter or common source and the other as a common base or common gate. The cascode improves input–output isolation (reduces reverse transmission), as there is no direct coupling from the output to input. This eliminates the Miller effect and thus contributes to a much higher bandwidth. History The use of a cascode (sometimes verbified to ''cascoding'') is a common technique for improving analog circuit performance, applicable to both vacuum tubes and transistors. The name "cascode" was coined in an article written by Frederick Vinton Hunt an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Analysis (electrical Circuits)
A network, in the context of electrical engineering and electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, all network components. There are many techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the techniques assume linear components. Except where stated, the methods described in this article are applicable only to ''linear'' network analysis. Definitions Equivalent circuits A useful procedure in network analysis is to simplify the network by reducing the number of components. This can be done by replacing physical components with other notional components that have the same effect. A particular technique might directly reduce the number of components, for instance by combining impedances in series. On the other hand, it might merely change the form into one in which the components can be reduced in a later operation. For instance, one might transform a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Voltage
The Early effect, named after its discoverer James M. Early, is the variation in the effective width of the base in a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) due to a variation in the applied base-to-collector voltage. A greater reverse bias across the collector–base junction, for example, increases the collector–base depletion width, thereby decreasing the width of the charge carrier portion of the base. Explanation In Figure 1, the neutral (i.e. active) base is green, and the depleted base regions are hashed light green. The neutral emitter and collector regions are dark blue and the depleted regions hashed light blue. Under increased collector–base reverse bias, the lower panel of Figure 1 shows a widening of the depletion region in the base and the associated narrowing of the neutral base region. The collector depletion region also increases under reverse bias, more than does that of the base, because the base is more heavily doped than the collector. The principle gover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha (%CE%B1) And Beta (%CE%B2)
Alpha (uppercase , lowercase ; grc, ἄλφα, ', or ell, άλφα, álfa) is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of one. Alpha is derived from the Phoenician letter aleph , which is the West Semitic word for " ox". Letters that arose from alpha include the Latin letter A and the Cyrillic letter А. Uses Greek In Ancient Greek, alpha was pronounced and could be either phonemically long ( ː or short ( . Where there is ambiguity, long and short alpha are sometimes written with a macron and breve today: . * = ' "a time" * = ' "tongue" In Modern Greek, vowel length has been lost, and all instances of alpha simply represent the open front unrounded vowel . In the polytonic orthography of Greek, alpha, like other vowel letters, can occur with several diacritic marks: any of three accent symbols (), and either of two breathing marks (), as well as combinations of these. It can also combine with the iota subscript (). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Thermal Voltage
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Q-point
In electronics, biasing is the setting of DC (direct current) operating conditions (current and voltage) of an active device in an amplifier. Many electronic devices, such as diodes, transistors and vacuum tubes, whose function is processing time-varying ( AC) signals, also require a steady (DC) current or voltage at their terminals to operate correctly. This current or voltage is called ''bias''. The AC signal applied to them is superposed on this DC bias current or voltage. The operating point of a device, also known as bias point, quiescent point, or Q-point, is the DC voltage or current at a specified terminal of an active device (a transistor or vacuum tube) with no input signal applied. A bias circuit is a portion of the device's circuit which supplies this steady current or voltage. Overview In electronics, 'biasing' usually refers to a fixed DC voltage or current applied to a terminal of an electronic component such as a diode, transistor or vacuum tube in a circuit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipolar Junction Transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar transistor allows a small current injected at one of its terminals to control a much larger current flowing between the terminals, making the device capable of amplification or switching. BJTs use two p–n junctions between two semiconductor types, n-type and p-type, which are regions in a single crystal of material. The junctions can be made in several different ways, such as changing the doping of the semiconductor material as it is grown, by depositing metal pellets to form alloy junctions, or by such methods as diffusion of n-type and p-type doping substances into the crystal. The superior predictability and performance of junction transistors quickly displaced the original point-contact transistor. Diffused transistors, along wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
65 Nanometer
The 65 nm process is an advanced lithographic node used in volume CMOS ( MOSFET) semiconductor fabrication. Printed linewidths (i.e. transistor gate lengths) can reach as low as 25 nm on a nominally 65 nm process, while the pitch between two lines may be greater than 130 nm. For comparison, cellular ribosomes are about 20 nm end-to-end. A crystal of bulk silicon has a lattice constant of 0.543 nm, so such transistors are on the order of 100 atoms across. Toshiba and Sony announced the 65 nm process in 2002, before Fujitsu and Toshiba began production in 2004, and then TSMC began production in 2005. By September 2007, Intel, AMD, IBM, UMC and Chartered were also producing 65 nm chips. While feature sizes may be drawn as 65 nm or less, the wavelengths of light used for lithography are 193 nm and 248 nm. Fabrication of sub-wavelength features requires special imaging technologies, such as optical proximity correction and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threshold Voltage
The threshold voltage, commonly abbreviated as Vth or VGS(th), of a field-effect transistor (FET) is the minimum gate-to-source voltage (VGS) that is needed to create a conducting path between the source and drain terminals. It is an important scaling factor to maintain power efficiency. When referring to a junction field-effect transistor (JFET), the threshold voltage is often called pinch-off voltage instead. This is somewhat confusing since ''pinch off'' applied to insulated-gate field-effect transistor (IGFET) refers to the channel pinching that leads to current saturation behaviour under high source–drain bias, even though the current is never off. Unlike ''pinch off'', the term ''threshold voltage'' is unambiguous and refers to the same concept in any field-effect transistor. Basic principles In n-channel ''enhancement-mode'' devices, a conductive channel does not exist naturally within the transistor, and a positive gate-to-source voltage is necessary to create one su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)
