|
Transdermal Continuous Oxygen Therapy
Transdermal Continuous Oxygen Therapy (TCOT, also known as Transdermal Continuous Oxygen Wound Therapy) is a wound closure technique for chronic and acute wounds which blankets a wound in oxygen on a 24-hour basis until the wound heals. Unlike hyperbaric oxygen treatment for chronic wounds, oxygen treatment used in this therapy is not systemic in nature and treats only the wound area. This treatment differs from topical oxygen treatments, as topical oxygen typically involves sporadic treatments of 1–3 hours several times per week, while TCOT treatment is 24/7 by nature. Overview Though early use focused on burns and surgical wounds, wider use of wounds treated with TCOT have become more common in diabetic foot ulcers, venous stasis and decubitus ulcers (pressure sores). TCOT involves inserting a thin tube which delivers the oxygen above the wound bed of a cleaned wound. An absorbent dressing is then placed above the tube and an occlusive or semi occlusive dressing is place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wound
A wound is a rapid onset of injury that involves laceration, lacerated or puncture wound, punctured skin (an ''open'' wound), or a bruise, contusion (a ''closed'' wound) from blunt force physical trauma, trauma or compression. In pathology, a ''wound'' is an acute injury that damages the epidermis of the skin. To healing, heal a wound, the body undertakes a series of actions collectively known as the wound healing process. Classification According to level of contamination, a wound can be classified as: * Clean wound – made under sterile conditions where there are no organisms present, and the skin is likely to heal without complications. * Contaminated wound – usually resulting from accidental injury; there are pathogenic organisms and foreign bodies in the wound. * Infected wound – the wound has pathogenic organisms present and multiplying, exhibiting clinical signs of infection (yellow appearance, soreness, redness, oozing pus). * Colonized wound – a chronic situation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frostbite
Frostbite is a skin injury that occurs when exposed to extreme low temperatures, causing the freezing of the skin or other tissues, commonly affecting the fingers, toes, nose, ears, cheeks and chin areas. Most often, frostbite occurs in the hands and feet. The initial symptoms are typically a feeling of cold and tingling or numbing. This may be followed by clumsiness with a white or bluish color to the skin. Swelling or blistering may occur following treatment. Complications may include hypothermia or compartment syndrome. People who are exposed to low temperatures for prolonged periods, such as winter sports enthusiasts, military personnel, and homeless individuals, are at greatest risk. Other risk factors include drinking alcohol, smoking, mental health problems, certain medications, and prior injuries due to cold. The underlying mechanism involves injury from ice crystals and blood clots in small blood vessels following thawing. Diagnosis is based on symptoms. Severity may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burn
A burn is an injury to skin, or other tissues, caused by heat, cold, electricity, chemicals, friction, or ultraviolet radiation (like sunburn). Most burns are due to heat from hot liquids (called scalding), solids, or fire. Burns occur mainly in the home or the workplace. In the home, risks are associated with domestic kitchens, including stoves, flames, and hot liquids. In the workplace, risks are associated with fire and chemical and electric burns. Alcoholism and smoking are other risk factors. Burns can also occur as a result of self-harm or violence between people (assault). Burns that affect only the superficial skin layers are known as superficial or first-degree burns. They appear red without blisters and pain typically lasts around three days. When the injury extends into some of the underlying skin layer, it is a partial-thickness or second-degree burn. Blisters are frequently present and they are often very painful. Healing can require up to eight weeks and scarri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
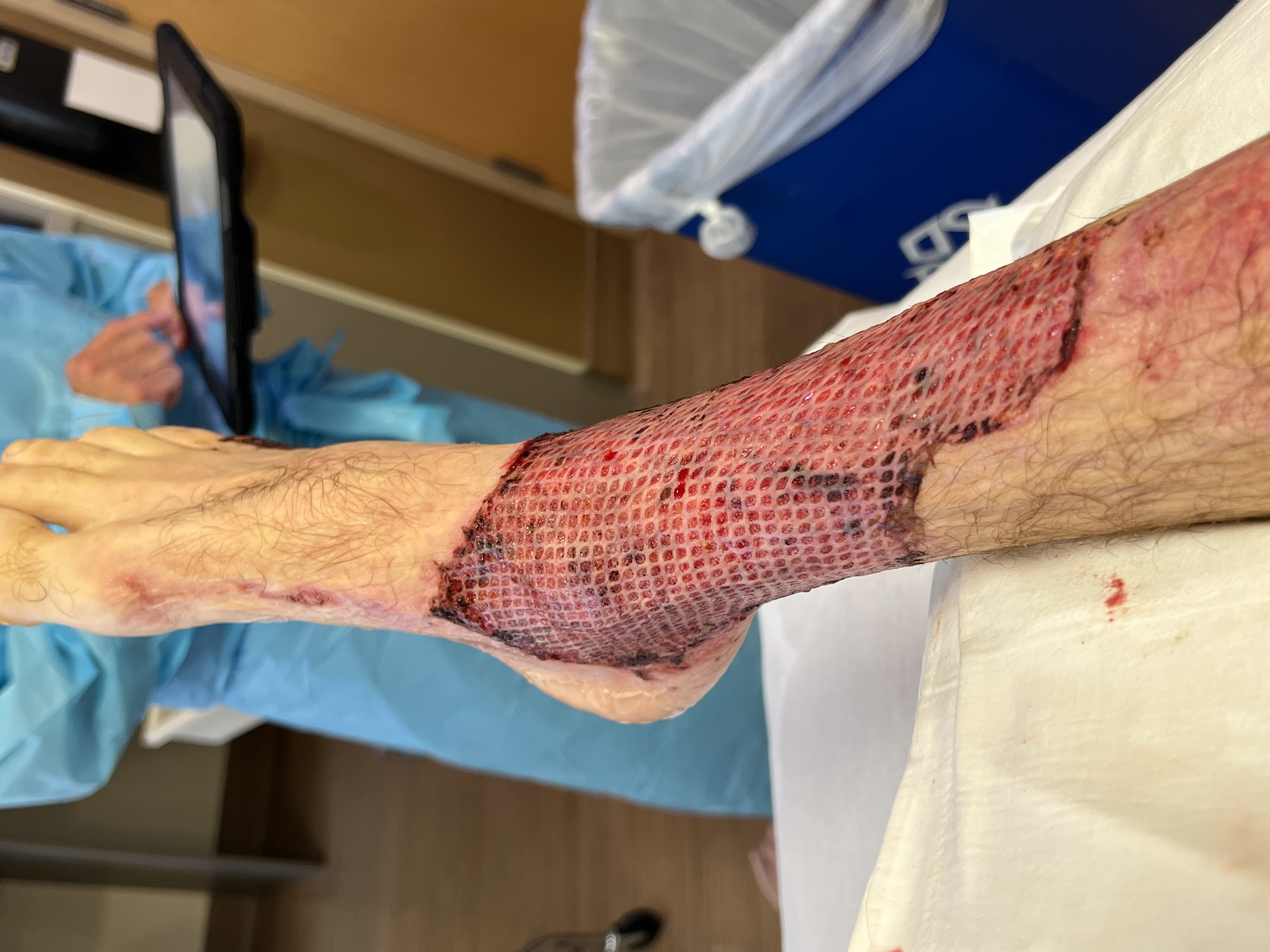
Skin Grafts
Skin grafting, a type of graft surgery, involves the transplantation of skin. The transplanted tissue is called a skin graft. Surgeons may use skin grafting to treat: * extensive wounding or trauma * burns * areas of extensive skin loss due to infection such as necrotizing fasciitis or purpura fulminans * specific surgeries that may require skin grafts for healing to occur - most commonly removal of skin cancers Skin grafting often takes place after serious injuries when some of the body's skin is damaged. Surgical removal (excision or debridement) of the damaged skin is followed by skin grafting. The grafting serves two purposes: reducing the course of treatment needed (and time in the hospital), and improving the function and appearance of the area of the body which receives the skin graft. There are two types of skin grafts: * The more common type involves removing a thin layer of skin from a healthy part of the body (the donor section) - like peeling a potato. * A full ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gangrene
Gangrene is a type of tissue death caused by a lack of blood supply. Symptoms may include a change in skin color to red or black, numbness, swelling, pain, skin breakdown, and coolness. The feet and hands are most commonly affected. If the gangrene is caused by an infectious agent, it may present with a fever or sepsis. Risk factors include diabetes, peripheral arterial disease, smoking, major trauma, alcoholism, HIV/AIDS, frostbite, influenza, dengue fever, malaria, chickenpox, plague, hypernatremia, radiation injuries, meningococcal disease, Group B streptococcal infection and Raynaud's syndrome. It can be classified as dry gangrene, wet gangrene, gas gangrene, internal gangrene, and necrotizing fasciitis. The diagnosis of gangrene is based on symptoms and supported by tests such as medical imaging. Treatment may involve surgery to remove the dead tissue, antibiotics to treat any infection, and efforts to address the underlying cause. Surgical efforts may include debr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-surgical Infections
Perioperative mortality has been defined as any death, regardless of cause, occurring within 30 days after surgery in or out of the hospital. Globally, 4.2 million people are estimated to die within 30 days of surgery each year. An important consideration in the decision to perform any surgical procedure is to weigh the benefits against the risks. Anesthesiologists and surgeons employ various methods in assessing whether a patient is in optimal condition from a medical standpoint prior to undertaking surgery, and various statistical tools are available. ASA score is the most well known of these. Intraoperative causes Immediate complications during the surgical procedure, e.g. bleeding or perforation of organs may have lethal sequelae. Complications following surgery Infection Countries with a low human development index (HDI) carry a disproportionately greater burden of surgical site infections (SSI) than countries with a middle or high HDI and might have higher rates of antibiot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin Ulcers
An ulcer is a sore on the skin or a mucous membrane, accompanied by the disintegration of tissue. Ulcers can result in complete loss of the epidermis and often portions of the dermis and even subcutaneous fat. Ulcers are most common on the skin of the lower extremities and in the gastrointestinal tract. An ulcer that appears on the skin is often visible as an inflamed tissue with an area of reddened skin. A skin ulcer is often visible in the event of exposure to heat or cold, irritation, or a problem with blood circulation. They can also be caused due to a lack of mobility, which causes prolonged pressure on the tissues. This stress in the blood circulation is transformed to a skin ulcer, commonly known as bedsores or decubitus ulcers. Ulcers often become infected, and pus forms. Signs and symptoms Skin ulcers appear as open craters, often round, with layers of skin that have eroded. The skin around the ulcer may be red, swollen, and tender. Patients may feel pain on the skin ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bedsore
Pressure ulcers, also known as pressure sores, bed sores or pressure injuries, are localised damage to the skin and/or underlying tissue that usually occur over a bony prominence as a result of usually long-term pressure, or pressure in combination with shear or friction. The most common sites are the skin overlying the sacrum, coccyx, heels, and hips, though other sites can be affected, such as the elbows, knees, ankles, back of shoulders, or the back of the cranium. Pressure ulcers occur due to pressure applied to soft tissue resulting in completely or partially obstructed blood flow to the soft tissue. Shear is also a cause, as it can pull on blood vessels that feed the skin. Pressure ulcers most commonly develop in individuals who are not moving about, such as those who are on chronic bedrest or consistently use a wheelchair. It is widely believed that other factors can influence the tolerance of skin for pressure and shear, thereby increasing the risk of pressure ulcer d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased appetite. If left untreated, diabetes can cause many health complications. Acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or death. Serious long-term complications include cardiovascular disease, stroke, chronic kidney disease, foot ulcers, damage to the nerves, damage to the eyes, and cognitive impairment. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin, or the cells of the body not responding properly to the insulin produced. Insulin is a hormone which is responsible for helping glucose from food get into cells to be used for energy. There are three main types of diabetes mellitus: * Type 1 diabetes results from failure of the pancreas to produce enough insulin due to lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Wound
A chronic wound is a wound that does not heal in an orderly set of stages and in a predictable amount of time the way most wounds do; wounds that do not heal within three months are often considered chronic. Chronic wounds seem to be detained in one or more of the phases of wound healing. For example, chronic wounds often remain in the inflammatory stage for too long. To overcome that stage and jump-start the healing process a number of factors need to be addressed such as bacterial burden, necrotic tissue, and moisture balance of the whole wound. In acute wounds, there is a precise balance between production and degradation of molecules such as collagen; in chronic wounds this balance is lost and degradation plays too large a role. Chronic wounds may never heal or may take years to do so. These wounds cause patients severe emotional and physical stress and create a significant financial burden on patients and the whole healthcare system. Acute and chronic wounds are at oppos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin Ulcer
An ulcer is a sore on the skin or a mucous membrane, accompanied by the disintegration of tissue. Ulcers can result in complete loss of the epidermis and often portions of the dermis and even subcutaneous fat. Ulcers are most common on the skin of the lower extremities and in the gastrointestinal tract. An ulcer that appears on the skin is often visible as an inflamed tissue with an area of reddened skin. A skin ulcer is often visible in the event of exposure to heat or cold, irritation, or a problem with blood circulation. They can also be caused due to a lack of mobility, which causes prolonged pressure on the tissues. This stress in the blood circulation is transformed to a skin ulcer, commonly known as bedsores or decubitus ulcers. Ulcers often become infected, and pus forms. Signs and symptoms Skin ulcers appear as open craters, often round, with layers of skin that have eroded. The skin around the ulcer may be red, swollen, and tender. Patients may feel pain on the skin a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |